Statistics of the received power for free space optical channels
... PDF of the normalized log irradiance ln(I) for a low order adaptively compensated Gaussian beam for the receiving apertures of diameter 5.6 mm(point receiver)(a), ρ0 /2 (b), ρ (c), and 3ρ /2 (d). Simulation results for turbulence strength Cn2 = 1 × 10−15 m−2/3 and propagation distance of 10 km are c ...
... PDF of the normalized log irradiance ln(I) for a low order adaptively compensated Gaussian beam for the receiving apertures of diameter 5.6 mm(point receiver)(a), ρ0 /2 (b), ρ (c), and 3ρ /2 (d). Simulation results for turbulence strength Cn2 = 1 × 10−15 m−2/3 and propagation distance of 10 km are c ...
Pulse Propagation in Optical Fibers
... dispersion strongly limits the bandwidth of the transmitted signal and may cause interference between symbols, we address several methods for reducing the effect of dispersion, which can be very efficient: the use of dispersion compensating fibers and the propagation of solitons. In non-linear syste ...
... dispersion strongly limits the bandwidth of the transmitted signal and may cause interference between symbols, we address several methods for reducing the effect of dispersion, which can be very efficient: the use of dispersion compensating fibers and the propagation of solitons. In non-linear syste ...
Design of Refractive Index Profile for Multimode Optical Fibers with
... However DMD occurs even in the LOMFs, and it can become critical during the passage to higher bit rates. Although there are VCSEL modulation limits, DMD is also one of the main reasons for using the parallel-optics transmission instead of serial transmission in IEEE 802.3ba standard of 40/100G, whic ...
... However DMD occurs even in the LOMFs, and it can become critical during the passage to higher bit rates. Although there are VCSEL modulation limits, DMD is also one of the main reasons for using the parallel-optics transmission instead of serial transmission in IEEE 802.3ba standard of 40/100G, whic ...
References
... as a diverging speckle beam. Their transversal coherence properties are ruled by the well known generalized Van Cittert-Zernike (VCZ) theorem[11,12], while their longitudinal properties appear to be still governed by ordinary diffraction behavior [5-7], as for the deep Fresnel case, they continue to ...
... as a diverging speckle beam. Their transversal coherence properties are ruled by the well known generalized Van Cittert-Zernike (VCZ) theorem[11,12], while their longitudinal properties appear to be still governed by ordinary diffraction behavior [5-7], as for the deep Fresnel case, they continue to ...
NGAO NGS WFS design review - Caltech Optical Observatories
... – to simply the size of moving parts while facilitating the two pupil sampling modes, we use the same collimator and post-lenslet relay for both the 63 and 5 sub-ap mode of operation. – We choose 48 pixels/sub-aperture (instead of 50 pixels/sub-ap) to enable 4x4 binned pixel/sub-aperture operation w ...
... – to simply the size of moving parts while facilitating the two pupil sampling modes, we use the same collimator and post-lenslet relay for both the 63 and 5 sub-ap mode of operation. – We choose 48 pixels/sub-aperture (instead of 50 pixels/sub-ap) to enable 4x4 binned pixel/sub-aperture operation w ...
S U P E R -R E S O LV... Scientific Background on the Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2014
... technique remains technically cumbersome and its applications have remained limited to surface studies. The scientific and technical breakthrough in super-resolved fluorescence microscopy has instead come in the form of far-field excitation techniques of two main types, as will be described in the ...
... technique remains technically cumbersome and its applications have remained limited to surface studies. The scientific and technical breakthrough in super-resolved fluorescence microscopy has instead come in the form of far-field excitation techniques of two main types, as will be described in the ...
super-resolved fluorescence microscopy
... technique remains technically cumbersome and its applications have remained limited to surface studies. The scientific and technical breakthrough in super-resolved fluorescence microscopy has instead come in the form of far-field excitation techniques of two main types, as will be described in the ...
