Electrical Excitation of Surface Plasmons
... tunnel junction. This is accomplished by refocusing the fields in the back focal plane of the objective on a CCD. The resulting image corresponds to the Fourier transform of Eq. (1). If the dominant contribution to light emission does indeed originate from a vertical dipole, we expect an intensity n ...
... tunnel junction. This is accomplished by refocusing the fields in the back focal plane of the objective on a CCD. The resulting image corresponds to the Fourier transform of Eq. (1). If the dominant contribution to light emission does indeed originate from a vertical dipole, we expect an intensity n ...
OpticalPosterLax
... between different deserializers; - signal integrity, by minimizing crosstalk and reflections. ...
... between different deserializers; - signal integrity, by minimizing crosstalk and reflections. ...
Fig. 1 - Computational Manufacturing and Materials Research Lab
... Remark. From this point forth in the analysis, the ambient medium is assumed to behave as a vacuum. Thus, there are no energetic losses as the electromagnetic rays passes through it. However, we assume that all electromagnetic energy that is absorbed by a particle becomes trapped, and not re-emitted ...
... Remark. From this point forth in the analysis, the ambient medium is assumed to behave as a vacuum. Thus, there are no energetic losses as the electromagnetic rays passes through it. However, we assume that all electromagnetic energy that is absorbed by a particle becomes trapped, and not re-emitted ...
1 Janaky Narayanan PC 5213 AY 2004
... atoms that are obtained when parts of the molecule are rotated about one of the bonds. A change in the conformation necessarily does not involve any breaking of covalent bonds. Groups that are connected by a single bond can undergo rotation leading to different relative orientations with respect to ...
... atoms that are obtained when parts of the molecule are rotated about one of the bonds. A change in the conformation necessarily does not involve any breaking of covalent bonds. Groups that are connected by a single bond can undergo rotation leading to different relative orientations with respect to ...
Unsupervised Color Decomposition of Histologically Stained Tissue
... exposure coefficients were inverted prior to the unmixing as they have no bearing on the staining process. In order to quantitatively evaluate the decomposition provided by NMF and ICA, we prepared a set of ground truth data using the following procedure. Using a set of four tissue samples, we first ...
... exposure coefficients were inverted prior to the unmixing as they have no bearing on the staining process. In order to quantitatively evaluate the decomposition provided by NMF and ICA, we prepared a set of ground truth data using the following procedure. Using a set of four tissue samples, we first ...
optical fiber communication
... Because GaAsP LEDs operate at a longer wavelength than GaAs LEDs (1.3 micrometers vs. ...
... Because GaAsP LEDs operate at a longer wavelength than GaAs LEDs (1.3 micrometers vs. ...
Optical Fiber Communication
... Because GaAsP LEDs operate at a longer wavelength than GaAs LEDs (1.3 micrometers vs. 0.81-0.87 micrometers), their output spectrum is wider by a factor of about 1.7. ...
... Because GaAsP LEDs operate at a longer wavelength than GaAs LEDs (1.3 micrometers vs. 0.81-0.87 micrometers), their output spectrum is wider by a factor of about 1.7. ...
Theoretical analysis of phase-matched second
... In conclusion, we have theoretically analyzed nonlinear propagation in birefringent waveguide material for the generation of coherent IR laser light by second-harmonic generation and by optical parametric oscillation. The specific guide material used in the calculation was ZnGeP2 on a GaP substrate. ...
... In conclusion, we have theoretically analyzed nonlinear propagation in birefringent waveguide material for the generation of coherent IR laser light by second-harmonic generation and by optical parametric oscillation. The specific guide material used in the calculation was ZnGeP2 on a GaP substrate. ...
Performance of synchronous optical receivers using atmospheric
... of atmospheric wave-front phase distortion to improve the performance of atmospheric systems has been an important field of study for many years. In particular, modal compensation method involves correction of several modes of an expansion of the total phase distortion in a set of basis functions. H ...
... of atmospheric wave-front phase distortion to improve the performance of atmospheric systems has been an important field of study for many years. In particular, modal compensation method involves correction of several modes of an expansion of the total phase distortion in a set of basis functions. H ...
