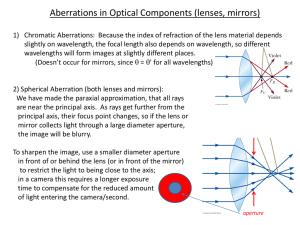
Physics 425L Optics Laboratory Chromatic Aberration
... optical rail so that it is directly over a whole number (distance from the beginning of the rail). ...
... optical rail so that it is directly over a whole number (distance from the beginning of the rail). ...
PART 3_ir spectra_01
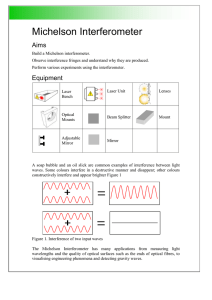
... An interferogram is generated because of the unique optics of an FT-IR instrument. The key components are a moveable mirror and beam splitter. The moveable mirror is responsible for the quality of the interferogram, and it is very important to move the mirror at constant speed. For this reason, the ...
... An interferogram is generated because of the unique optics of an FT-IR instrument. The key components are a moveable mirror and beam splitter. The moveable mirror is responsible for the quality of the interferogram, and it is very important to move the mirror at constant speed. For this reason, the ...
optics(conceptuals)
... What is the phase difference between two particles on a wavefront? (i) A plane wavefront is incident normally on a convex lens. Draw the refracted wavefront. (ii) Draw the wavefronts emerging out of a convex lens when a point source of light is placed at its focus. Sketch the variation of intensity ...
... What is the phase difference between two particles on a wavefront? (i) A plane wavefront is incident normally on a convex lens. Draw the refracted wavefront. (ii) Draw the wavefronts emerging out of a convex lens when a point source of light is placed at its focus. Sketch the variation of intensity ...
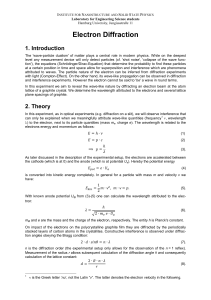
Electron Diffraction
... attributed to waves. The particle nature of the electron can be inferred from diffraction experiments with light (Compton-Effect). On the other hand, its wave-like propagation can be observed in diffraction and interference experiments. However the electron cannot be said to 'be' a wave in round ter ...
... attributed to waves. The particle nature of the electron can be inferred from diffraction experiments with light (Compton-Effect). On the other hand, its wave-like propagation can be observed in diffraction and interference experiments. However the electron cannot be said to 'be' a wave in round ter ...
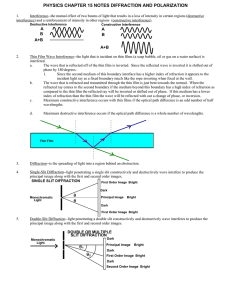
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
... Since the second medium of this boundary interface has a higher index of refraction it appears to the incident light ray as a fixed boundary much like the rope inverting when fixed at the wall. b. The wave that is refracted and transmitted through the thin film is just bent towards the normal. When ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.