Lecture 6: Waves Review and Examples PLEASE REVIEW ON
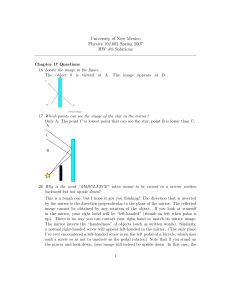
... The positions of the principal maxima occur at φ = 0, ±2π, ±4π, ... where φ is the phase between adjacent slits. θ = 0, ±λ/d, ±2λ/d, ... The intensity at the peak of a principal maximum goes as N2. 3 slits: Atot = 3A1 ⇒ Itot = 9I1. N slits: IN = N2I1. Between two principal maxima there are N-1 zeros ...
... The positions of the principal maxima occur at φ = 0, ±2π, ±4π, ... where φ is the phase between adjacent slits. θ = 0, ±λ/d, ±2λ/d, ... The intensity at the peak of a principal maximum goes as N2. 3 slits: Atot = 3A1 ⇒ Itot = 9I1. N slits: IN = N2I1. Between two principal maxima there are N-1 zeros ...
PHYSICS 504 OPTICS REVIEW: Important things to remember: 1
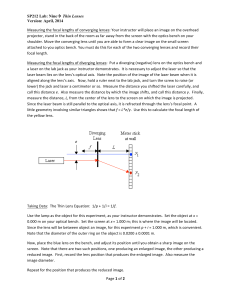
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
... diameter pipeline that lies between them. By means of a fully labelled ray diagram and appropriate calculations, explain how it is possible for Marlin and Nemo to see each other from their present positions. Justify your answer. Air ...
Exposure and Imaging
... – The best lenses used in projection lithography have NA = 0.3 - 0.4 – A lens with NA = 0.50 is a f/1.00 lens: its focal length and effective diameter are the same! – The largest NA lenses ever made were a NA = 0.54 and a NA = 0.60 by Nikon. ...
... – The best lenses used in projection lithography have NA = 0.3 - 0.4 – A lens with NA = 0.50 is a f/1.00 lens: its focal length and effective diameter are the same! – The largest NA lenses ever made were a NA = 0.54 and a NA = 0.60 by Nikon. ...
Phys342_Syl.pdf
... Recommended Text: Introduction to Optics, 3rd Edition, by Pedrotti, Pedrotti, and Pedrotti (Pearson, Addison-Wesley, 2006); This text is recommended but not strictly required; if you have access to a different optics text, it might be suitable, come see me. Grading: Homework ...
... Recommended Text: Introduction to Optics, 3rd Edition, by Pedrotti, Pedrotti, and Pedrotti (Pearson, Addison-Wesley, 2006); This text is recommended but not strictly required; if you have access to a different optics text, it might be suitable, come see me. Grading: Homework ...
BLUE PRINT FOR QUESTION PAPER APPLIED PHYSICS – II (R
... Interference in thin film – Introduction, interference due to reflected and transmitted light by thin transparent parallel film, origin of colours in thin film, Wedge shaped thin film, Newton’s rings Applications of interference- Determination of thickness of very thin wire or foil, determination of ...
... Interference in thin film – Introduction, interference due to reflected and transmitted light by thin transparent parallel film, origin of colours in thin film, Wedge shaped thin film, Newton’s rings Applications of interference- Determination of thickness of very thin wire or foil, determination of ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... scanned in a plane containing the optical axis and the scattered light intensity was recorded as a function of the position. Scanning was performed by a scan stage that offered independently controlled x, y, and z axes (Photon Control, Cambridge, England). The bead was scanned 1.5 pm along the optic ...
... scanned in a plane containing the optical axis and the scattered light intensity was recorded as a function of the position. Scanning was performed by a scan stage that offered independently controlled x, y, and z axes (Photon Control, Cambridge, England). The bead was scanned 1.5 pm along the optic ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... The principle of confocal microscopy was described prior to the invention of lasers [Ref Minsky Patent 1957]. However, today most confocal systems use lasers for illumination. The confocal imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of ...
... The principle of confocal microscopy was described prior to the invention of lasers [Ref Minsky Patent 1957]. However, today most confocal systems use lasers for illumination. The confocal imaging system can operate either in transmission or reflection, as shown in Fig. 1. In both cases, the out of ...
HW #8 Solutions
... 27 Compare the interference patterns of yellow and green light due to a double slit. Which has the wider interference pattern and why? The width of the interference pattern is determined by the ratio of the slit width to the wavelength. The larger the wavelength, the broader the interference pattern ...
... 27 Compare the interference patterns of yellow and green light due to a double slit. Which has the wider interference pattern and why? The width of the interference pattern is determined by the ratio of the slit width to the wavelength. The larger the wavelength, the broader the interference pattern ...
Nanofabrication with Holographic Optical Tweezers
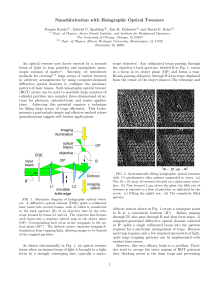
... An optical tweezer uses forces exerted by a focused beam of light to trap particles and manipulate mesoscopic volumes of matter1 . Recently, we introduced methods for creating2–4 large arrays of optical tweezers in arbitrary arrangements by using computer-designed diffractive optical elements to con ...
... An optical tweezer uses forces exerted by a focused beam of light to trap particles and manipulate mesoscopic volumes of matter1 . Recently, we introduced methods for creating2–4 large arrays of optical tweezers in arbitrary arrangements by using computer-designed diffractive optical elements to con ...
Lithography - 123seminarsonly.com
... Descum - removal of thin layer of resist scum that may occlude open regions in pattern, helps to open up corners. ...
... Descum - removal of thin layer of resist scum that may occlude open regions in pattern, helps to open up corners. ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.