Basic Wavefront Aberration Theory for Optical Metrology
... counterclockwise direction, -and the zero angle is along the x axis when looking at the pupil plane from the image plane. This is the definition used for interferogram analysis by many of the computer-aided lens design and wavefront analysis programs. Another common definition that will not be used ...
... counterclockwise direction, -and the zero angle is along the x axis when looking at the pupil plane from the image plane. This is the definition used for interferogram analysis by many of the computer-aided lens design and wavefront analysis programs. Another common definition that will not be used ...
Modern Optical Engineering
... A new, simple, and easily understood derivation of the conservation of brightness and radiance has been added. New or expanded tables of brightness, illumination, and reflectance have been included, and the searchlight figure is improved. New equations for telescope (or afocal) component powers, eye ...
... A new, simple, and easily understood derivation of the conservation of brightness and radiance has been added. New or expanded tables of brightness, illumination, and reflectance have been included, and the searchlight figure is improved. New equations for telescope (or afocal) component powers, eye ...
RAY OPTICS NOTES - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... electromagnetic radiation of any “color,” temporal frequency, and wavelength. This is more general than the definition put forth by humanocentrics (e.g., color scientists), but is much more reasonable in our field, where we want to take advantage of all measureable radiation to learn information abo ...
... electromagnetic radiation of any “color,” temporal frequency, and wavelength. This is more general than the definition put forth by humanocentrics (e.g., color scientists), but is much more reasonable in our field, where we want to take advantage of all measureable radiation to learn information abo ...
The effects of longitudinal chromatic aberration and a shift in the
... of the M-cone fundamental is varied. Because M-cone contrast varies with the plane of focus we calculated M-cone contrast when the eye is focused to maximize luminance contrast for the different Mcone spectra and for when the eye is focused at 555 nm, the peak of the Vk function for the normal M-con ...
... of the M-cone fundamental is varied. Because M-cone contrast varies with the plane of focus we calculated M-cone contrast when the eye is focused to maximize luminance contrast for the different Mcone spectra and for when the eye is focused at 555 nm, the peak of the Vk function for the normal M-con ...
Chapter 32 Optical Images
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
... the ways in which these two systems accommodate. That is, the difference between how an eye adjusts and how a camera adjusts (or can be adjusted) to form a focused image for objects at both large and short distances from the camera. ...
File
... image and interpret it as being upright. To show this directly, try this simple experiment. Poke a small hole in a card using a pin and, holding the card a few inches away, look through the hole at a lightbulb. While doing so, move the head of the pin between the hole and your eye; you’ll see an ups ...
... image and interpret it as being upright. To show this directly, try this simple experiment. Poke a small hole in a card using a pin and, holding the card a few inches away, look through the hole at a lightbulb. While doing so, move the head of the pin between the hole and your eye; you’ll see an ups ...
The Optics of the Spherical Fish Lens
... Typical values he reported are 1.336 for the eye media (Nmed), 1.38 for the cortical index (No), and 1.51 for the core index (IV,,,). Mattheissen used the concept of total index, which is that index a homogeneous lens would require to have the same paraxial focal length as an inhomogeneous lens of t ...
... Typical values he reported are 1.336 for the eye media (Nmed), 1.38 for the cortical index (No), and 1.51 for the core index (IV,,,). Mattheissen used the concept of total index, which is that index a homogeneous lens would require to have the same paraxial focal length as an inhomogeneous lens of t ...
Binoculars - shapes and lenses
... higher magnification in this article, making these much easier to use. They are the Bushnell Falcon, about $24, and the Tasco Essentials Zip, about $25, March 2015 Amazon.com prices. With shipping, this would come up to about $30. Another variation seen in miniatures places the two objectives closer ...
... higher magnification in this article, making these much easier to use. They are the Bushnell Falcon, about $24, and the Tasco Essentials Zip, about $25, March 2015 Amazon.com prices. With shipping, this would come up to about $30. Another variation seen in miniatures places the two objectives closer ...
Expressive Chromatic Accumulation Buffering for Defocus Blur
... Besides the conventional pinhole lens model, the thinlens model effectively abstracts a real lens in terms solely of the focal length [20, 2]. While efficient, its use has been mostly in the defocus blur, since it does not capture other aberrations. The later thick-lens approximation is better in te ...
... Besides the conventional pinhole lens model, the thinlens model effectively abstracts a real lens in terms solely of the focal length [20, 2]. While efficient, its use has been mostly in the defocus blur, since it does not capture other aberrations. The later thick-lens approximation is better in te ...
