Factors controlling heat exchange between the human body and its
... 1. To demonstrate the dependence of the focal depth on the distance of the object, find the clear reduced and magnified images of an object in the Bessel arrangement. Fix the lens in the positions relating to these images formations and, by moving the object through systematic (e.g. ±0,5cm) distance ...
... 1. To demonstrate the dependence of the focal depth on the distance of the object, find the clear reduced and magnified images of an object in the Bessel arrangement. Fix the lens in the positions relating to these images formations and, by moving the object through systematic (e.g. ±0,5cm) distance ...
the optical (light) microscope
... and daylight colour characteristics. Light intensity, however, can be adjusted only by the use of neutral-density filters. Tungsten-halogen filament lamps are also widely used for their high intensity and high colour temperature. Light intensity can be controlled by varying the current or by use o ...
... and daylight colour characteristics. Light intensity, however, can be adjusted only by the use of neutral-density filters. Tungsten-halogen filament lamps are also widely used for their high intensity and high colour temperature. Light intensity can be controlled by varying the current or by use o ...
Chester F - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... 9. The Center for Imaging Science is considering putting a small telescope, equipped with CCD camera (at the telescope focal plane), on the roof of the Carlson building. The telescope would be a 16" (~ 0.4 m) diameter f/10 reflector. It is estimated that (1) telescope vibrations, due to such things ...
... 9. The Center for Imaging Science is considering putting a small telescope, equipped with CCD camera (at the telescope focal plane), on the roof of the Carlson building. The telescope would be a 16" (~ 0.4 m) diameter f/10 reflector. It is estimated that (1) telescope vibrations, due to such things ...
Lab 11 - Optical Ray Tracing
... optics. By successively applying the laws of reflection and refraction on the optical surface (lens, mirror, screen, iris, etc.), a light ray can be propagated from the source to they target and thereby generating an approximate property of the optical system. To simplify computation and usage, a nu ...
... optics. By successively applying the laws of reflection and refraction on the optical surface (lens, mirror, screen, iris, etc.), a light ray can be propagated from the source to they target and thereby generating an approximate property of the optical system. To simplify computation and usage, a nu ...
LAB 1 - SIMPLE DIFFRACTION, FOURIER OPTICS AND ACOUSTO
... through the center of the iris that is integrated in the spatial filter. You should use the tilt settings to back-reflect this into the laser, not the vertical or horizontal adjustment knobs. Now placing the screen in front of the spatial filter (such as a business card from the supplies drawer), sl ...
... through the center of the iris that is integrated in the spatial filter. You should use the tilt settings to back-reflect this into the laser, not the vertical or horizontal adjustment knobs. Now placing the screen in front of the spatial filter (such as a business card from the supplies drawer), sl ...
Here
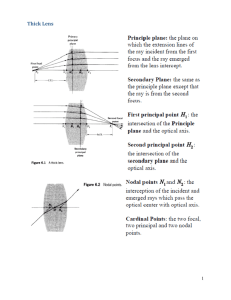
... line joining CV is th eoptical or principal axis. The index of refraction of the medium is n2 whilst that of the initial medium is n1 . – A point source is placed at s0 , with s0 called the object distance. – Table 5.1, p. 154 gives the sign convention used when looking at spherical refracting surfa ...
... line joining CV is th eoptical or principal axis. The index of refraction of the medium is n2 whilst that of the initial medium is n1 . – A point source is placed at s0 , with s0 called the object distance. – Table 5.1, p. 154 gives the sign convention used when looking at spherical refracting surfa ...
Part 1
... fields oscillate in perpendicular directions and the wave travels in a direction perpendicular to each field’s oscillation axis. For a wave traveling along the x-axis in a non-conducting medium, the fields obey the wave equations of the form ...
... fields oscillate in perpendicular directions and the wave travels in a direction perpendicular to each field’s oscillation axis. For a wave traveling along the x-axis in a non-conducting medium, the fields obey the wave equations of the form ...
Physics 212 HW17 - University of St. Thomas
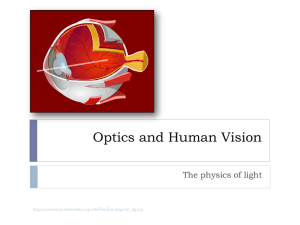
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
... which is typically 2.45 cm behind the lens. The eye’s lens is special in that it can change its focal length in order to focus images from very far and very close onto the retina, which stays 2.45 cm away. The average person with “20/20 vision” can focus on objects at infinity and objects no closer ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.