Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
Experimental observation of the far field diffraction patterns of
... [1-7]. In particular, concentric ring intensity distribution pattern can be induced in the far field of a beam after propagation through a nonlinear material. This effect of spatial phase-modulation (SPM) is due to the intensitydependent complex refractive index and it has been observed in several s ...
... [1-7]. In particular, concentric ring intensity distribution pattern can be induced in the far field of a beam after propagation through a nonlinear material. This effect of spatial phase-modulation (SPM) is due to the intensitydependent complex refractive index and it has been observed in several s ...
Document
... Kelvin Force Microscopy (KFM): • Records forces between tip and sample • Measures Surface Potential • Allows indirect measurement of local resistance ...
... Kelvin Force Microscopy (KFM): • Records forces between tip and sample • Measures Surface Potential • Allows indirect measurement of local resistance ...
110 mid-term 2011Solutions
... level. These excitations relax back down to a lower, possibly not ground state, energy level – the energy difference is emitted as an emission particle with X-ray energy lower than the incident but specific to the excitation. Every element has different possible transitions between ground and higher ...
... level. These excitations relax back down to a lower, possibly not ground state, energy level – the energy difference is emitted as an emission particle with X-ray energy lower than the incident but specific to the excitation. Every element has different possible transitions between ground and higher ...
Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... History of discovery of diffraction The effects of diffraction of light were first observed and characterized by Francesco Maria Grimaldi in the 17th century. James Gregory (1638–1675) observed the diffraction patterns caused by a bird feather. Thomas Young performed a celebrated experiment in 1803 ...
... History of discovery of diffraction The effects of diffraction of light were first observed and characterized by Francesco Maria Grimaldi in the 17th century. James Gregory (1638–1675) observed the diffraction patterns caused by a bird feather. Thomas Young performed a celebrated experiment in 1803 ...
HW2_ASTR 289_2016_v2
... ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of θ are seconds of arc and the units of h are mm? [Since a full circle is 2π radians = 360 deg, one arc second ≈ 4.85 microradians.] b) At an observing wavelength of 2 microns, how many resolution elements (λ / D) would there be within one second of arc? ...
... ii) What is the ratio θ / h where the units of θ are seconds of arc and the units of h are mm? [Since a full circle is 2π radians = 360 deg, one arc second ≈ 4.85 microradians.] b) At an observing wavelength of 2 microns, how many resolution elements (λ / D) would there be within one second of arc? ...
x-ray powder diffraction analysis as a tool in
... clay fractions (oriented samples) was carried out by Powder X-ray diffractometry, using a Panalytical X’Pert PRO MPD (PW3040/60) diffractometer with ...
... clay fractions (oriented samples) was carried out by Powder X-ray diffractometry, using a Panalytical X’Pert PRO MPD (PW3040/60) diffractometer with ...
What are we studying in the EPR lab?
... • The systems of crystal are anisotropic and thus the magnitude of hyperfine coupling constants, the important magnetic parameters to assign the free radicals, depend strongly on orientation in external magnetic field. • In order to calculate the hyperfine coupling constants (which are generally des ...
... • The systems of crystal are anisotropic and thus the magnitude of hyperfine coupling constants, the important magnetic parameters to assign the free radicals, depend strongly on orientation in external magnetic field. • In order to calculate the hyperfine coupling constants (which are generally des ...
FRAUNHOFER and FRESNEL DIFFRACTION
... A. Fraunhofer Diffraction With a point source and without lenses, we can satisfy the conditions for Fraunhofer diffraction by a particular object only if it is a sufficiently large distance from both the source and the observing screen. For a single slit of width b, the Fraunhofer condition without ...
... A. Fraunhofer Diffraction With a point source and without lenses, we can satisfy the conditions for Fraunhofer diffraction by a particular object only if it is a sufficiently large distance from both the source and the observing screen. For a single slit of width b, the Fraunhofer condition without ...
TO THE POSSIBILITY OF CALCULATION
... However actual images are not monochromatic, but polychromatic. It turns out that under narrow band conditions (as is the case of imaging systems) one can consider the amplitude impulse response to be approximately constant (hλ,F(u,v) hF(u,v)). Even so, under polychromatic incoherent illumination ...
... However actual images are not monochromatic, but polychromatic. It turns out that under narrow band conditions (as is the case of imaging systems) one can consider the amplitude impulse response to be approximately constant (hλ,F(u,v) hF(u,v)). Even so, under polychromatic incoherent illumination ...
Wave Equation - web page for staff
... L. A Gaussian beam of diameter 0.5 cm to e-2 relavtive power density for λ = 0.63 μm is incident on the first lens. The value of L is constained such that the e-2 relative power density locus is contained within the aperture of the second lens. ...
... L. A Gaussian beam of diameter 0.5 cm to e-2 relavtive power density for λ = 0.63 μm is incident on the first lens. The value of L is constained such that the e-2 relative power density locus is contained within the aperture of the second lens. ...
Chester F - RIT Center for Imaging Science
... 3. The performance of an optical system in the spatial frequency domain can be characterized by its Modulation Transfer Function (MTF). The Contrast Sensitivity Function (CSF) is used to describe response of the human visual system in the spatial frequency domain. Describe the MTF and the CSF, clea ...
... 3. The performance of an optical system in the spatial frequency domain can be characterized by its Modulation Transfer Function (MTF). The Contrast Sensitivity Function (CSF) is used to describe response of the human visual system in the spatial frequency domain. Describe the MTF and the CSF, clea ...
UV-Vis Absorption Spectroscopy
... Effect of Scattered Radiation at Wavelength Extremes of an Instrument Wavelength extremes of an instrument are dependent on type of source, detector and optical components used in the manufacture of the instrument. Outside the working range of the instrument, it is not possible to use it for accura ...
