High-Power Diode Lasers under External Optical Feedback
... A reduction of the laser threshold by 20 percent caused by the presence of external feedback has been reported by Takiguchi et al. [5] for 808 nm emitting devices. Hempel et al. [8] reported an emission power increase by 2.3 percent for other 808 nm emitting devices, which have originally been desig ...
... A reduction of the laser threshold by 20 percent caused by the presence of external feedback has been reported by Takiguchi et al. [5] for 808 nm emitting devices. Hempel et al. [8] reported an emission power increase by 2.3 percent for other 808 nm emitting devices, which have originally been desig ...
Optical Sources - BYU -- ECEn 466 Course Information
... The optical fiber support a set of discrete modes Qualitatively these modes can be thought of as different propagation angles ...
... The optical fiber support a set of discrete modes Qualitatively these modes can be thought of as different propagation angles ...
Size Influence on the Propagation Loss Induced by Sidewall
... Silicon–silicon dioxide (Si–SiO ) waveguides benefit from a large refractive index difference, inducing a high electromagnetic field confinement in the silicon guiding layer which in turn allows reducing the waveguide size to submicrometer values [3]. Nevertheless, in order to use SOI waveguides for ...
... Silicon–silicon dioxide (Si–SiO ) waveguides benefit from a large refractive index difference, inducing a high electromagnetic field confinement in the silicon guiding layer which in turn allows reducing the waveguide size to submicrometer values [3]. Nevertheless, in order to use SOI waveguides for ...
Effect of group-delay ripples on dispersion
... phase reversal. In Region I 共c 苷 p兲, the center frequency of the soliton is aligned with one of the minima of the dispersion ripples. The effective grating dispersion is always anomalous, i.e., b # 0, because we have chosen g , 0. When T0 is large, the dispersion varies rapidly in a pulse bandwidth. ...
... phase reversal. In Region I 共c 苷 p兲, the center frequency of the soliton is aligned with one of the minima of the dispersion ripples. The effective grating dispersion is always anomalous, i.e., b # 0, because we have chosen g , 0. When T0 is large, the dispersion varies rapidly in a pulse bandwidth. ...
Point spread function engineering in confocal scanning microscopy
... The improvement of the performance of optical microscopes has aimed many researches along the last decades. Conventional wide-field microscopes are close to reach their maximum efficiency through the use of the available objectives with numerical apertures (NA) up to 1.4. However, when using this ki ...
... The improvement of the performance of optical microscopes has aimed many researches along the last decades. Conventional wide-field microscopes are close to reach their maximum efficiency through the use of the available objectives with numerical apertures (NA) up to 1.4. However, when using this ki ...
Chapter 4 Optical Resonator
... 4 matrix. (a) Determine the 4 x 4 ray-transfer matrix of a distance d in free space. (b) Determine the 4 X 4 ray-transfer matrix of a thin cylindrical lens with focal length f oriented in the y direction. The cylindrical lens has focal length f for rays in the y-z plane, and no focusing power for ra ...
... 4 matrix. (a) Determine the 4 x 4 ray-transfer matrix of a distance d in free space. (b) Determine the 4 X 4 ray-transfer matrix of a thin cylindrical lens with focal length f oriented in the y direction. The cylindrical lens has focal length f for rays in the y-z plane, and no focusing power for ra ...
Passive Light and Viewpoint Sensitive Display of 3D Content
... however they all consider restricted subsets of lightsensitive effects. For example, some displays consider only 2D surfaces. Other displays consider 3D targets, but assume that the viewer position is fixed. An alternative model considers only distant light sources, which produce spatiallyinvariant ...
... however they all consider restricted subsets of lightsensitive effects. For example, some displays consider only 2D surfaces. Other displays consider 3D targets, but assume that the viewer position is fixed. An alternative model considers only distant light sources, which produce spatiallyinvariant ...
here - Optoelectronics Research Centre
... because of the intensity noise, the clarity of the OCT image can be sacrificed even though much finer axial resolution can be obtained when using this technology. Using a commercial supercontinuum SC450 (Fianium, UK) source, its performance in terms of its interference signal shape and its relative ...
... because of the intensity noise, the clarity of the OCT image can be sacrificed even though much finer axial resolution can be obtained when using this technology. Using a commercial supercontinuum SC450 (Fianium, UK) source, its performance in terms of its interference signal shape and its relative ...
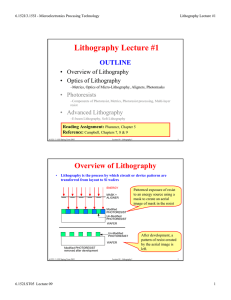
Lithography Lecture #1
... Observation of the light intensity at a distance R (usually at the focal length f) shows the above circular diffraction pattern. The diffraction pattern has a diameter (of central maximum) equal to q1. ...
... Observation of the light intensity at a distance R (usually at the focal length f) shows the above circular diffraction pattern. The diffraction pattern has a diameter (of central maximum) equal to q1. ...
Increasing the Resolution of Far
... with Carl Zeiss. Studying the image formation in light microscopy, Ernst Abbe realized the importance of the wave nature of light and its central role in the resolution issue(2). He found a fundamental limit that still bears his name. When imaging a point-like object with a lens, the point is imaged ...
... with Carl Zeiss. Studying the image formation in light microscopy, Ernst Abbe realized the importance of the wave nature of light and its central role in the resolution issue(2). He found a fundamental limit that still bears his name. When imaging a point-like object with a lens, the point is imaged ...
Wave optical simulations of x-ray nano
... domain, modern synchrotron sources are different in horizontal and vertical direction. This often is simplified by an elliptical distribution of electrons around their orbit [9,10]. At least in vertical direction “rather coherent” beams can be expected, while in the horizontal direction the degree o ...
... domain, modern synchrotron sources are different in horizontal and vertical direction. This often is simplified by an elliptical distribution of electrons around their orbit [9,10]. At least in vertical direction “rather coherent” beams can be expected, while in the horizontal direction the degree o ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.