Time-of-flight optical ranging system based on time
... output is split off and provides a timing signal that starts a time-to-amplitude converter ~TAC!. The remaining laser signal is directed toward the target, and the scattered return signal is routed to a photoncounting detector, which stops the TAC on arrival of the first photon. The TAC produces an ...
... output is split off and provides a timing signal that starts a time-to-amplitude converter ~TAC!. The remaining laser signal is directed toward the target, and the scattered return signal is routed to a photoncounting detector, which stops the TAC on arrival of the first photon. The TAC produces an ...
297.4 kB
... The past ten years have seen much interest in the application of deformation/strain measurement techniques for the inspection and monitoring of works of art, covering point-strain measurements using resistance-strain gauges and fibre-optic sensors, as well as full-field optical measurement approache ...
... The past ten years have seen much interest in the application of deformation/strain measurement techniques for the inspection and monitoring of works of art, covering point-strain measurements using resistance-strain gauges and fibre-optic sensors, as well as full-field optical measurement approache ...
Associate Professor Shien
... (1). Investigation and application of WADM in a passive optical ring networks. Optical add/drop and optical cross-connect and are crucial functions in a metropolitan area network. The possible solutions for WADM are thin film based WADM, array waveguide grating (AWG) based WADM and fiber Bragg grati ...
... (1). Investigation and application of WADM in a passive optical ring networks. Optical add/drop and optical cross-connect and are crucial functions in a metropolitan area network. The possible solutions for WADM are thin film based WADM, array waveguide grating (AWG) based WADM and fiber Bragg grati ...
Optics - Frederiksen
... This simple, high intensity light is very suitable for experiments with lenses, prisms and optical gratings. The light source itself is a small festoon lamp with the filament aligned with the supporting rod making it easy to position on an optical bench. The long, narrow filament is ideal for perfor ...
... This simple, high intensity light is very suitable for experiments with lenses, prisms and optical gratings. The light source itself is a small festoon lamp with the filament aligned with the supporting rod making it easy to position on an optical bench. The long, narrow filament is ideal for perfor ...
Thermal Lensing in a Nd:YAG Laser Rod
... obtained with the gas laser. However, the deviation is within the accuracy of these two methods which we believe is in the order of 20%. In order to check the degree of physical distortion in the flatness of the rod ends under pump light an experiment as shown in Fig. 5 was performed. The collimated ...
... obtained with the gas laser. However, the deviation is within the accuracy of these two methods which we believe is in the order of 20%. In order to check the degree of physical distortion in the flatness of the rod ends under pump light an experiment as shown in Fig. 5 was performed. The collimated ...
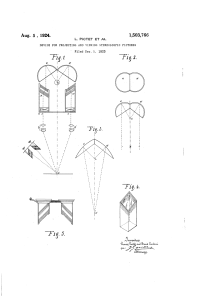
Device for projecting and viewing stereoscopic pictures
... ing to the invention use is made not only of the backward rays, but also of the lateral sess the disadvantage that they have a right rays which are usually lost. In this manner and a wrong side, one of theends having about twice as many rays are utilized and to be placed before the eyes: if the othe ...
... ing to the invention use is made not only of the backward rays, but also of the lateral sess the disadvantage that they have a right rays which are usually lost. In this manner and a wrong side, one of theends having about twice as many rays are utilized and to be placed before the eyes: if the othe ...
Assessment of optical systems by means of point
... in a craftmanship way, without the feedback from reliable and objective optical measurement. Generally speaking, one could say that he modern epoch of high-quality instrument making has started with the pioneering work by Joseph von Fraunhofer who combined his gifts in optical design with a professi ...
... in a craftmanship way, without the feedback from reliable and objective optical measurement. Generally speaking, one could say that he modern epoch of high-quality instrument making has started with the pioneering work by Joseph von Fraunhofer who combined his gifts in optical design with a professi ...
Shaping the focal intensity distribution using spatial coherence
... the lens plane will result in the same intensity distribution at focus. For instance, one could use a coherent laser field transmitted through a rotating ground-glass plate with the desired correlations. This coherence shaping of the intensity distribution at focus holds promise as a new technique f ...
... the lens plane will result in the same intensity distribution at focus. For instance, one could use a coherent laser field transmitted through a rotating ground-glass plate with the desired correlations. This coherence shaping of the intensity distribution at focus holds promise as a new technique f ...
Lecture 3
... interact with light in a manner that is dependent upon the orientation of the crystalline lattice with respect to the incident light. When light enters the optical axis (c) of anisotropic crystals, it acts in a manner similar to interaction with isotropic crystals and passes through at a single velo ...
... interact with light in a manner that is dependent upon the orientation of the crystalline lattice with respect to the incident light. When light enters the optical axis (c) of anisotropic crystals, it acts in a manner similar to interaction with isotropic crystals and passes through at a single velo ...
1 L2: Reflection and Refraction c3.L2 REFLECTION AND
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
... Colours of objects can be explained by supposing that their surfaces reflect different proportions of the various frequency (or wavelength) components of the incident light. Different mixes of these components produce the different visual sensations that we call colour. It is worth noting in passing ...
... 1. A Quartz crystal of thickness 0.001 m vibrates in its fundamental frequency. Calculate its frequency. (Given that E= 7.9X1010 and ρ = 2650Kg/m3 for quartz) 2. An ultrasonic interferometer used to measure the velocity in sea water. If the distance between two constructive anti nodes is 0.55 mm. Co ...
Single-plane multiple speckle pattern phase retrieval
... and non-planarity issues. The calculated distances for the proposed AOsystem are evaluated experimentally using the conventional free-space phase retrieval setup. Two distance ranges are investigated depending on whether the measurement planes satisfy the Nyquist detector sampling condition or not. ...
... and non-planarity issues. The calculated distances for the proposed AOsystem are evaluated experimentally using the conventional free-space phase retrieval setup. Two distance ranges are investigated depending on whether the measurement planes satisfy the Nyquist detector sampling condition or not. ...
Document
... 37- Interference of light: it result from superposing of the light waves produced from 2 sources having the same frequency and amplitude and the same direction of propagation and phase 38- Coherent sound source: they are sources whose waves have the same phase and frequency and amplitude 39- Interfe ...
... 37- Interference of light: it result from superposing of the light waves produced from 2 sources having the same frequency and amplitude and the same direction of propagation and phase 38- Coherent sound source: they are sources whose waves have the same phase and frequency and amplitude 39- Interfe ...
Document
... When a ray of light travelling in air falls upon a glass surface, part of the ray is reflected from the surface while the other part of the ray enters the glass and deviates from its original path. The latter ray is said to be refracted. For EM waves travelling in an isotropic, nonincident ray condu ...
... When a ray of light travelling in air falls upon a glass surface, part of the ray is reflected from the surface while the other part of the ray enters the glass and deviates from its original path. The latter ray is said to be refracted. For EM waves travelling in an isotropic, nonincident ray condu ...
Panoramic Imaging with Horizontal Stereo - CS
... Regular images are created by perspective projections: scene points are projected onto the image surface along projection lines passing through a single point, called the “optical center” or the “viewpoint”. Multiple viewpoint projections use different viewpoints for different viewing direction, and ...
... Regular images are created by perspective projections: scene points are projected onto the image surface along projection lines passing through a single point, called the “optical center” or the “viewpoint”. Multiple viewpoint projections use different viewpoints for different viewing direction, and ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.