Nondiffracting Light Beams for Long Ranges
... lence than the surrounding region (side lobs). Furthermore the LRNB is more stable than general collimated or focused beams. The fact has been reported quantitatively [11]. Secondly, it was become clear from computer simulations that, over a long range, the main lobe width is smaller than that of n ...
... lence than the surrounding region (side lobs). Furthermore the LRNB is more stable than general collimated or focused beams. The fact has been reported quantitatively [11]. Secondly, it was become clear from computer simulations that, over a long range, the main lobe width is smaller than that of n ...
A simple demonstration of frustrated total internal reflection
... 共5兲–共7兲 and note that n, n2 − 1, and cos 0 are of the order of 1. It is then easy to see that the exponential approximation can be made for d ⲏ / 4. We will be considering this limit, that is, when the coupling between the two high refractive index media is exponential. Also note that, although t ...
... 共5兲–共7兲 and note that n, n2 − 1, and cos 0 are of the order of 1. It is then easy to see that the exponential approximation can be made for d ⲏ / 4. We will be considering this limit, that is, when the coupling between the two high refractive index media is exponential. Also note that, although t ...
Observation of optical polarization Möbius strips
... different scalar topological charges. In this scheme, a nonparaxial 3D polarization topology is generated at the beams’ intersection plane (15). Analytical calculations revealed spectacular 3D-polarization topologies in the form of twisted ribbons and Möbius strips (16). Möbius strips are 3D objects ...
... different scalar topological charges. In this scheme, a nonparaxial 3D polarization topology is generated at the beams’ intersection plane (15). Analytical calculations revealed spectacular 3D-polarization topologies in the form of twisted ribbons and Möbius strips (16). Möbius strips are 3D objects ...
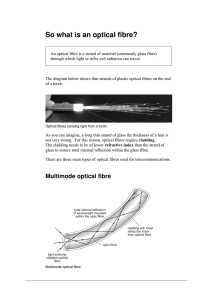
optical fibres
... The glass strand inside this optical fibre is only 3–5 µm (3 –5 x 10–6 m) in diameter and only transmits a single impulse at any one time. Only one light wave can fit inside the inner core at one time. An impulse of light travels through the high refractive index material centre. Because there is no ...
... The glass strand inside this optical fibre is only 3–5 µm (3 –5 x 10–6 m) in diameter and only transmits a single impulse at any one time. Only one light wave can fit inside the inner core at one time. An impulse of light travels through the high refractive index material centre. Because there is no ...
Revista Mexicana de Física . Simulation of Michelson and
... Almost every physics lab at the undergraduate level includes the Michelson and Young experiments in the Optics program. This is important not only from the historical point of view but also for the didactic development of a General Physics course [1]. In this paper, these popular optical experiments ...
... Almost every physics lab at the undergraduate level includes the Michelson and Young experiments in the Optics program. This is important not only from the historical point of view but also for the didactic development of a General Physics course [1]. In this paper, these popular optical experiments ...
Capacity of coherent free-space optical links using
... system performance. Later analyses have attempted to overcome these limitations and fully characterize the statistics of heterodyne optical systems by assuming a highly simplified model of atmospheric effects [8,9]. An alternate approach, aimed at overcoming the limitations of previous work, is base ...
... system performance. Later analyses have attempted to overcome these limitations and fully characterize the statistics of heterodyne optical systems by assuming a highly simplified model of atmospheric effects [8,9]. An alternate approach, aimed at overcoming the limitations of previous work, is base ...
Spider Silk: The Mother Nature`s Biological Superlens
... the 100 nm separation lines. Similar to figure 3d, the spider silk in figure S1 unmistakably resolves the pattern while under reflection mode. However, the spider silk projects the pattern at an angled image. The angled image is expected and can be described by the laws of refraction and convex lens ...
... the 100 nm separation lines. Similar to figure 3d, the spider silk in figure S1 unmistakably resolves the pattern while under reflection mode. However, the spider silk projects the pattern at an angled image. The angled image is expected and can be described by the laws of refraction and convex lens ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.