Monochromatic plane waves ( ) Plane waves have straight wave fronts
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Refractive index
... called optically sparser while the medium with higher refractive index is called optically denser. When light is refracted into the optically sparser medium, the refractive angle can be 90 degrees for certain incident angle. This incident angle is called critical and for angles of incidence above th ...
... called optically sparser while the medium with higher refractive index is called optically denser. When light is refracted into the optically sparser medium, the refractive angle can be 90 degrees for certain incident angle. This incident angle is called critical and for angles of incidence above th ...
Total Internal Reflection and Critical Angle File
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
... Optical fibres are replacing electrical cables for the transmission of information. ...
Reflection of Light
... • Because the surface is not smooth, the light rays are scattered in many directions. This is called diffuse reflection. • The laws of reflection still apply to rough surfaces! ...
... • Because the surface is not smooth, the light rays are scattered in many directions. This is called diffuse reflection. • The laws of reflection still apply to rough surfaces! ...
How do eye glasses work? BUT first, let`s review!
... They travel as vibrations in electrical and ...
... They travel as vibrations in electrical and ...
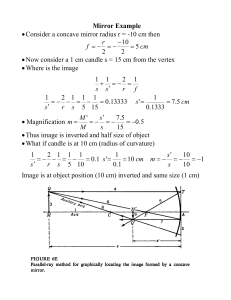
Mirror Example • Consider a concave mirror radius r =
... Then direct ray from T through focus point F (ray 5) and beyond Now direct ray from object top Q through radius C (ray 8) This intersects ray 5 at image Q’ (point 9) This correctly shows both position and magnification of object This really shows how the light rays are travelling Eg Ray ...
... Then direct ray from T through focus point F (ray 5) and beyond Now direct ray from object top Q through radius C (ray 8) This intersects ray 5 at image Q’ (point 9) This correctly shows both position and magnification of object This really shows how the light rays are travelling Eg Ray ...
Plane mirrors
... Reflection Reflection- occurs when an object or wave bounces back off a surface through which it cannot pass. Law of Reflection- all waves obey this law. 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirror ...
... Reflection Reflection- occurs when an object or wave bounces back off a surface through which it cannot pass. Law of Reflection- all waves obey this law. 1. The angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. II. Mirrors 1. There are 3 types of mirrors: Plane, concave, and convex. A. Plane Mirror ...
A list of some commonly used formulas in optics
... fields remain in perpendicular planes parallel to the propagation vector k, as shown below. ...
... fields remain in perpendicular planes parallel to the propagation vector k, as shown below. ...
6.2 Refraction
... When propagating from a higher refractive index region into a region with a lower refractive index, the largest angle that will be transmitted is the critical angle. Light impinging on the refractive index boundary at angles greater than the critical angle will undergo ____________________. The wave ...
... When propagating from a higher refractive index region into a region with a lower refractive index, the largest angle that will be transmitted is the critical angle. Light impinging on the refractive index boundary at angles greater than the critical angle will undergo ____________________. The wave ...
PH 481 - Physics | Oregon State University
... Ambient light in the room will cause an offset in your measurement. You can measure this offset by blocking the laser beam, but be careful to do it without changing the ambient light (i.e., the reflection of light from you may be the major source of light). Record the reflected power for both S and ...
... Ambient light in the room will cause an offset in your measurement. You can measure this offset by blocking the laser beam, but be careful to do it without changing the ambient light (i.e., the reflection of light from you may be the major source of light). Record the reflected power for both S and ...
A solution to Maxwell`s equations in free space
... of 1km from the antenna, find (a) the amplitude of the electric and magnetic field strengths, and (b) the energy incident normally on a square plate of side 10cm in 5min. ...
... of 1km from the antenna, find (a) the amplitude of the electric and magnetic field strengths, and (b) the energy incident normally on a square plate of side 10cm in 5min. ...
11.1 law of reflection and curved mirrors
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
... An image can be larger or smaller or the same as your object A = attitude. An image can be upright or inverted compared to the original object or can be laterally inverted (left and right switch) L = location. The distance between the image and mirror and whether the image is made in front or behind ...
Unit Study Guide - Lighthouse Christian Academy
... light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object normal - the line drawn from the point of incidence perpendicular (at 90°) to an optical devi ...
... light entering the eye; controls the size of the pupil lens – a curved, transparent device that causes light to refract as it passes through; gathers light from an object and produces an image of the object normal - the line drawn from the point of incidence perpendicular (at 90°) to an optical devi ...
Critical angle - Kelso High School
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
Review - misshoughton.net
... Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Critical angle Pr ...
... Using mirror and magnification equations appropriately 4. Refraction of Light Definition, properties, characteristics Index of refraction Dispersion 5. Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection Definition, properties, characteristics Large angles of incidence Critical angle Pr ...
Light+and+Sound.+RM1
... There are two types of lenses : converging and diverging. Converging lenses disperse light rays that pass through them to one location Diverging lenses disperse light rays that pass through them in all directions ...
... There are two types of lenses : converging and diverging. Converging lenses disperse light rays that pass through them to one location Diverging lenses disperse light rays that pass through them in all directions ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.