RESOLVING POWER AND MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION
... (which are coherently illuminated each but incoherently with respect to each other) then the corresponding peaks are considered resolved according to the Rayleigh criterion when the central peak of one pattern falls into the first minimum aside the main peak of the other pattern. Under that conditio ...
... (which are coherently illuminated each but incoherently with respect to each other) then the corresponding peaks are considered resolved according to the Rayleigh criterion when the central peak of one pattern falls into the first minimum aside the main peak of the other pattern. Under that conditio ...
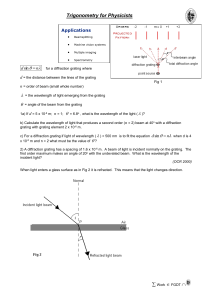
trigonometry
... 2) A diffraction grating has a spacing of 1.6 x 10-6 m. A beam of light is incident normally on the grating. The first order maximum makes an angle of 20o with the undeviated beam. What is the wavelength of the incident light? (OCR 2000) When light enters a glass surface as in Fig 2 it is refracted. ...
... 2) A diffraction grating has a spacing of 1.6 x 10-6 m. A beam of light is incident normally on the grating. The first order maximum makes an angle of 20o with the undeviated beam. What is the wavelength of the incident light? (OCR 2000) When light enters a glass surface as in Fig 2 it is refracted. ...
Procedure - K Street Studio
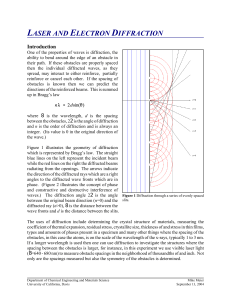
... 3. The laser source is a small 0.5 mW “lecture” laser pointer and the fixtures which hold the laser and the specimens can be as simple as a couple of standard laboratory stands with appropriate clamps plus a pair of tweezers to hold the tiny specimens. The surface on which to project the diffraction ...
... 3. The laser source is a small 0.5 mW “lecture” laser pointer and the fixtures which hold the laser and the specimens can be as simple as a couple of standard laboratory stands with appropriate clamps plus a pair of tweezers to hold the tiny specimens. The surface on which to project the diffraction ...
Crystallography: An introduction
... Development of high through-put (HTP) methods in crystallography has considerably reduced the time needed to solve a crystal structure while minimizing the need for human ...
... Development of high through-put (HTP) methods in crystallography has considerably reduced the time needed to solve a crystal structure while minimizing the need for human ...
Student project proposal
... The lysozyme protein was used as model system since is readily forming 3D crystals in broad spectrum of chemical conditions. Final dimensions of the grown protein crystal depend on physical and biochemical system parameters like: protein concentration, pH, temperature or concentration of precipitat ...
... The lysozyme protein was used as model system since is readily forming 3D crystals in broad spectrum of chemical conditions. Final dimensions of the grown protein crystal depend on physical and biochemical system parameters like: protein concentration, pH, temperature or concentration of precipitat ...
Flanged Sample Compartment Flanged Beam Splitter Holder
... The 78150 Beam Splitter Mount holds a 2 inch (51 mm) square beam splitter, up to 0.25 inch (6 mm) thick, at a 45° angle. Since it can be coupled directly to Oriel light sources, monochromators, and detectors via the 1.5 Inch Series flanges, it is a convenient device for splitting a beam in an enclos ...
... The 78150 Beam Splitter Mount holds a 2 inch (51 mm) square beam splitter, up to 0.25 inch (6 mm) thick, at a 45° angle. Since it can be coupled directly to Oriel light sources, monochromators, and detectors via the 1.5 Inch Series flanges, it is a convenient device for splitting a beam in an enclos ...
Lecture 1. Introduction. Nature of light, geometric optics.
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
... •The parallel rays converge at the second focal point F‘. •The first focal point is at the front. All rays originated at This point become parallel to the axis after the lens. ...
