Ultrahigh-resolution full-field optical coherence microscopy using
... 7.8 dB could theoretically be obtained when M = ∞ . In practice, however, the FWD should not be indefinitely increased because the number of photons converted into electrons is limited by the brightness of the light source. Additionally, the sensitivity enhancement is not significant above a certain ...
... 7.8 dB could theoretically be obtained when M = ∞ . In practice, however, the FWD should not be indefinitely increased because the number of photons converted into electrons is limited by the brightness of the light source. Additionally, the sensitivity enhancement is not significant above a certain ...
High-resolution Measurement of Refractive Index Based on Resonant Tunneling Effect
... Obviously, such a PBG may be viewed as a perfect mirror and is particularly useful for constructing the resonant cavities in the optical region, and only the resonant frequencies can be captured by this cavity. We can conjecture that the resonant frequency of the sharp peaks would shift when the ref ...
... Obviously, such a PBG may be viewed as a perfect mirror and is particularly useful for constructing the resonant cavities in the optical region, and only the resonant frequencies can be captured by this cavity. We can conjecture that the resonant frequency of the sharp peaks would shift when the ref ...
Estimating the velocity profile and acoustical quantities of a
... 0.05, 0.07, 0.10, 0.13, 0.19 m), and, finally, for the farfield at 1 m distance. For a particular frequency at 13.72 kHz (ka = 8.0423), the magnitude of the sound pressure is plotted in Fig. 2 (solid curve ‘p meas’). Using the same procedure as described above for the first simulation, the inverse p ...
... 0.05, 0.07, 0.10, 0.13, 0.19 m), and, finally, for the farfield at 1 m distance. For a particular frequency at 13.72 kHz (ka = 8.0423), the magnitude of the sound pressure is plotted in Fig. 2 (solid curve ‘p meas’). Using the same procedure as described above for the first simulation, the inverse p ...
Horizontal Distance Measurement
... • Microwave: two positive units, GPS replaced them for most engineering applications such as hydrographic surveys ...
... • Microwave: two positive units, GPS replaced them for most engineering applications such as hydrographic surveys ...
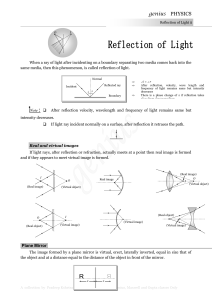
Interference3
... • For monochromatic light beam incident on a wedge shaped film , are constant. So change in path difference is only due to varying thickness of the film. At a particular point thickness is constant. So we get a bright or dark fringe at that point due to constant path difference. • Thickness of t ...
... • For monochromatic light beam incident on a wedge shaped film , are constant. So change in path difference is only due to varying thickness of the film. At a particular point thickness is constant. So we get a bright or dark fringe at that point due to constant path difference. • Thickness of t ...
Optical Coherence Tomography as a diagnostic tool
... backscattering properties of tissues. The light reflected off a sample is interfered with a reference wave utilizing a technique known as low-coherence interferometry. An interference signal arises when the optical pathlength difference between the two arms of a Michelson interferometer is within th ...
... backscattering properties of tissues. The light reflected off a sample is interfered with a reference wave utilizing a technique known as low-coherence interferometry. An interference signal arises when the optical pathlength difference between the two arms of a Michelson interferometer is within th ...
Molmer Kalus
... ”Ten kisses from the princess” “Ask him,” said the princess, “if he will be satisfied with ten kisses from one of my ...
... ”Ten kisses from the princess” “Ask him,” said the princess, “if he will be satisfied with ten kisses from one of my ...
Electromagnetic forces for an arbitrary optical trapping of a spherical
... missing mechanical measurements in the world of microorganisms and cells that could be correlated to biochemical information. The importance of understanding the optical forces in dielectric beads under different incident beam conditions comes from the fact that they are the natural transducer for f ...
... missing mechanical measurements in the world of microorganisms and cells that could be correlated to biochemical information. The importance of understanding the optical forces in dielectric beads under different incident beam conditions comes from the fact that they are the natural transducer for f ...
Stereochemistry at Tetrahedral Centers
... • To identify such stereoisomers, we must be able to identify chiral molecules • A chiral object is NOT identical to its mirror image • You are a chiral object. Look in a mirror and raise your right hand. Your mirror image raises his or her left hand. • You can test whether two objects are identical ...
... • To identify such stereoisomers, we must be able to identify chiral molecules • A chiral object is NOT identical to its mirror image • You are a chiral object. Look in a mirror and raise your right hand. Your mirror image raises his or her left hand. • You can test whether two objects are identical ...
Optimized back-focal-plane interferometry directly measures forces
... connected the measurements of positions and of momenta. The deflection of the light cone used by Ghislain and Webb naturally contains information on the change in the momentum of the photons, as S. Smith et al. [12] noticed shortly thereafter. If this light is captured with a lens that fulfills the ...
... connected the measurements of positions and of momenta. The deflection of the light cone used by Ghislain and Webb naturally contains information on the change in the momentum of the photons, as S. Smith et al. [12] noticed shortly thereafter. If this light is captured with a lens that fulfills the ...
Optical aberration
An optical aberration is a departure of the performance of an optical system from the predictions of paraxial optics. In an imaging system, it occurs when light from one point of an object does not converge into (or does not diverge from) a single point after transmission through the system. Aberrations occur because the simple paraxial theory is not a completely accurate model of the effect of an optical system on light, rather than due to flaws in the optical elements.Aberration leads to blurring of the image produced by an image-forming optical system. Makers of optical instruments need to correct optical systems to compensate for aberration.The articles on reflection, refraction and caustics discuss the general features of reflected and refracted rays.