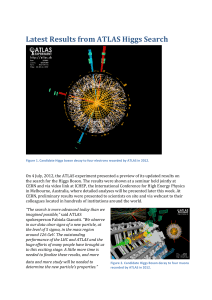
Slide 1
... measure the solar flux with neutral current (NC), charges current (CC) and elastic scattering (mixed NC and CC) CC: νe + d → e− + p + p ...
... measure the solar flux with neutral current (NC), charges current (CC) and elastic scattering (mixed NC and CC) CC: νe + d → e− + p + p ...
No Slide Title - Webcast
... Z particles decays “democratically” into all possible quark-anti quark pairs (sometimes accompanied by one or more gluons and all possible lepton-anti lepton pairs. Quarks and gluons seen as jets, and charged leptons as single tracks neutrino-anti neutrino pairs are NOT observed However, the number ...
... Z particles decays “democratically” into all possible quark-anti quark pairs (sometimes accompanied by one or more gluons and all possible lepton-anti lepton pairs. Quarks and gluons seen as jets, and charged leptons as single tracks neutrino-anti neutrino pairs are NOT observed However, the number ...
Review of the Safety of LHC Collisions
... Fig. 1: The spectrum of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, as measured by several experiments [5]. Every cosmic ray with an energy shown in this plot, namely above 1017 eV, liberates in its collision with the atmosphere more energy in its centre-ofmass frame than does a proton-proton collision at the L ...
... Fig. 1: The spectrum of ultra-high-energy cosmic rays, as measured by several experiments [5]. Every cosmic ray with an energy shown in this plot, namely above 1017 eV, liberates in its collision with the atmosphere more energy in its centre-ofmass frame than does a proton-proton collision at the L ...
"Applications of nuclear physics"()
... together, but is significant for two protons on opposite sides of a large nucleus. Another feature of the force between two nucleons is that it changes from being attractive to repulsive at very short distances so that two nucleons cannot overlap (under normal conditions) in a nucleus. The nuclear f ...
... together, but is significant for two protons on opposite sides of a large nucleus. Another feature of the force between two nucleons is that it changes from being attractive to repulsive at very short distances so that two nucleons cannot overlap (under normal conditions) in a nucleus. The nuclear f ...
MU08-CHAPTER6.doc
... an aurora of mysticism, entities of matter regarded as being of supernatural nature, not possible to be explain in a rational way. One also are taking about “hidden parameters” in this context. But it is fully clear, that the existence of the atomic constants says a lot about the quantum mechanical ...
... an aurora of mysticism, entities of matter regarded as being of supernatural nature, not possible to be explain in a rational way. One also are taking about “hidden parameters” in this context. But it is fully clear, that the existence of the atomic constants says a lot about the quantum mechanical ...
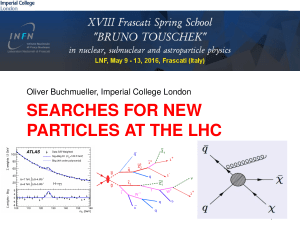
SEARCHES FOR NEW PARTICLES AT THE LHC
... science (some which go to the heart of our existence): about the origin, evolution and composition of our universe. In particular, what is the origin of mass? what constitutes dark matter? do we live in more than 3 space dimensions? why is the universe composed of matter, and not antimatter? ...
... science (some which go to the heart of our existence): about the origin, evolution and composition of our universe. In particular, what is the origin of mass? what constitutes dark matter? do we live in more than 3 space dimensions? why is the universe composed of matter, and not antimatter? ...