Chapter 18 - Handbook of Optics
... replace difficult-to-fabricate paraboloids in light houses. The objective relies upon the overcorrected spherical aberration produced by the negative first surface to cancel the undercorrected spherical aberration produced by the focusing, reflective surface. The chromatic aberration of the Mangin i ...
... replace difficult-to-fabricate paraboloids in light houses. The objective relies upon the overcorrected spherical aberration produced by the negative first surface to cancel the undercorrected spherical aberration produced by the focusing, reflective surface. The chromatic aberration of the Mangin i ...
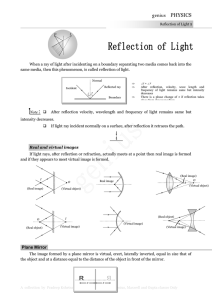
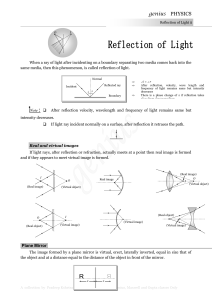
genius PHYSICS
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
Colours of opaque object - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
... A ray of light makes an angle of 10 o with the horizontal above it and strikes a plane mirror which is inclined at an angle to the horizontal. The angle for which the reflected ray becomes vertical is (a) 40o ...
Surplus Shed
... HASTINGS TRIPLET - UNMOUNTED These are typically used as high power magnifiers. Cemented three element design provides the ultimate in distortion and spherical aberration free, color correct viewing. 15mm diameter, 10x magnification. Surface quality 60/40. Unused L1865D $18.50 ...
... HASTINGS TRIPLET - UNMOUNTED These are typically used as high power magnifiers. Cemented three element design provides the ultimate in distortion and spherical aberration free, color correct viewing. 15mm diameter, 10x magnification. Surface quality 60/40. Unused L1865D $18.50 ...
Ch 03 - Aberrations
... In the preceding section on coma, we introduced the terms “tangential” and “sagittal”; a fuller discussion of these terms is appropriate at this point. If a lens system is represented by a drawing of its axial section, rays which lie in the plane of the drawing are called meridional or tangential ra ...
... In the preceding section on coma, we introduced the terms “tangential” and “sagittal”; a fuller discussion of these terms is appropriate at this point. If a lens system is represented by a drawing of its axial section, rays which lie in the plane of the drawing are called meridional or tangential ra ...
Accommodation demand and deprivation in kitten ocular
... The effects of accommodation demand and deprivation on the development of ocular optics was investigated in four groups of kittens (total n = 29). Group 1 consisted of five normal kittens; group 2 (nine kittens) had monocular radial keratotomy to induce relative hypermetropia and more accommodation ...
... The effects of accommodation demand and deprivation on the development of ocular optics was investigated in four groups of kittens (total n = 29). Group 1 consisted of five normal kittens; group 2 (nine kittens) had monocular radial keratotomy to induce relative hypermetropia and more accommodation ...
Accommodation demand and deprivation in kitten ocular
... lens focal length differences in these eyes were approximately the same as those of the radial keratotomy group. In all three treated groups, the interocular differences were greater for the anterior focal length, especially in the fourth group in which the ratio of differences anterior to posterior ...
... lens focal length differences in these eyes were approximately the same as those of the radial keratotomy group. In all three treated groups, the interocular differences were greater for the anterior focal length, especially in the fourth group in which the ratio of differences anterior to posterior ...
lab 1 GEO Optics
... mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further analysis. Your group needs to focus an optical apparatus at known positions within the protein soluti ...
... mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further analysis. Your group needs to focus an optical apparatus at known positions within the protein soluti ...
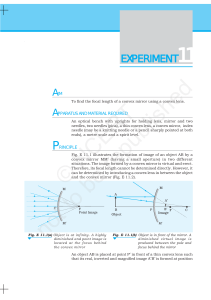
© NCERT not to be republished
... A convex lens L1 converges the light rays starting from the object AB to form a real and inverted image A′B′ at position I1 [Fig. E 12.2(a)]. If a concave diverging lens L2 is inserted between the lens L1 and point I 1 as shown in Fig. E 12.2 (b), for concave lens L2 image A′ B′ behaves as virtual o ...
... A convex lens L1 converges the light rays starting from the object AB to form a real and inverted image A′B′ at position I1 [Fig. E 12.2(a)]. If a concave diverging lens L2 is inserted between the lens L1 and point I 1 as shown in Fig. E 12.2 (b), for concave lens L2 image A′ B′ behaves as virtual o ...
