
Diffraction
... In addition to the diffraction at a slit, in this experiment, the diffraction grating is also observed. The diffraction grating is a generalization of the diffraction at a double slit, which is an experiment with extreme importance in physics because of the transition from classical physics to quant ...
... In addition to the diffraction at a slit, in this experiment, the diffraction grating is also observed. The diffraction grating is a generalization of the diffraction at a double slit, which is an experiment with extreme importance in physics because of the transition from classical physics to quant ...
Handout 7
... There’s a subtle distinction here between increasing the resolution available in the image itself by using a larger objective (at least up to the limit imposed by the seeing), and increasing the magnification of the image as you’ve done when observing visually by changing to a shorter focal-length e ...
... There’s a subtle distinction here between increasing the resolution available in the image itself by using a larger objective (at least up to the limit imposed by the seeing), and increasing the magnification of the image as you’ve done when observing visually by changing to a shorter focal-length e ...
Poisson’s spot with molecules Please share
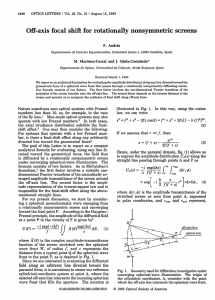
... The two sets of model calculations shown in Fig. 4 correspond to a disk with 共continuous line兲 and without 共dashed lines兲 edge roughness, revealing its effect on the Poissonspot intensity. At the closest distance considerable dampening may be noted while at the farthest position the difference to an ...
... The two sets of model calculations shown in Fig. 4 correspond to a disk with 共continuous line兲 and without 共dashed lines兲 edge roughness, revealing its effect on the Poissonspot intensity. At the closest distance considerable dampening may be noted while at the farthest position the difference to an ...
EXPERIMENT Q-5 Electron Diffraction Abstract References Pre-Lab
... Connect the filament leads from the electron tube to the 6.3Volt terminals on the power supply, asking an instructor for assistance in identifying the various leads. Connect the red and black accelerating voltage leads to the "+" and "-" high voltage power supply terminals, respectively. WARNING!! T ...
... Connect the filament leads from the electron tube to the 6.3Volt terminals on the power supply, asking an instructor for assistance in identifying the various leads. Connect the red and black accelerating voltage leads to the "+" and "-" high voltage power supply terminals, respectively. WARNING!! T ...
Acousto-Optic Devices - Panasonic Industrial Devices
... Wavelength dispersion of diffracting direction(angle) in the range of optical wavelength at acousto-optic tunable filter. ...
... Wavelength dispersion of diffracting direction(angle) in the range of optical wavelength at acousto-optic tunable filter. ...
Imaging
... and separated by a distance d. •The line connecting the camera lens centers is called the baseline. •Let baseline be perpendicular to the line of sight of the cameras. •Let the x axis of the three-dimensional world coordinate system be parallel to the ...
... and separated by a distance d. •The line connecting the camera lens centers is called the baseline. •Let baseline be perpendicular to the line of sight of the cameras. •Let the x axis of the three-dimensional world coordinate system be parallel to the ...
Off-axis focal shift for rotationally nonsymmetric screens
... is no focal shift. However, when the Fresnel number is small, z cannot be ignored, and the factor 1/(f + z) outside the integral shifts the irradiance peak to negative values of z i.e., toward the aperture, resulting in the focal-shift effect. It is interesting to point out that, as point A moves fr ...
... is no focal shift. However, when the Fresnel number is small, z cannot be ignored, and the factor 1/(f + z) outside the integral shifts the irradiance peak to negative values of z i.e., toward the aperture, resulting in the focal-shift effect. It is interesting to point out that, as point A moves fr ...
Lenses (docx)
... In this lab activity you will apply the lens (and mirror) equation to single lens and lens/mirror combination experiments. You will A. find the focal length of a converging lens (single lens setup). B. find the focal length of a diverging lens (two component setup). C. explore a lens/mirror combinat ...
... In this lab activity you will apply the lens (and mirror) equation to single lens and lens/mirror combination experiments. You will A. find the focal length of a converging lens (single lens setup). B. find the focal length of a diverging lens (two component setup). C. explore a lens/mirror combinat ...
Lab 7, The Basics of Optics and Telescopes
... Objectives: This lab will give students a basic understanding of how lenses and telescopes work. Students will measure the properties of lenses, and make a telescope. Introduction: The most important purpose of a telescope is to gather light. This makes it possible to observe objects that are too fa ...
... Objectives: This lab will give students a basic understanding of how lenses and telescopes work. Students will measure the properties of lenses, and make a telescope. Introduction: The most important purpose of a telescope is to gather light. This makes it possible to observe objects that are too fa ...
Resolution Power And Intensity Distribution Using Synthetic Square
... number of rows and columns are choosing (T=2,4,6,8,10),that mean the apertures allow light to pass through it are (2,8,18,32,50) . The two cases (G=1,G=-1) are solved , the result appear similar in two cases at ideal system or contain focus error and aberrations which are chosen in research. Figure ...
... number of rows and columns are choosing (T=2,4,6,8,10),that mean the apertures allow light to pass through it are (2,8,18,32,50) . The two cases (G=1,G=-1) are solved , the result appear similar in two cases at ideal system or contain focus error and aberrations which are chosen in research. Figure ...
Airy disk
In optics, the Airy disk (or Airy disc) and Airy pattern are descriptions of the best focused spot of light that a perfect lens with a circular aperture can make, limited by the diffraction of light. The Airy disk is of importance in physics, optics, and astronomy.The diffraction pattern resulting from a uniformly-illuminated circular aperture has a bright region in the center, known as the Airy disk which together with the series of concentric bright rings around is called the Airy pattern. Both are named after George Biddell Airy. The disk and rings phenomenon had been known prior to Airy; John Herschel described the appearance of a bright star seen through a telescope under high magnification for an 1828 article on light for the Encyclopedia Metropolitana:...the star is then seen (in favourable circumstances of tranquil atmosphere, uniform temperature, &c.) as a perfectly round, well-defined planetary disc, surrounded by two, three, or more alternately dark and bright rings, which, if examined attentively, are seen to be slightly coloured at their borders. They succeed each other nearly at equal intervals round the central disc....However, Airy wrote the first full theoretical treatment explaining the phenomenon (his 1835 ""On the Diffraction of an Object-glass with Circular Aperture"").Mathematically, the diffraction pattern is characterized by the wavelength of light illuminating the circular aperture, and the aperture's size. The appearance of the diffraction pattern is additionally characterized by the sensitivity of the eye or other detector used to observe the pattern.The most important application of this concept is in cameras and telescopes. Owing to diffraction, the smallest point to which a lens or mirror can focus a beam of light is the size of the Airy disk. Even if one were able to make a perfect lens, there is still a limit to the resolution of an image created by this lens. An optical system in which the resolution is no longer limited by imperfections in the lenses but only by diffraction is said to be diffraction limited.









![Spherical mirrors in the paraxial approximation [Pages 181-187]. Assignment 2](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008539460_1-d375c81ee0822c3c0b88887d5bbb056f-300x300.png)










![13.1_Lens_Forming_Images_-_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008538239_1-d1798f6d27c8a2d8c0931d41a70fff89-300x300.png)