CHAPTER 2 The nucleus and radioactive decay - Cin
... very precisely by keeping the electric and magnetic fields constant and measuring the difference in radii of curvature, which we can do more precisely. By convention, the 12C atom is taken to be exactly 12.000000 units on the atomic mass scale, against which all other masses are calibrated. The mass ...
... very precisely by keeping the electric and magnetic fields constant and measuring the difference in radii of curvature, which we can do more precisely. By convention, the 12C atom is taken to be exactly 12.000000 units on the atomic mass scale, against which all other masses are calibrated. The mass ...
The Atom - Effingham County Schools
... the observed properties of cathode rays that led to the discovery of the electron Summarize the experiment carried out by Rutherford and his co-workers that led to the discovery of the nucleus ...
... the observed properties of cathode rays that led to the discovery of the electron Summarize the experiment carried out by Rutherford and his co-workers that led to the discovery of the nucleus ...
here - IFT
... give off such charges, he expected that his electrometer would be less affected when he raised it high off the ground. But he was surprised to find an increased level of activity after he scaled the tower. The explanation: Subatomic particles rain down from space. Although the source of these partic ...
... give off such charges, he expected that his electrometer would be less affected when he raised it high off the ground. But he was surprised to find an increased level of activity after he scaled the tower. The explanation: Subatomic particles rain down from space. Although the source of these partic ...
hierarchy of matter-particles
... tetron, hexton, neutron, positron, electron, proton, deuteron, atom, molecule. ...
... tetron, hexton, neutron, positron, electron, proton, deuteron, atom, molecule. ...
transparencies - Indico
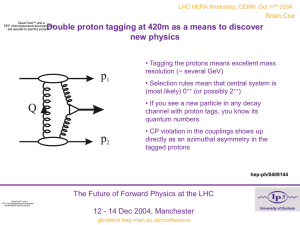
... Double proton tagging at 420m as a means to discover new physics • Tagging the protons means excellent mass resolution (~ several GeV) • Selection rules mean that central system is (most likely) 0++ (or possibly 2++) • If you see a new particle in any decay channel with proton tags, you know its qua ...
... Double proton tagging at 420m as a means to discover new physics • Tagging the protons means excellent mass resolution (~ several GeV) • Selection rules mean that central system is (most likely) 0++ (or possibly 2++) • If you see a new particle in any decay channel with proton tags, you know its qua ...
Lecture 3 : Atoms and the Atomic Theory Early Chemical
... Caption: (a) Deflection of cathode rays in an electric field. The beam of cathode rays is deflected as it travels from left to right in the field of the electrically charged condenser plates (E). The deflection corresponds to that expected of negatively charged particles - away from the negatively c ...
... Caption: (a) Deflection of cathode rays in an electric field. The beam of cathode rays is deflected as it travels from left to right in the field of the electrically charged condenser plates (E). The deflection corresponds to that expected of negatively charged particles - away from the negatively c ...
I can
... SC.8.P.8.1 Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by using models to explain the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases. SC.8.P.9.1 Explore the Law of Conservation of Mass by demonstrating and concluding that mass is conserved when substances undergo physical ...
... SC.8.P.8.1 Explore the scientific theory of atoms (also known as atomic theory) by using models to explain the motion of particles in solids, liquids, and gases. SC.8.P.9.1 Explore the Law of Conservation of Mass by demonstrating and concluding that mass is conserved when substances undergo physical ...
What`s Inside the Nucleus?
... 1. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the largest and highest-energy particle accelerator, colliding opposing beams of protons at 99.999999% of the speed of light. 2. Will test various predictions of high-energy physics, including the existence of the Higgs boson and other new particles. 3. 27 kilom ...
... 1. The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) is the largest and highest-energy particle accelerator, colliding opposing beams of protons at 99.999999% of the speed of light. 2. Will test various predictions of high-energy physics, including the existence of the Higgs boson and other new particles. 3. 27 kilom ...
Chapter 33: The Atomic Nucleus and Radioactivity
... The amount of radiation from a point source is inversely proportional to the distance from the source. If a Geiger counter 1 meter from a small sample reads 360 counts per minute, what will be its counting rate 2 meters from the source? 3 meters from the source? Ans. Doubling the distance will resul ...
... The amount of radiation from a point source is inversely proportional to the distance from the source. If a Geiger counter 1 meter from a small sample reads 360 counts per minute, what will be its counting rate 2 meters from the source? 3 meters from the source? Ans. Doubling the distance will resul ...
Collapse of virialised pebble clumps
... Representative particle approach Collision between swarm i and swarm k (1000 representative particles) ...
... Representative particle approach Collision between swarm i and swarm k (1000 representative particles) ...