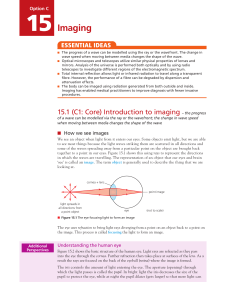
Option C – Imaging
... transparent materials (such as glass or plastic) use the effect shown in Figure 15.3 to focus light and form images. This usually involves light travelling from an object through air and then through a transparent lens that has two smooth, curved surfaces. Refraction then occurs at both surfaces as ...
... transparent materials (such as glass or plastic) use the effect shown in Figure 15.3 to focus light and form images. This usually involves light travelling from an object through air and then through a transparent lens that has two smooth, curved surfaces. Refraction then occurs at both surfaces as ...
IN 175 SkyView Pro 8 EQ
... center the object in telescope eyepiece, and then adjust the finder scope bracket’s alignment thumbscrews until the star or planet is centered on the finder’s crosshairs. Focusing the finder scope If, when you look through the finder scope, the images appear somewhat out of focus, you will need to r ...
... center the object in telescope eyepiece, and then adjust the finder scope bracket’s alignment thumbscrews until the star or planet is centered on the finder’s crosshairs. Focusing the finder scope If, when you look through the finder scope, the images appear somewhat out of focus, you will need to r ...
A correlation of thin lens approximation to thick
... corresponding to S min and the relationship between S min and Coddington position factor P. As an application, when the formulation given above is applied to the optical glasses and other lens materials, the results can be evaluated. In addition, this can also be expanded to thick lenses. The variat ...
... corresponding to S min and the relationship between S min and Coddington position factor P. As an application, when the formulation given above is applied to the optical glasses and other lens materials, the results can be evaluated. In addition, this can also be expanded to thick lenses. The variat ...
and the matrix
... image formation by spherical surfaces. As such it complements the usual treatment and may well be used along with another text. The text "Fundamentals of Optics" by F. A. Jenkins and H. E. White (Toronto, McGraw-Hill, 3rd ed., 1957) has been referred to throughout as it uses a sign convention which ...
... image formation by spherical surfaces. As such it complements the usual treatment and may well be used along with another text. The text "Fundamentals of Optics" by F. A. Jenkins and H. E. White (Toronto, McGraw-Hill, 3rd ed., 1957) has been referred to throughout as it uses a sign convention which ...
lenses - Van Buren Public Schools
... What Types of Images Are Formed by Convex and Concave Lenses? 1. Cut off a one-centimeter length from the end of a drinking straw. 2. Cover one end of the short straw segment with a piece of transparent tape. 3. Place the taped end of the straw over a small object such as a letter or numeral in a ne ...
... What Types of Images Are Formed by Convex and Concave Lenses? 1. Cut off a one-centimeter length from the end of a drinking straw. 2. Cover one end of the short straw segment with a piece of transparent tape. 3. Place the taped end of the straw over a small object such as a letter or numeral in a ne ...
Understanding Microscopy And Filtering Techniques
... Although the four-component infinity-corrected digital video microscope system is simple, it offers little adaptability. If adding additional optical components into the optical plane is necessary for an application, the seven-component system is the ideal choice. The extra optical elements include ...
... Although the four-component infinity-corrected digital video microscope system is simple, it offers little adaptability. If adding additional optical components into the optical plane is necessary for an application, the seven-component system is the ideal choice. The extra optical elements include ...
Eyepiece

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is so named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through the device. The objective lens or mirror collects light and brings it to focus creating an image. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.An eyepiece consists of several ""lens elements"" in a housing, with a ""barrel"" on one end. The barrel is shaped to fit in a special opening of the instrument to which it is attached. The image can be focused by moving the eyepiece nearer and further from the objective. Most instruments have a focusing mechanism to allow movement of the shaft in which the eyepiece is mounted, without needing to manipulate the eyepiece directly.The eyepieces of binoculars are usually permanently mounted in the binoculars, causing them to have a pre-determined magnification and field of view. With telescopes and microscopes, however, eyepieces are usually interchangeable. By switching the eyepiece, the user can adjust what is viewed. For instance, eyepieces will often be interchanged to increase or decrease the magnification of a telescope. Eyepieces also offer varying fields of view, and differing degrees of eye relief for the person who looks through them.