Document
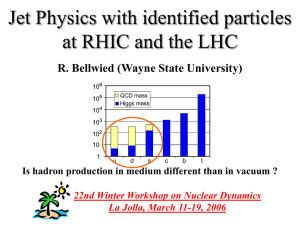
... for production mechanism. Clustering favors baryon production JETSET is clearly favored by the data. Correlated L-Lbar pairs are produced predominantly in the same jet, i.e. short range compensation of quantum numbers. ...
... for production mechanism. Clustering favors baryon production JETSET is clearly favored by the data. Correlated L-Lbar pairs are produced predominantly in the same jet, i.e. short range compensation of quantum numbers. ...
Radioactivity 1. To learn the types of radioactive decay 2. To learn to
... 2. To learn to write nuclear equations for radioactive decay 3. To learn how one element may be changed to another by particle bombardment 4. To learn about radiation detection instruments 5. To understand half-life ...
... 2. To learn to write nuclear equations for radioactive decay 3. To learn how one element may be changed to another by particle bombardment 4. To learn about radiation detection instruments 5. To understand half-life ...
Ch4_S1A
... stream of charged particles that interacted with the air in the tube and caused the air to glow. • Thomson observed that the beam was repelled by the negatively charged plate and attracted by the positively charged plate. ...
... stream of charged particles that interacted with the air in the tube and caused the air to glow. • Thomson observed that the beam was repelled by the negatively charged plate and attracted by the positively charged plate. ...
E=mc2: energy and matter entwined - School of Physics
... Particle physicists accelerate protons or electrons with velocities very close to c then collide them….to produce new particles… ...
... Particle physicists accelerate protons or electrons with velocities very close to c then collide them….to produce new particles… ...
2.1 2. NUCLEAR PHENOMENOLOGY We turn now to
... has no bound state. Finally, nuclear forces saturate. This describes that fact that a nucleon in a typical nucleus experiences attractive interactions only with a limited number of the many other nucleons. The evidence for this is shown in Fig.2.1, where we see that the binding energy per nucleon is ...
... has no bound state. Finally, nuclear forces saturate. This describes that fact that a nucleon in a typical nucleus experiences attractive interactions only with a limited number of the many other nucleons. The evidence for this is shown in Fig.2.1, where we see that the binding energy per nucleon is ...
Chapter 8, Lecture 1
... Christenson, J et al. (1964); Phys. Rev. ett. 13 338 © Nobel Foundation 1980 ...
... Christenson, J et al. (1964); Phys. Rev. ett. 13 338 © Nobel Foundation 1980 ...
Atomic Structure and the Properties of Matter (Chapter 11)
... Hydrogen makes up 90% of all the matter in the universe. Scientists believe that hydrogen is the origin atom, just like Adam & Eve. There is something really interesting about hydrogen: what is meant by empty space is that there exist only one hydrogen atom per 1 m3. Space is not really empty but pr ...
... Hydrogen makes up 90% of all the matter in the universe. Scientists believe that hydrogen is the origin atom, just like Adam & Eve. There is something really interesting about hydrogen: what is meant by empty space is that there exist only one hydrogen atom per 1 m3. Space is not really empty but pr ...
Strong CP violation in hot QCD: from heavy ion collisions to cosmology
... Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 214 (1979). J. R. Abo-Shaeer, C. Raman, J. M. Vogels, and W. Ketterle, Observation of Vortex Lattices in Bose-Einstein ...
... Phys. Rev. Lett. 43, 214 (1979). J. R. Abo-Shaeer, C. Raman, J. M. Vogels, and W. Ketterle, Observation of Vortex Lattices in Bose-Einstein ...
Part 1: CERN`s Big European Bubble Chamber 1970`s
... 2) c) +1: The particle curves in a direction opposite that of the kaons and therefore must be positive. However, this seems to be violating the conservation of charge. This is clarified in the next question. 3) c) The kaon has interacted with a proton: A positive was produced and all the particles h ...
... 2) c) +1: The particle curves in a direction opposite that of the kaons and therefore must be positive. However, this seems to be violating the conservation of charge. This is clarified in the next question. 3) c) The kaon has interacted with a proton: A positive was produced and all the particles h ...
atomic nuclei without neutrons
... Protons and neutrons consist of three quarks, the electron is supposed to be an indivisible particle. As singular particles, electrons only occur in the electron shells around the atomic nucleus and do not occur inside the atomic nucleus. Free neutrons are unstable and decay into one proton, one ele ...
... Protons and neutrons consist of three quarks, the electron is supposed to be an indivisible particle. As singular particles, electrons only occur in the electron shells around the atomic nucleus and do not occur inside the atomic nucleus. Free neutrons are unstable and decay into one proton, one ele ...
nuclear physics - The Physics Cafe
... In the alpha-particle scattering experiment, it was observed that most of the alpha particles pass through the thin gold foil with small deflections. Which of the following is not a correct conclusion inferred from the experiment? ...
... In the alpha-particle scattering experiment, it was observed that most of the alpha particles pass through the thin gold foil with small deflections. Which of the following is not a correct conclusion inferred from the experiment? ...
The relevance of proton-proton physics for the understanding
... non-isotropic string decay (JETSET) for production mechanism. Clustering favors baryon production JETSET is clearly favored by the data. Correlated L-Lbar pairs are produced predominantly in the same jet, i.e. short range compensation of quantum numbers. ...
... non-isotropic string decay (JETSET) for production mechanism. Clustering favors baryon production JETSET is clearly favored by the data. Correlated L-Lbar pairs are produced predominantly in the same jet, i.e. short range compensation of quantum numbers. ...