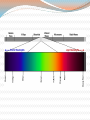
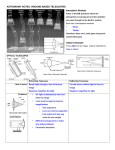
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Telescopes
Schneider Kreuznach wikipedia , lookup
Reflector sight wikipedia , lookup
Lens (optics) wikipedia , lookup
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Anti-reflective coating wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Retroreflector wikipedia , lookup