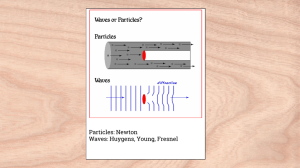
Particles: Newton Waves: Huygens, Young, Fresnel
... Academie des Sciences for 1819, which was awarded for the best work on diffraction ; -- established the theory that light is a transverse wave; -- invented the Fresnel lens for lighthouses. ...
... Academie des Sciences for 1819, which was awarded for the best work on diffraction ; -- established the theory that light is a transverse wave; -- invented the Fresnel lens for lighthouses. ...
refl and refr, mirrors
... Index of Refraction Every material has an index of refraction that determines its optical properties Indices of refraction determine bending, by law of refraction Index of refraction also determines the speed of light within the material v=c/n generally, v
... Index of Refraction Every material has an index of refraction that determines its optical properties Indices of refraction determine bending, by law of refraction Index of refraction also determines the speed of light within the material v=c/n generally, v
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... Light travels through an optical medium with a lower speed than c, as atoms in the medium absorb, reemit, and scatter the light. For example, the refractive index for diamond is n = 2.419, so the speed of ligth in diamond = c/n c 3.00 × 10 8 m/s ...
... Light travels through an optical medium with a lower speed than c, as atoms in the medium absorb, reemit, and scatter the light. For example, the refractive index for diamond is n = 2.419, so the speed of ligth in diamond = c/n c 3.00 × 10 8 m/s ...
SNC2D Optics Review
... Partial reflection and refraction occurs when an incidence ray strikes a new medium and some of the light rays are reflected and some of the light rays are refracted. Examples: light reflecting and refracting off of surface of the water, rear-view mirrors The amount of reflection depends on 1. The t ...
... Partial reflection and refraction occurs when an incidence ray strikes a new medium and some of the light rays are reflected and some of the light rays are refracted. Examples: light reflecting and refracting off of surface of the water, rear-view mirrors The amount of reflection depends on 1. The t ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 2. State why crosswires cannot be used in Huygen’s eyepiece? 3. What are coherent sources? 4. In Newton’s rings experiment, the diameter of the 8th ring changes from 1.4cm to 1.27cm when a liquid is introduced between the lens and the plate. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid. 5. Define re ...
... 2. State why crosswires cannot be used in Huygen’s eyepiece? 3. What are coherent sources? 4. In Newton’s rings experiment, the diameter of the 8th ring changes from 1.4cm to 1.27cm when a liquid is introduced between the lens and the plate. Calculate the refractive index of the liquid. 5. Define re ...
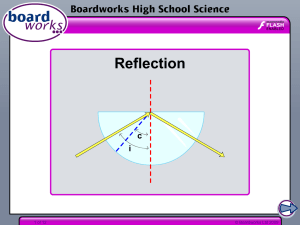
law of reflection
... Concave mirrors are converging mirrors, as they reflect rays of light towards a focal point (F). If a light source is placed at the focal point, the mirror will produce a beam of parallel light rays. The distance between the mirror and the focal point is called the focal length (ƒ). ƒ becomes smalle ...
... Concave mirrors are converging mirrors, as they reflect rays of light towards a focal point (F). If a light source is placed at the focal point, the mirror will produce a beam of parallel light rays. The distance between the mirror and the focal point is called the focal length (ƒ). ƒ becomes smalle ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... Concepts developed: 1. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they ...
... Concepts developed: 1. The law of reflection states that the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they ...
Optics01
... that the intensity of light from a point source varies inversely with the square of the distance from the source 1608Hans Lippershey (Netherlands). Constructed a telescope with a converging objective lens and a diverging eye lens 1610Galileo Galilei (Italy). Using his telescope, Galileo reported sev ...
... that the intensity of light from a point source varies inversely with the square of the distance from the source 1608Hans Lippershey (Netherlands). Constructed a telescope with a converging objective lens and a diverging eye lens 1610Galileo Galilei (Italy). Using his telescope, Galileo reported sev ...
Geometric optics
... cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal reflection occurs. This is particularly common as an optical phenomenon, where light waves are involved, but it occurs with many types of waves, such as electromagnetic waves in ...
... cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal reflection occurs. This is particularly common as an optical phenomenon, where light waves are involved, but it occurs with many types of waves, such as electromagnetic waves in ...
Ch14 Review
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
4.Bending Light PhET
... Go back onto the internet page. Google “Refraction.” 13. Find 5 different pictures of refraction in the REAL WORLD. Paste them into a WORD document. Ask me to come over and show it to me. Teacher Signature: ______________ ...
... Go back onto the internet page. Google “Refraction.” 13. Find 5 different pictures of refraction in the REAL WORLD. Paste them into a WORD document. Ask me to come over and show it to me. Teacher Signature: ______________ ...
Sample Problems for Final
... 530 nm) illuminates the upper surface of the wedge at normal incidence. Approximately how far from the edge of the wedge (where it tapers to zero thickness) does the first maximum in the reflected light occur? Assume that the wedge is surrounded by air, and that the index of refraction of the glass ...
... 530 nm) illuminates the upper surface of the wedge at normal incidence. Approximately how far from the edge of the wedge (where it tapers to zero thickness) does the first maximum in the reflected light occur? Assume that the wedge is surrounded by air, and that the index of refraction of the glass ...
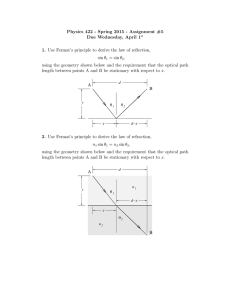
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
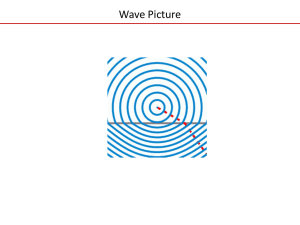
Wave Picture
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
... Snell's law seems to require in some cases (whenever the angle of incidence is large enough) that the sine of the angle of refraction be greater than one. This of course is impossible, and the light in such cases is completely reflected by the boundary, a phenomenon known as total internal reflectio ...
Polarization Practice
... 9. A bright source of light is viewed through two polarizers whose preferred directions are initially parallel. Calculate the angle through which one sheet should be turned to reduce the transmitted intensity to half its original value. ...
... 9. A bright source of light is viewed through two polarizers whose preferred directions are initially parallel. Calculate the angle through which one sheet should be turned to reduce the transmitted intensity to half its original value. ...
Retroreflector

A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflects light back to its source with a minimum of scattering. In a retroreflector an electromagnetic wavefront is reflected back along a vector that is parallel to but opposite in direction from the wave's source. The angle of incidence at which the device or surface reflects light in this way is greater than zero, unlike a planar mirror, which does this only if the mirror is exactly perpendicular to the wave front, having a zero angle of incidence.