Microscopy - Frank`s Hospital Workshop
... structures emit light no matter if they are in focus or not. This means that an image of a certain structure is always blurred by the contribution of light from structures which are out of focus. This phenomenon becomes apparent as a loss of contrast especially when using objectives with a high reso ...
... structures emit light no matter if they are in focus or not. This means that an image of a certain structure is always blurred by the contribution of light from structures which are out of focus. This phenomenon becomes apparent as a loss of contrast especially when using objectives with a high reso ...
15. Atmospheric Channel Effects and the Impact on
... by several orders of magnitude. Usually all weather phenomena (and thus also cloud coverage) happen inside the troposphere, which extends up to a height of 11 km. In reference [4] the maximum cirrus altitude is given with approximately 19 km. The influence of the atmosphere on an optical link from a ...
... by several orders of magnitude. Usually all weather phenomena (and thus also cloud coverage) happen inside the troposphere, which extends up to a height of 11 km. In reference [4] the maximum cirrus altitude is given with approximately 19 km. The influence of the atmosphere on an optical link from a ...
Three-Dimensional Simulation of Vertical-Cavity Surface
... Therefore it is essential to use materials with large enough index contrast to achieve the necessary feedback level. A second stringent condition on mirror formation is the need for matching the lattice constants to avoid mechanical stress in the DBRs. These two restrictions usually demand quaternar ...
... Therefore it is essential to use materials with large enough index contrast to achieve the necessary feedback level. A second stringent condition on mirror formation is the need for matching the lattice constants to avoid mechanical stress in the DBRs. These two restrictions usually demand quaternar ...
Chapter 2 - Handbook of Optics
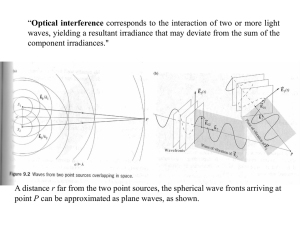
... metrology tool. The wavelength of light is used as the unit of measurement. Interferometers can be configured to measure small variations in distance, index, or wavelength. When two monochromatic waves are interfered, the interference fringes exist not only in the plane of observation, but throughou ...
... metrology tool. The wavelength of light is used as the unit of measurement. Interferometers can be configured to measure small variations in distance, index, or wavelength. When two monochromatic waves are interfered, the interference fringes exist not only in the plane of observation, but throughou ...
Ellipsometry of light scattering from multilayer coatings
... n 5 0.8 1 j6 with j2 5 21. A better agreement could be found by fitting the measurements and obtaining a more accurate value for the Al complex refractive index, but such an inverse problem is not our purpose here. In Fig. 5 the sample under study at 633 nm has a design given as HLHLH~6L!HLHLH, wher ...
... n 5 0.8 1 j6 with j2 5 21. A better agreement could be found by fitting the measurements and obtaining a more accurate value for the Al complex refractive index, but such an inverse problem is not our purpose here. In Fig. 5 the sample under study at 633 nm has a design given as HLHLH~6L!HLHLH, wher ...
Resonant bio- and chemical sensors using low-refractive
... MOFs can be mass-produced using commercial fiber draw tower in a very cost-effective manner. Fifth, the MOFs can potentially be scaled up into a two-dimensional array with small dimensions, which is suitable for making into portable point-of-care devices for simultaneous on-site detection of differen ...
... MOFs can be mass-produced using commercial fiber draw tower in a very cost-effective manner. Fifth, the MOFs can potentially be scaled up into a two-dimensional array with small dimensions, which is suitable for making into portable point-of-care devices for simultaneous on-site detection of differen ...
Lecture 16 - University of St Andrews
... Picture credit: http://www.tpub.com/neets/tm/108-3.htm Optical Fibres and Telecommunications – Real World Networks ...
... Picture credit: http://www.tpub.com/neets/tm/108-3.htm Optical Fibres and Telecommunications – Real World Networks ...
Refractive-Index-Matched Indium--Tin
... indium–tin-oxide (ITO) electrodes which are used to induce a bias to the LC. The top and the bottom ITO electrodes should have properties of high optical transmittance and low sheet resistance. However, mismatch in refractive index between ITO, LC, and glass results in Fresnel reflection losses at ea ...
... indium–tin-oxide (ITO) electrodes which are used to induce a bias to the LC. The top and the bottom ITO electrodes should have properties of high optical transmittance and low sheet resistance. However, mismatch in refractive index between ITO, LC, and glass results in Fresnel reflection losses at ea ...
Optimization of axial resolution in a confocal microscope with
... with D-shaped apertures exhibits a poorer axial resolution than in the conventional confocal microscope with circular apertures, the behavior is different with a finite-sized detector. It is of practical significance that for a given finite-sized detector there is an optimum configuration (value of ...
... with D-shaped apertures exhibits a poorer axial resolution than in the conventional confocal microscope with circular apertures, the behavior is different with a finite-sized detector. It is of practical significance that for a given finite-sized detector there is an optimum configuration (value of ...
Principles and techniques of digital holographic microscopy
... Holography was invented in 1948 by Dennis Gabor in an effort to improve the resolution of the electron microscope, where the correction of electron lens aberrations posed increasing technical difficulty. Instead of attempting to perfect the electron imaging lens, Gabor dispensed it altogether and re ...
... Holography was invented in 1948 by Dennis Gabor in an effort to improve the resolution of the electron microscope, where the correction of electron lens aberrations posed increasing technical difficulty. Instead of attempting to perfect the electron imaging lens, Gabor dispensed it altogether and re ...
TIE-27 Stress in optical glass
... fine annealing with ideally crossing the strain point as slow as possible. In reality this is often not feasible due to two main reasons: First it is uneconomical because very small annealing rates increase the overall annealing time and therefore the cost of the glass. The second reason is that the ...
... fine annealing with ideally crossing the strain point as slow as possible. In reality this is often not feasible due to two main reasons: First it is uneconomical because very small annealing rates increase the overall annealing time and therefore the cost of the glass. The second reason is that the ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.