Transmission Electron Microscopy
... The conventional TEM imaging mode, often referred as bright field imaging (BF), is based on the sample illumination by a collimated and broad electron beam. Figure 5 presents a simplified electron ray path diagram for the most common TEM configurations, BF and electron diffraction. In a simplified w ...
... The conventional TEM imaging mode, often referred as bright field imaging (BF), is based on the sample illumination by a collimated and broad electron beam. Figure 5 presents a simplified electron ray path diagram for the most common TEM configurations, BF and electron diffraction. In a simplified w ...
EDS system
... • Beryllium (Be) is highly robust, but strongly absorbs low energy X-rays meaning that only elements from sodium (Na) can be detected. • Polymer-based thin windows can be made much thinner than Be windows and therefore are transparent to much lower energy X-rays, many allowing detection of X-rays do ...
... • Beryllium (Be) is highly robust, but strongly absorbs low energy X-rays meaning that only elements from sodium (Na) can be detected. • Polymer-based thin windows can be made much thinner than Be windows and therefore are transparent to much lower energy X-rays, many allowing detection of X-rays do ...
Observation of sagittal X-ray diffraction by surface acoustic waves in
... Experimental setup: M1 is a parabolic mirror that makes the beam parallel. The desired X-ray energy between the SAWs and the radiation is then selected with a double-crystal Si(111) monochromator and the beam is focused onto the wavelength, as in equation (2). Fig. 5 sample with a second mirror, M2. ...
... Experimental setup: M1 is a parabolic mirror that makes the beam parallel. The desired X-ray energy between the SAWs and the radiation is then selected with a double-crystal Si(111) monochromator and the beam is focused onto the wavelength, as in equation (2). Fig. 5 sample with a second mirror, M2. ...
A Glimpse of the Future What are soft x-rays anyway?
... The Power of Soft X-rays Polarized X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Liquid crystal alignment on surfaces X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Ferromagnetic alignment on an antiferromagnetic surface Time Dependent X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Switching of magnetic nano-structures with spin currents A Glimpse of t ...
... The Power of Soft X-rays Polarized X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy Liquid crystal alignment on surfaces X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Ferromagnetic alignment on an antiferromagnetic surface Time Dependent X-Ray Spectro-Microscopy Switching of magnetic nano-structures with spin currents A Glimpse of t ...
Lecture 1 TEM
... ionizations are particularly useful for detecting the elemental components of a material. With some care, and looking at a wide range of energy losses, one can determine the types of atoms, and the numbers of atoms of each type, being struck by the beam. The scattering angle (that is, the amount th ...
... ionizations are particularly useful for detecting the elemental components of a material. With some care, and looking at a wide range of energy losses, one can determine the types of atoms, and the numbers of atoms of each type, being struck by the beam. The scattering angle (that is, the amount th ...
Total Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometer
... characteristics of the conventional x-ray sources, such as the angular divergence and the intensity at the sample position. In this work, a new type of the x-ray optical device with two curved mirrors was tested experimentally. INTRODUCTION The idea and first demonstration of TXRF were presented in ...
... characteristics of the conventional x-ray sources, such as the angular divergence and the intensity at the sample position. In this work, a new type of the x-ray optical device with two curved mirrors was tested experimentally. INTRODUCTION The idea and first demonstration of TXRF were presented in ...
Fourier Transform IR Spectroscopy
... • FT – IR can take wavelength readings across the whole IR region simultaneously and smoothly, making this a very rapid technique. • The technique is non-invasive and non-destructive. Its resolution of .125 cm-1 is not spectacular in comparison to other vibrational techniques and it will not give th ...
... • FT – IR can take wavelength readings across the whole IR region simultaneously and smoothly, making this a very rapid technique. • The technique is non-invasive and non-destructive. Its resolution of .125 cm-1 is not spectacular in comparison to other vibrational techniques and it will not give th ...
Suman-AE-AOTFIntro-2..
... Where ∆n is the birefringence of the the TeO2 crystal, Vα and fα are the velocity and frequency of the acoustic wave, and α is a complex parameter depending on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the freq ...
