Diffraction Intensity, resolving power, Xray diffraction
... Ans: No, for example the wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm, but the plane spacing in NaCl is 0.28nm. UV is 100nm to 380nm so that won’t work either. How can we observe crystal diffraction and understand the atomic structure of a crystal (or a protein) ? Ans: use coherent x-rays Copyright © 2 ...
... Ans: No, for example the wavelength of visible light is 400-700 nm, but the plane spacing in NaCl is 0.28nm. UV is 100nm to 380nm so that won’t work either. How can we observe crystal diffraction and understand the atomic structure of a crystal (or a protein) ? Ans: use coherent x-rays Copyright © 2 ...
Optical Diffraction and Image Formation
... in space and time. Fields emerging from different points can only interfere, if they are coherent. Heated filaments emit short wave trains, which do not have any phase correlation, as the emission of light is a statistical process. In addition, these wavelets possess wavelengths distributed over the ...
... in space and time. Fields emerging from different points can only interfere, if they are coherent. Heated filaments emit short wave trains, which do not have any phase correlation, as the emission of light is a statistical process. In addition, these wavelets possess wavelengths distributed over the ...
Observing Angular Deviations in the Specular Reflection of a Light
... he law of reflection states that when a plane wave (or light ray) falls on the boundary between two homogeneous media, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Plane waves are infinitely extended and thus cannot exist in nature. A beam is the closest approximation of a ray that we ...
... he law of reflection states that when a plane wave (or light ray) falls on the boundary between two homogeneous media, the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection. Plane waves are infinitely extended and thus cannot exist in nature. A beam is the closest approximation of a ray that we ...
Physics 102 Lab 8: Measuring wavelengths with a
... FIG. 1: Geometry determining the conditions for diffraction from a multi-wire grating ...
... FIG. 1: Geometry determining the conditions for diffraction from a multi-wire grating ...
The Spectrophotometer
... reading on the absorption dial must be due to the solute, since the solvent has been “zeroed out”. ...
... reading on the absorption dial must be due to the solute, since the solvent has been “zeroed out”. ...
How I discovered phase contrast
... Here is one more remarkable historic point. Whereas all the other achievements of Abbe’s were greatly appreciated by all practical microscope users, his theory of image formation was firmly rejected by most of them. To the physicist this may seem incredible, especially when he remembers Abbe’s exper ...
... Here is one more remarkable historic point. Whereas all the other achievements of Abbe’s were greatly appreciated by all practical microscope users, his theory of image formation was firmly rejected by most of them. To the physicist this may seem incredible, especially when he remembers Abbe’s exper ...
Reflection of X-rays with change of frequency
... pulsation capable of giving periodic stratifications of the electron density of the crystal. Excluding the case of small glancing angles, we see from (1) that the wavelength A* of the stratificationsmust be comparable with that of the incident X-rays, and would therefore also be of the same order of ...
... pulsation capable of giving periodic stratifications of the electron density of the crystal. Excluding the case of small glancing angles, we see from (1) that the wavelength A* of the stratificationsmust be comparable with that of the incident X-rays, and would therefore also be of the same order of ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction
... 2. Place the laser at the end of the optical rail. Write down its wavelength. Align the laser beam parallel to the rail. Set the mesh with the largest available period onto the optical rail immediately behind the laser. Place the screen onto the rail, 15-20 cm away from its other end. Place L1 (it ...
... 2. Place the laser at the end of the optical rail. Write down its wavelength. Align the laser beam parallel to the rail. Set the mesh with the largest available period onto the optical rail immediately behind the laser. Place the screen onto the rail, 15-20 cm away from its other end. Place L1 (it ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... extremely faint and an intense light source is therefore required; 2. The lines are relatively broad and it is hard to locate their center accurately. ...
... extremely faint and an intense light source is therefore required; 2. The lines are relatively broad and it is hard to locate their center accurately. ...
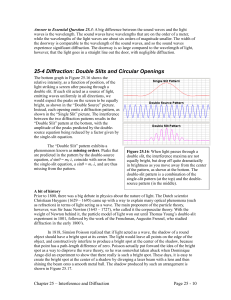
25-4 Diffraction: Double Slits and Circular Openings
... opening (commonly called a circular aperture), such as the one we all look through, the pupil in each of our own eyes. For a circular opening, the angle at which the first zero occurs in a diffraction pattern is given by: (Eq. 25.7: The first zero in a diffraction pattern from a circular aperture) w ...