... technique remains technically cumbersome and its applications have remained limited to surface studies. The scientific and technical breakthrough in super-resolved fluorescence microscopy has instead come in the form of far-field excitation techniques of two main types, as will be described in the ...
Gaussian Beam Optics [Hecht Ch. 13.1 pages 594
... Unfortunately, the output from real-life lasers is not truly Gaussian (although helium neon lasers and argon-ion lasers are a very close approximation). To accommodate this variance, a quality factor, M2 (called the “M-squared” factor), has been defined to describe the deviation of the laser beam fr ...
... Unfortunately, the output from real-life lasers is not truly Gaussian (although helium neon lasers and argon-ion lasers are a very close approximation). To accommodate this variance, a quality factor, M2 (called the “M-squared” factor), has been defined to describe the deviation of the laser beam fr ...
INVESTIGATION OF INJECTION MOLDING PROCESS FOR HIGH
... 1.1 Research Motivation A lens is an optical device that transmits or refracts light to either concentrate or diverge. It is usually formed from a piece of shaped high purity glass or plastic. A high precision lens is manufactured with very high tolerances, and a slight defect in the lens can cause ...
... 1.1 Research Motivation A lens is an optical device that transmits or refracts light to either concentrate or diverge. It is usually formed from a piece of shaped high purity glass or plastic. A high precision lens is manufactured with very high tolerances, and a slight defect in the lens can cause ...
CARMENES in SPIE 2014. Building a fiber link for CARMENES
... CARMENES is a high-resolution spectroscopy project for the 3.5 m telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory, consisting of two R ∼ 82000 echelle spectrographs, one for the visual range from 550 nm to 950 nm (VIS) and one for the near infrared range from 950 nm to 1700 nm (NIR). The main scientific goal ...
... CARMENES is a high-resolution spectroscopy project for the 3.5 m telescope at the Calar Alto Observatory, consisting of two R ∼ 82000 echelle spectrographs, one for the visual range from 550 nm to 950 nm (VIS) and one for the near infrared range from 950 nm to 1700 nm (NIR). The main scientific goal ...
Profiling Atmospheric Turbulence with Single Star
... A generalised SCIDAR (SCIntillation Detection And Ranging) system for characterising atmospheric parameters using single star scintillation is presented. Astronomical scintillation is the variation in apparent luminosity of a distant object, such as a star, viewed through the atmosphere. Scintillati ...
... A generalised SCIDAR (SCIntillation Detection And Ranging) system for characterising atmospheric parameters using single star scintillation is presented. Astronomical scintillation is the variation in apparent luminosity of a distant object, such as a star, viewed through the atmosphere. Scintillati ...
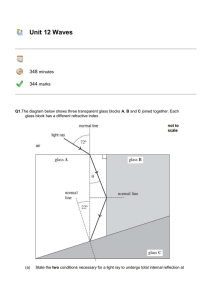
AS Waves and Optics
... (a) In an experiment, a narrow beam of white light from a filament lamp is directed at normal incidence at a diffraction grating. Complete the diagram in the figure below to show the light beams transmitted by the grating, showing the zero-order beam and the ...
... (a) In an experiment, a narrow beam of white light from a filament lamp is directed at normal incidence at a diffraction grating. Complete the diagram in the figure below to show the light beams transmitted by the grating, showing the zero-order beam and the ...
Optical switches
... Optical fiber characteristics • Dispersion is an undesirable phenomenon in optical fibers • causes an initially narrow light pulse to spread out as it propagates along the fiber • There are different causes for dispersion • modal dispersion • chromatic dispersion • Modal dispersion • occurs in multi ...
... Optical fiber characteristics • Dispersion is an undesirable phenomenon in optical fibers • causes an initially narrow light pulse to spread out as it propagates along the fiber • There are different causes for dispersion • modal dispersion • chromatic dispersion • Modal dispersion • occurs in multi ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.