... Effect of Scattered Radiation at Wavelength Extremes of an Instrument Wavelength extremes of an instrument are dependent on type of source, detector and optical components used in the manufacture of the instrument. Outside the working range of the instrument, it is not possible to use it for accura ...
Supplementary Material for
... Fig. S1 Examples of CCD image of the fringe patterns for single slides. Thinner fringes with uniform spacing are present in all images as a result of interference within the CCD assembly. Measuring the spacing of the thicker fringes, a, yields the wedge angle between the two faces of each slides, wh ...
... Fig. S1 Examples of CCD image of the fringe patterns for single slides. Thinner fringes with uniform spacing are present in all images as a result of interference within the CCD assembly. Measuring the spacing of the thicker fringes, a, yields the wedge angle between the two faces of each slides, wh ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
Document
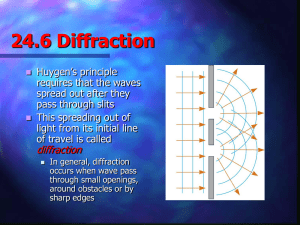
... Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves when they meet an obstruction. It can occur with any type of wave… Diffraction also occurs when any group of waves of a finite size is propagating; for example… Diffraction is one particular type of wave interference, caused by the partial obstructio ...
... Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves when they meet an obstruction. It can occur with any type of wave… Diffraction also occurs when any group of waves of a finite size is propagating; for example… Diffraction is one particular type of wave interference, caused by the partial obstructio ...
Femtosecond powder diffraction with a laser-driven hard X
... of the three-dimensional electron density. Thus, spatially resolved maps of electronic charge density can be derived from X-ray diffraction patterns. There is a variety of powerful X-ray diffraction methods such as Bragg diffraction of monochromatic X-rays from single crystals or polycrystalline mat ...
... of the three-dimensional electron density. Thus, spatially resolved maps of electronic charge density can be derived from X-ray diffraction patterns. There is a variety of powerful X-ray diffraction methods such as Bragg diffraction of monochromatic X-rays from single crystals or polycrystalline mat ...
Synthesis and application of water-bearing large single
... physics. An anticipated task for advancing the relevant research is to create homogeneous single crystals of candidate deepmantle water-bearing minerals of 1 mm or larger in sizes, which is necessary for applying them for the Time-of-Flight (TOF) single-crystal Laue diffraction method at a third-gen ...
... physics. An anticipated task for advancing the relevant research is to create homogeneous single crystals of candidate deepmantle water-bearing minerals of 1 mm or larger in sizes, which is necessary for applying them for the Time-of-Flight (TOF) single-crystal Laue diffraction method at a third-gen ...
Natural Micron-Scale Roughness of Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
... Discussion: We find that the changes in spectral shape occur for all samples at Ra10 values >0.2 µm. This suggests that when observing natural surfaces using thermal infrared spectroscopy, assessments of the surface roughness of the sample can be made by analyzing changes in shapes of primary spectr ...
... Discussion: We find that the changes in spectral shape occur for all samples at Ra10 values >0.2 µm. This suggests that when observing natural surfaces using thermal infrared spectroscopy, assessments of the surface roughness of the sample can be made by analyzing changes in shapes of primary spectr ...
Microscopy Basics
... transform of the object transmission function O. The image I is the inverse Fourier transform of W ...
... transform of the object transmission function O. The image I is the inverse Fourier transform of W ...
Single Slit Diffraction & Gratings
... The principle of polarization: A transverse wave is linearly polarized when its vibrations always occur along one direction. (a) The rope passes a slit parallel to the vibrations, but (b) does not pass through a slit that is perpendicular to the ...
... The principle of polarization: A transverse wave is linearly polarized when its vibrations always occur along one direction. (a) The rope passes a slit parallel to the vibrations, but (b) does not pass through a slit that is perpendicular to the ...
Scanning transmission soft x-ray microscopy at beamline X
... (HFO) (Fe2O3*9H2O) into the stable counterparts goethite (FeOOH) and/or hematite (Fe2O3), actinides and their homologues (lanthanides) can be incorporated into the goethite/hematite structure and therefore change the mobility and bioavailability drastically. As pointed out by Gloter et al.1 the inte ...
... (HFO) (Fe2O3*9H2O) into the stable counterparts goethite (FeOOH) and/or hematite (Fe2O3), actinides and their homologues (lanthanides) can be incorporated into the goethite/hematite structure and therefore change the mobility and bioavailability drastically. As pointed out by Gloter et al.1 the inte ...
( NONLINEAR OPTICS PHYC/ECE 568) Homework #4, Due Thu Sept. 24
... Sinc2 function which is taken to be (kL)=2 with L denoting the length of the nonlinear crystal. Hint: Use the first-order term in the Taylor series expansion of k( ). b. Discuss how your results in (a) explains the limitation on the SHG-efficiency when ultrashort laser ...
... Sinc2 function which is taken to be (kL)=2 with L denoting the length of the nonlinear crystal. Hint: Use the first-order term in the Taylor series expansion of k( ). b. Discuss how your results in (a) explains the limitation on the SHG-efficiency when ultrashort laser ...
TEM - UiO
... Dark field images (two beam condition) If a sample is crystalline, many of the electrons will undergo elastic scattering from the various (hkl) planes. This scattering produces many diffracted beams. If any of these diffracted beams is allowed to pass through the objective aperture a dark field imag ...
... Dark field images (two beam condition) If a sample is crystalline, many of the electrons will undergo elastic scattering from the various (hkl) planes. This scattering produces many diffracted beams. If any of these diffracted beams is allowed to pass through the objective aperture a dark field imag ...