Muscular System - Anoka-Hennepin School District
... • H-Zone: a narrow center area of the A-band that contains only thick filaments. • I-Band: The lighter area on either side of the A-band that is made up of thin filaments. • The alternating darker A-bands and lighter Ibands give the mucle it striated appearance. ...
... • H-Zone: a narrow center area of the A-band that contains only thick filaments. • I-Band: The lighter area on either side of the A-band that is made up of thin filaments. • The alternating darker A-bands and lighter Ibands give the mucle it striated appearance. ...
Muscle
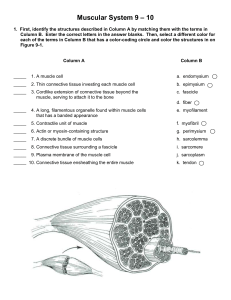
... and color in the coding circle and corresponding muscles on Figure 10-1. ____________________________ Used to form the horizontal frown cease on the forehead or to raise your eyebrows ____________________________ Prime mover of head flexion; a two-headed muscle ____________________________ Prime mov ...
... and color in the coding circle and corresponding muscles on Figure 10-1. ____________________________ Used to form the horizontal frown cease on the forehead or to raise your eyebrows ____________________________ Prime mover of head flexion; a two-headed muscle ____________________________ Prime mov ...
JAOCR at the Viewbox
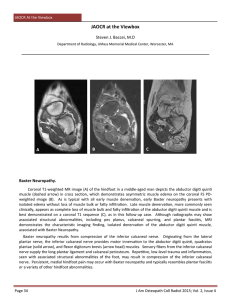
... Coronal T1-weighted MR image (A) of the hindfoot in a middle-aged man depicts the abductor digiti quinti muscle (dashed arrow) in cross section, which demonstrates asymmetric muscle edema on the coronal FS PDweighted image (B). As is typical with all early muscle denervation, early Baxter neuropathy ...
... Coronal T1-weighted MR image (A) of the hindfoot in a middle-aged man depicts the abductor digiti quinti muscle (dashed arrow) in cross section, which demonstrates asymmetric muscle edema on the coronal FS PDweighted image (B). As is typical with all early muscle denervation, early Baxter neuropathy ...
Color Atlas of Human Anatomy - ReadingSample - Beck-Shop
... bursa of the latissimus dorsi lies immediately before the junction of both muscles. The latissimus dorsi provides the muscular basis of the posterior axillary fold. It lowers the raised arm and adducts it. When the arm is adducted, it pulls it backward and medially, and rotates it so far medially th ...
... bursa of the latissimus dorsi lies immediately before the junction of both muscles. The latissimus dorsi provides the muscular basis of the posterior axillary fold. It lowers the raised arm and adducts it. When the arm is adducted, it pulls it backward and medially, and rotates it so far medially th ...
Webquest- Skeletal and Muscular System
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
... 14 Where are involuntary muscles found and how do they move? ...
histology of muscles
... 1. Sarcolemma: the plasma membrane of a muscle cell 2. Sarcoplasm: the cytoplasm of the muscle cell 3. Sarcoplasmic reticulum: the endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle cell 4. Sarcosome: the mitochondria of a muscle cell 5. Sarcomere: the contractile or functional unit of muscle There are specialized i ...
... 1. Sarcolemma: the plasma membrane of a muscle cell 2. Sarcoplasm: the cytoplasm of the muscle cell 3. Sarcoplasmic reticulum: the endoplasmic reticulum of a muscle cell 4. Sarcosome: the mitochondria of a muscle cell 5. Sarcomere: the contractile or functional unit of muscle There are specialized i ...
DEVELOPMENT OF MUSCLES
... • The first indication of myogenesis is the elongation of nuclei and cell bodies of the mesenchymal cells, and they are differentiated into Myoblast • These myoblasts fuse and form large elongated ,multinucleated tubes the Myotubes. The growth of the muscle depends of the rate of fusion of Myotubes ...
... • The first indication of myogenesis is the elongation of nuclei and cell bodies of the mesenchymal cells, and they are differentiated into Myoblast • These myoblasts fuse and form large elongated ,multinucleated tubes the Myotubes. The growth of the muscle depends of the rate of fusion of Myotubes ...
period of contraction
... reaches a point when it is unable to relax completely and the force of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a ...
... reaches a point when it is unable to relax completely and the force of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a ...
Skeletal Muscle Contraction
... reaches a point when it is unable to relax completely and the force of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a ...
... reaches a point when it is unable to relax completely and the force of individual twitches combine by the process of summation. • If the sustained contraction lacks any relaxation, it is called a ...
Anatomy Lecture 8 – The Pharynx and Esophagus
... o The Z-Line was shifted up. o Causes Dysphasia Achalasia o The Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) opens less frequently (primary) or is completely paralyzed (secondary). o This leads to reduced or absent peristalsis, which then causes esophageal obstruction o Loss of Enteric Innervation, which norm ...
... o The Z-Line was shifted up. o Causes Dysphasia Achalasia o The Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES) opens less frequently (primary) or is completely paralyzed (secondary). o This leads to reduced or absent peristalsis, which then causes esophageal obstruction o Loss of Enteric Innervation, which norm ...