... Where ∆n is the birefringence of the the TeO2 crystal, Vα and fα are the velocity and frequency of the acoustic wave, and α is a complex parameter depending on the design of the AOTF. The wavelength of the light that is selected by this diffraction can therefore be varied simply by changing the freq ...
Free-electron lasers
... Motivation: Photo-synthesis converts light from the sun very effective into chemical energy that triggers the conversion of CO2 to O2. If Photo-synthesis would be fully understood then it could be maybe used as an alternative source of energy. The involved proteins have been studied in synchrotron l ...
... Motivation: Photo-synthesis converts light from the sun very effective into chemical energy that triggers the conversion of CO2 to O2. If Photo-synthesis would be fully understood then it could be maybe used as an alternative source of energy. The involved proteins have been studied in synchrotron l ...
Electron Diffraction
... level any measurement device will only detect particles (cf. 'shot noise', 'collapse of the wave function'), the equations (Schrödinger/Dirac-Equation) that determine the probability to find these particles at a certain position in time and space allow for superposition and interference which are ph ...
... level any measurement device will only detect particles (cf. 'shot noise', 'collapse of the wave function'), the equations (Schrödinger/Dirac-Equation) that determine the probability to find these particles at a certain position in time and space allow for superposition and interference which are ph ...
Secondary electrons
... difficult to detect with the petrographic microscope -Determining size of very small mineral phases ...
... difficult to detect with the petrographic microscope -Determining size of very small mineral phases ...
electron diffraction - Department of Physics | Oregon State
... The atoms of a crystal lattice are the diffracting objects in this experiment. When any radiation (electron waves or X rays, for example) is incident on a crystal lattice, the planes of atoms act like reflecting planes, and the radiation is reflected from successive planes. This experiment uses a sc ...
... The atoms of a crystal lattice are the diffracting objects in this experiment. When any radiation (electron waves or X rays, for example) is incident on a crystal lattice, the planes of atoms act like reflecting planes, and the radiation is reflected from successive planes. This experiment uses a sc ...
Electron diffraction - Physics | Oregon State University
... parallax errors. To get a good value for the diameter of a ring that appears as a thick line on the screen, try measuring the inner and outer diameters and take their average. The accelerating voltage should be varied from 2.5 kV to 5 kV in steps of 0.5 kV. For each voltage setting, adjust the focu ...
... parallax errors. To get a good value for the diameter of a ring that appears as a thick line on the screen, try measuring the inner and outer diameters and take their average. The accelerating voltage should be varied from 2.5 kV to 5 kV in steps of 0.5 kV. For each voltage setting, adjust the focu ...
MLSystems Lab 1 - Fourier v4 - RIT
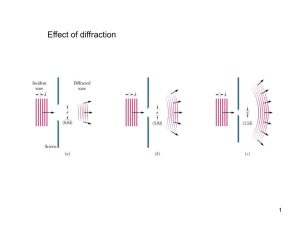
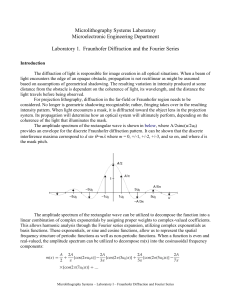
... The diffraction of light is responsible for image creation in all optical situations. When a beam of light encounters the edge of an opaque obstacle, propagation is not rectilinear as might be assumed based on assumptions of geometrical shadowing. The resulting variation in intensity produced at som ...
... The diffraction of light is responsible for image creation in all optical situations. When a beam of light encounters the edge of an opaque obstacle, propagation is not rectilinear as might be assumed based on assumptions of geometrical shadowing. The resulting variation in intensity produced at som ...
LBS-100 System
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...
... LBS-100 Attenuator The LBS-100 system that is not as compact as the LBS-300 above but has larger aperture, and has versions for longer wavelengths. The system contains the mounting frame, 1 wedge beam splitter and several attenuators. The exit end of the LBS-100 is standard C mount thread so all our ...