On Morphing Neutrinos and Why They Must Have Mass
... The idea of mixing, which might seem counterintuitive when applied to particles, has a powerful classical analog in the analysis of polarized light, whether it’s via Faraday rotation,11 the response of a linear polarizer,12 or the behavior of circular light in an ordinary birefringent material. For ...
... The idea of mixing, which might seem counterintuitive when applied to particles, has a powerful classical analog in the analysis of polarized light, whether it’s via Faraday rotation,11 the response of a linear polarizer,12 or the behavior of circular light in an ordinary birefringent material. For ...
Particle Tracing Minicourse
... Mathematical Particle Tracing – Specify the equations of motion using Massless, Newtonian, Lagrangian or Hamiltonian formulations. – Complete freedom over the equations solved allows, for example, ray tracing to be modeled. ...
... Mathematical Particle Tracing – Specify the equations of motion using Massless, Newtonian, Lagrangian or Hamiltonian formulations. – Complete freedom over the equations solved allows, for example, ray tracing to be modeled. ...
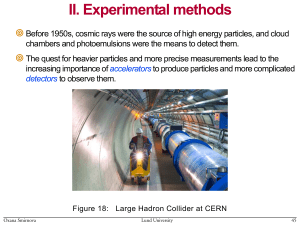
Accelerators - Particle Physics, Lund University
... Here q is electric charge of a particle, velocity v/c , Lorentz factor (1-2)-1/2, and is the radius of the orbit. For relativistic particles E/mc2 energy loss increases as E4/m4 , becoming very significant for high-energy light particles (electrons) Radio-frequency power is limited ...
... Here q is electric charge of a particle, velocity v/c , Lorentz factor (1-2)-1/2, and is the radius of the orbit. For relativistic particles E/mc2 energy loss increases as E4/m4 , becoming very significant for high-energy light particles (electrons) Radio-frequency power is limited ...
10.3 Artificial Transmutation
... This painting of an alchemist’s laboratory was made around 1570. For centuries, these early scientists, known as alchemists, tried to use chemical reactions to make gold. The alchemists failed in their attempts to turn lead into gold. ...
... This painting of an alchemist’s laboratory was made around 1570. For centuries, these early scientists, known as alchemists, tried to use chemical reactions to make gold. The alchemists failed in their attempts to turn lead into gold. ...
New Theories of Gravitation and Particle Model Chongxi Yu
... What is the bonding force? We believe the bonding forces come from c-particles orbit A-particle, may not one to one, but just like electrons orbit a mixture of protons and neutrons, but c-particles may or may not orbit the mixture of A-particles and A -particles, c-particles may orbit only Aparticl ...
... What is the bonding force? We believe the bonding forces come from c-particles orbit A-particle, may not one to one, but just like electrons orbit a mixture of protons and neutrons, but c-particles may or may not orbit the mixture of A-particles and A -particles, c-particles may orbit only Aparticl ...
Linköping University Post Print Simulation study of the filamentation of
... rearranged through the growing plasma waves into filaments, which are separated by electromagnetic fields [2]. This is also the case for the instability driven by counterstreaming beams of charged particles, which is commonly referred to as the beam-Weibel instability or the filamentation instabilit ...
... rearranged through the growing plasma waves into filaments, which are separated by electromagnetic fields [2]. This is also the case for the instability driven by counterstreaming beams of charged particles, which is commonly referred to as the beam-Weibel instability or the filamentation instabilit ...
observational evidence for dark matter
... rotational motion of stars within the disc allows us to weigh a galaxy. In the same way that the speed of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun is dictated by both the mass it is in orbit around, and how far away it is from that mass, the orbital speed of a star revolving around the centre of a spir ...
... rotational motion of stars within the disc allows us to weigh a galaxy. In the same way that the speed of the Earth in its orbit around the Sun is dictated by both the mass it is in orbit around, and how far away it is from that mass, the orbital speed of a star revolving around the centre of a spir ...
FlerasLectures - University of Oklahoma
... constituents of matter and radiation, and the interactions between them. It is also called "high energy physics", because many elementary particles do not occur under normal circumstances in nature, but can be created and detected during energetic collisions of other particles, as is done in particl ...
... constituents of matter and radiation, and the interactions between them. It is also called "high energy physics", because many elementary particles do not occur under normal circumstances in nature, but can be created and detected during energetic collisions of other particles, as is done in particl ...