Manual Muscle Testing - Harrison High School
... Coordinate the muscle testing findings with other standard diagnostic procedures The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better ...
... Coordinate the muscle testing findings with other standard diagnostic procedures The amount of pressure used to test may vary between persons performing the test. The amount of strength loss must be greater than approximately 20to 30% to be dependably measurable Comparison of both sides is a better ...
Anatomy and Physiology Exam I
... In striations of muscle fibers, the light bands are referred to as? ...
... In striations of muscle fibers, the light bands are referred to as? ...
Cartilage - UTCOM2013
... myoglobin content, low glycogen conent, large white fibers have low myoglobin and high glycogen content, EM Level: T tubules seen at junction of A and I bands, H bands=thick filaments only, held apart by crossbridging proteins (M line) Cardiac: Striated appearance, short, branched fibers, centrally ...
... myoglobin content, low glycogen conent, large white fibers have low myoglobin and high glycogen content, EM Level: T tubules seen at junction of A and I bands, H bands=thick filaments only, held apart by crossbridging proteins (M line) Cardiac: Striated appearance, short, branched fibers, centrally ...
Q = quadratus lumborum The quadratus lumborum (QL) muscle is a
... The QL can be a common source of lower back pain as it connects to the pelvis as well as the vertebra. The cause of pain can be when the erector spinae back muscles are weak or inhibited, which can occur through poor posture for long periods of time such as in a seated position. The QL will take ove ...
... The QL can be a common source of lower back pain as it connects to the pelvis as well as the vertebra. The cause of pain can be when the erector spinae back muscles are weak or inhibited, which can occur through poor posture for long periods of time such as in a seated position. The QL will take ove ...
Chap 10 - Muscles
... long axis of the muscle (e.g., sartorius) Fusiform – spindle-shaped muscles (e.g., biceps brachii) Pennate – short fascicles that attach obliquely to a central tendon running the length of the muscle (e.g., rectus femoris) Convergent – fascicles converge from a broad origin to a single tendon insert ...
... long axis of the muscle (e.g., sartorius) Fusiform – spindle-shaped muscles (e.g., biceps brachii) Pennate – short fascicles that attach obliquely to a central tendon running the length of the muscle (e.g., rectus femoris) Convergent – fascicles converge from a broad origin to a single tendon insert ...
Mucles of the Leg * I included spinal levels
... Divide the muscles into those that do plantar flexion and those that do dorsiflexion Look at the spinal levels and actions of the tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior muscles Note that the popliteus muscle is located just posterior to the knee, while the other muscles are along the shafts ...
... Divide the muscles into those that do plantar flexion and those that do dorsiflexion Look at the spinal levels and actions of the tibialis anterior and tibialis posterior muscles Note that the popliteus muscle is located just posterior to the knee, while the other muscles are along the shafts ...
Intrinsic laryngeal muscles
... INTRINSIC LARYNGEAL MUSCLES they have their attachment within the larynx they are concerned with the control of vocal fold behaviour: abduction adduction tensioning ...
... INTRINSIC LARYNGEAL MUSCLES they have their attachment within the larynx they are concerned with the control of vocal fold behaviour: abduction adduction tensioning ...
The Muscular System Terms
... Flexor Carpi Ulnaris - muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (Ulna) adduct the hand Adductor Longus - adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh Sartorius - narrow muscle extending obliquely from the front of the hip to the inner side of the tibia External Obl ...
... Flexor Carpi Ulnaris - muscle of the human forearm that acts to flex and (Ulna) adduct the hand Adductor Longus - adductor muscles of the hip, its main function is to adduct the thigh Sartorius - narrow muscle extending obliquely from the front of the hip to the inner side of the tibia External Obl ...
Tissues & Organs of Humans
... some bones produce red blood cells acts as a reservoir for calcium ...
... some bones produce red blood cells acts as a reservoir for calcium ...
Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the
... Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the diaphragm that are important to its function. (March 2011) ...
... Q2 Outline the principal anatomical features of the diaphragm that are important to its function. (March 2011) ...
Skeletal muscle

Skeletal muscle is a form of striated muscle tissue which is under the voluntary control of the somatic nervous system. It is one of three major muscle types, the others being cardiac muscle and smooth muscle. Most skeletal muscles are attached to bones by bundles of collagen fibers known as tendons.Skeletal muscle is made up of individual muscle cells or myocytes, known as muscle fibers. They are formed from the fusion of developmental myoblasts (a type of embryonic progenitor cell that gives rise to a muscle cell) in a process known as myogenesis. Muscle fibres are cylindrical, and multinucleated.Muscle fibers are in turn composed of myofibrils. The myofibrils are composed of actin and myosin filaments, repeated in units called sarcomeres, the basic functional units of the muscle fiber. The sarcomere is responsible for the striated appearance of skeletal muscle, and forms the basic machinery necessary for muscle contraction. The term muscle refers to multiple bundles of muscle fibers called fascicles. All muscles also contain connective tissue arranged in layers of fasciae. Each muscle is enclosed in a layer of fascia; each fascicle is enclosed by a layer of fascia and each individual muscle fiber is also enclosed in a layer of fascia.