PPT - Tensors for Tots
... If the crests and troughs of the two waves arrive at the screen at the same time, then the waves interfere constructively and a bright band appears on the screen. If the crest of one wave arrives at the same time as the trough of the other wave, then the waves interfere destructively and cancel eac ...
... If the crests and troughs of the two waves arrive at the screen at the same time, then the waves interfere constructively and a bright band appears on the screen. If the crest of one wave arrives at the same time as the trough of the other wave, then the waves interfere destructively and cancel eac ...
trigonometry
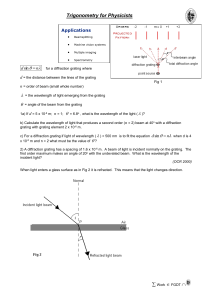
... c) For a diffraction grating if light of wavelength ( ) = 500 nm is to fit the equation x 10-5 m and n = 2 what must be the value of ? ...
... c) For a diffraction grating if light of wavelength ( ) = 500 nm is to fit the equation x 10-5 m and n = 2 what must be the value of ? ...
Optics - Tensors for Tots
... If the crests and troughs of the two waves arrive at the screen at the same time, then the waves interfere constructively and a bright band appears on the screen. If the crest of one wave arrives at the same time as the trough of the other wave, then the waves interfere destructively and cancel eac ...
... If the crests and troughs of the two waves arrive at the screen at the same time, then the waves interfere constructively and a bright band appears on the screen. If the crest of one wave arrives at the same time as the trough of the other wave, then the waves interfere destructively and cancel eac ...
Lecture 34 - UConn Physics
... The centers of two slits of width a are a distance d apart. Is it possible that the first minimum of the interference pattern occurs at the location of the first minimum of the diffraction pattern for light of wavelength l ? ...
... The centers of two slits of width a are a distance d apart. Is it possible that the first minimum of the interference pattern occurs at the location of the first minimum of the diffraction pattern for light of wavelength l ? ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
... Remove any slides attached to the slide holder. At the back focal plane we see a single focal spot. The position of the spot locates the ‘dc level’ of illumination of the beam entering the lens. Any other spots appearing on the card indicate the presence of other spatial frequencies. Remove the card ...
Lect03_Bi177_MicroscopeOptics
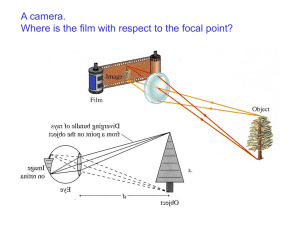
... Homework 1: The index of refraction changes with wavelength (index is larger in blue than red). How would you need to modify this diagram of the rays of red light to make it appropriate for blue light? ...
... Homework 1: The index of refraction changes with wavelength (index is larger in blue than red). How would you need to modify this diagram of the rays of red light to make it appropriate for blue light? ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.