* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Heart
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
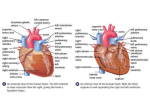
The Heart human heart The Heart The heart is a cone-shaped, muscular organ about the size of a fist. It is located between the lungs directly behind the sternum and is tilted so that the apex (pointed end) is oriented to the left. Grab a red and a blue marker! Composition of the Heart The heart is mostly made up of cardiac muscle tissue known as myocardium. The heart lies within a thick, membranous sac that secretes a small amount of lubricating fluid. This sac is called the pericardium. The inner surface of the heart is lined with connective tissue and endothelial tissue. This is known as the endocardium. Composition of the Heart The heart is mostly made up of cardiac muscle tissue known as myocardium. The heart lies within a thick, membranous sac that secretes a small amount of lubricating fluid. This sac is called the pericardium. The inner surface of the heart is lined with connective tissue and endothelial tissue. This is known as the endocardium. Myocardium Muscle Tissue Chambers of the Heart The heart has four chambers: Two upper, thin-walled chambers are called atria (singular atrium). The atria receive blood. The right atrium receives blood from the body via the superior vena cava. The left atrium receives blood from the lungs via the pulmonary veins. Chambers of the Heart Chambers of the Heart Two lower, thick-walled chambers called ventricles. Ventricles pump the blood. The right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs via the pulmonary arteries. The left ventricle pumps blood to the body via the aorta. Chambers of the Heart Valves of the Heart The heart has four valves which direct the flow of blood and prevent its backward movement. Two valves are found between the atria and ventricles and are called atrioventricular valves (a.v). The a.v. valve on the right side of the heart is called the tricuspid valve because it has three flaps or cusps. The a.v. valve on the left is called the bicuspid (mitral) valve – it has 2 flaps. Valves of the Heart Two valves are found between the ventricles and their attached vessels. These are known as the semi-lunar valves – their flaps resemble half-moons. The pulmonary semilunar valve is found between the right ventricle and the pulmonary arteries. Blood is pumped through this valve on its way to the lungs. The aortic semilunar valve is found between the left ventricle and the aorta. Blood is pumped through this valve on its way to the body tissues. The valves of the heart are supported by strong fibrous strings called chordae tendinae. Major vessels There are five major blood vessels that lead into and out of the heart. The superior vena cava carries oxygen poor blood to the heart from the upper portion of the body. Blood from this vessel enters the right atrium. The inferior vena cava carries oxygen poor blood to the heart from the lower portion of the body. Blood from this vessel enters the right atrium. Major Vessels The pulmonary arteries carry blood from the heart to the lungs. Blood carried in this vessel exits the heart from the right ventricle. The pulmonary veins carry oxygen rich blood from the lungs to the heart. Blood from this vessel enters the left atrium. The aorta carries blood from the heart to the body tissues. Blood carried in this vessel exits the heart from the left ventricle. Passage of Blood through the Heart 1. Oxygen poor blood enters right atrium via superior and inferior vena cava. 2. Right atrium sends blood through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. 3. Right ventricle pumps blood though the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary arteries which go to the lungs. 4. Blood becomes oxygenated in the lungs and then enters the left atrium via the pulmonary veins. Passage of Blood through the Heart 5. Left atrium sends blood through the bicuspid valve to the left ventricle. 6. Left ventricle pumps blood through the aortic semilunar valve into the aorta. 7. The aorta delivers oxygen rich blood to the body. Blood flow videos http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H04d3rJCLCE http ://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SvAVu-7E2gA