The Refraction of Light
... • As angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction increases • The angle of incidence which results in the angle of refraction becoming 90o is known as the critical angle • If the angle of incidence increases past the critical angle the refracted ray will no longer exit the medium. Instead, ...
... • As angle of incidence increases, the angle of refraction increases • The angle of incidence which results in the angle of refraction becoming 90o is known as the critical angle • If the angle of incidence increases past the critical angle the refracted ray will no longer exit the medium. Instead, ...
reflection, refraction, lense and optical instruments
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
... The apparatus consists of an optical bench which serves as a convenient holder for objects, lenses and a ground glass screen for locating images. The object is an arrow painted on a piece of ground glass illuminated from behind by a collimated light bulb. Measure the focal point of the 5cm convergin ...
ch.16_18 vocabulary
... diffuse reflection. Forms a virtual, erect image the same size as the object and the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front Object-source of diverging light rays; may be luminous or illuminated Image-reproduction of object formed with mirrors or lenses Virtual image-point from whi ...
... diffuse reflection. Forms a virtual, erect image the same size as the object and the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front Object-source of diverging light rays; may be luminous or illuminated Image-reproduction of object formed with mirrors or lenses Virtual image-point from whi ...
12.5 Total Internal Reflection
... The critical angle is the angle of incidence which gives an angle of refraction of 90º. If you increase the angle of incidence past the critical angle, the refracted ray no longer exits the medium. This is called total internal reflection. ...
... The critical angle is the angle of incidence which gives an angle of refraction of 90º. If you increase the angle of incidence past the critical angle, the refracted ray no longer exits the medium. This is called total internal reflection. ...
Lecture 16 - Purdue Physics
... • Incident light: the light striking the mirror. • Normal line: a line perpendicular to the surface of the mirror at the point where the light hits it. • Angle of incidence: angle between the incident beam and the normal line. • Angle of reflection: angle between the reflected beam and the normal li ...
... • Incident light: the light striking the mirror. • Normal line: a line perpendicular to the surface of the mirror at the point where the light hits it. • Angle of incidence: angle between the incident beam and the normal line. • Angle of reflection: angle between the reflected beam and the normal li ...
Optics Review
... 5. Find the image of an object that is 2.0 cm from a concave mirror. The center of curvature is 3 cm. Be sure to include at least 2 light rays, and describe the image using SALT. 6. Find the image of an object that is 4.0 cm from a convex mirror. The center of curvature is 5 cm. Be sure to include a ...
... 5. Find the image of an object that is 2.0 cm from a concave mirror. The center of curvature is 3 cm. Be sure to include at least 2 light rays, and describe the image using SALT. 6. Find the image of an object that is 4.0 cm from a convex mirror. The center of curvature is 5 cm. Be sure to include a ...
Homework Questions - science
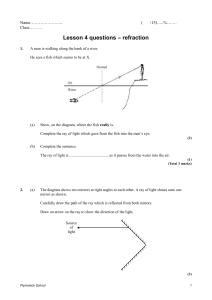
... Light can also be made to change direction as it passes into and out from a block of glass. Complete the ray diagram below. ...
... Light can also be made to change direction as it passes into and out from a block of glass. Complete the ray diagram below. ...
Announcements
... because light travels SLOWER inside some materials than others. The speed of light inside any materials is always less than in vacuum, v(inside) < c. ...
... because light travels SLOWER inside some materials than others. The speed of light inside any materials is always less than in vacuum, v(inside) < c. ...
Theory - BrainMass
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Ⅱ. Bundles of tiny rods or fibers of clear glass or plastic in orderly array, used to transmit light images. ...
... Ⅱ. Bundles of tiny rods or fibers of clear glass or plastic in orderly array, used to transmit light images. ...
Chapter 36 Summary – Magnetism
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
... Directions: #1-6, are true/false. Write the sentence and explain why it’s true, or how to make it true. #7-23 are multiple choice. Write the question and correct answer and explain why. 1) Diffuse reflection occurs when light is refracted in many directions from a rough surface. 2) Reflection occurs ...
RAY OPTICS notes
... The angle of reflection (i.e., the angle between reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface or the mirror) equals the angle of incidence (angle between incident ray and the normal). ...
... The angle of reflection (i.e., the angle between reflected ray and the normal to the reflecting surface or the mirror) equals the angle of incidence (angle between incident ray and the normal). ...
full Lab Facts summary
... • In a solid prism retroreflector, the beam undergoes total internal reflection at each surface. • A beam entering normal to the base will be incident upon each face at a 55˚ angle (cos-1(1/√3)) [1]. • S- and p-polarization components reflect from each face differently based on the Fresnel reflectio ...
... • In a solid prism retroreflector, the beam undergoes total internal reflection at each surface. • A beam entering normal to the base will be incident upon each face at a 55˚ angle (cos-1(1/√3)) [1]. • S- and p-polarization components reflect from each face differently based on the Fresnel reflectio ...
trigonometry
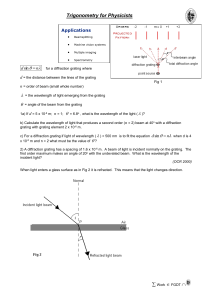
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
... b) If light arrives at an angle of 15o to the normal at an air-to-glass boundary for which the refractive index is 1.5, what is the expected angle of refraction? 4) The Refractive Index for an air-to-diamond boundary is about 2.42. If light arrives at an angle of 60o to the normal at an air-to-diamo ...
PHYS 242 BLOCK 11 NOTES Sections 33.1 to 33.7 Geometrical
... However, for any angle of incidence greater than or equal to the critical angle θcrit, all of the incident light reflects (therefore, none refracts), a phenomenon called total internal reflection. See Figure 33.13a. When θa = θcrit, θb nb = 90˚. Therefore, Snell’s law gives na sin θcrit = nb sin 90˚ ...
... However, for any angle of incidence greater than or equal to the critical angle θcrit, all of the incident light reflects (therefore, none refracts), a phenomenon called total internal reflection. See Figure 33.13a. When θa = θcrit, θb nb = 90˚. Therefore, Snell’s law gives na sin θcrit = nb sin 90˚ ...
optical quality standards
... n is the average refractive index for material in visible δ is the Peak to Valley departure for flatness of one surface 2(n-1) is the worst case contribution of both surfaces ...
... n is the average refractive index for material in visible δ is the Peak to Valley departure for flatness of one surface 2(n-1) is the worst case contribution of both surfaces ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... Neat Index of Refraction Stuff Experiments done at Harvard in 1999 were able to slow light down to 17 m/s (compare to vacuum speed of 3x108 m/s). The experiments involved the propagation of laser light into a Bose-Einstein condensate of gaseous Rb. Later experiments could actually stop the light ...
... Neat Index of Refraction Stuff Experiments done at Harvard in 1999 were able to slow light down to 17 m/s (compare to vacuum speed of 3x108 m/s). The experiments involved the propagation of laser light into a Bose-Einstein condensate of gaseous Rb. Later experiments could actually stop the light ...
Optical Fibres
... Find the critical angle for the glass block for total internal reflection to occur where the light getting in at one end undergoes repeated total internal reflection, even when the fibre is bent, emerging at the other end... ...
... Find the critical angle for the glass block for total internal reflection to occur where the light getting in at one end undergoes repeated total internal reflection, even when the fibre is bent, emerging at the other end... ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.