... opening (commonly called a circular aperture), such as the one we all look through, the pupil in each of our own eyes. For a circular opening, the angle at which the first zero occurs in a diffraction pattern is given by: (Eq. 25.7: The first zero in a diffraction pattern from a circular aperture) w ...
CavityRingDown_Acous..
... Hermitia second rank permittivity tensor Scalar permeability Heterodyne: interaction between two oscillations of unlike frequencies that forms other oscillations, specifically those with a frequency equal to the frequency difference of the former oscillations. Transducer is usually a piezoelectric c ...
... Hermitia second rank permittivity tensor Scalar permeability Heterodyne: interaction between two oscillations of unlike frequencies that forms other oscillations, specifically those with a frequency equal to the frequency difference of the former oscillations. Transducer is usually a piezoelectric c ...
Direct index of refraction measurement at extreme
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
... is given by the square of its coefficient [2(1/π)(1/π)]2 = 4/π 4 , which is a factor of 4 increase in optical throughput as compared with separate grating and zoneplate. Since the membranes on which these optical elements are fabricated have finite absorption, there is an additional gain of efficiency du ...
Part II
... occurs when the path difference is an integral number of wavelengths. • Note that line CE = d = distance between the 2 layers • So: DE d sin EF d sin DE EF 2d sin • Giving: n 2d sin This is called the Bragg Law ...
... occurs when the path difference is an integral number of wavelengths. • Note that line CE = d = distance between the 2 layers • So: DE d sin EF d sin DE EF 2d sin • Giving: n 2d sin This is called the Bragg Law ...
In this lab you will use the phenomenon of interference... thickness of thin films. Two interference techniques, Michelson and... Thin Film Measurement 1 Introduction
... using the micrometer on the mirror to measure the difference in zero path length between the thin film and no film. The second technique uses the step height change in the interference pattern much like the Fizeau technique. Set up the experiment as shown in Figure 1. The alignment of the set up is ...
... using the micrometer on the mirror to measure the difference in zero path length between the thin film and no film. The second technique uses the step height change in the interference pattern much like the Fizeau technique. Set up the experiment as shown in Figure 1. The alignment of the set up is ...
Mineral definition and classification
... This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement that is often expressed in the geometric form that the crystal takes. Even when the mineral grains are too small to see or are irregularly shaped, the underlying crystal structure is always periodic, and can be determine ...
... This crystal structure is based on regular internal atomic or ionic arrangement that is often expressed in the geometric form that the crystal takes. Even when the mineral grains are too small to see or are irregularly shaped, the underlying crystal structure is always periodic, and can be determine ...
Optics Observations
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
... Short wavelength linespread functions are much broader than middle wavelength ...
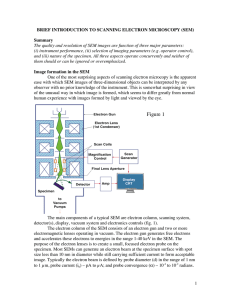
Introduction to Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
... Contamination can be reduced in first place by improving the vacuum in the specimen chamber. Also anti-contamination devices can be employed, which cool area in the close vicinity of the specimen so that hydrocarbon migration is reduced. This can be achieved also by cooling directly the sample. Anot ...
... Contamination can be reduced in first place by improving the vacuum in the specimen chamber. Also anti-contamination devices can be employed, which cool area in the close vicinity of the specimen so that hydrocarbon migration is reduced. This can be achieved also by cooling directly the sample. Anot ...
Diffraction and Interference * Learning Outcomes
... Diffraction Gratings Diffraction gratings are pieces of transparent material with lines etched on it. The lines prevent light from passing through, so light passing between the lines behaves as if it passed through slits (i.e. it diffracts). Gratings are usually described as having some number ...
... Diffraction Gratings Diffraction gratings are pieces of transparent material with lines etched on it. The lines prevent light from passing through, so light passing between the lines behaves as if it passed through slits (i.e. it diffracts). Gratings are usually described as having some number ...
Homework Set #2 Due: 1-25-12 Review problem / tutorial on gratings.
... of some property of the substrate. The modulated quantity can be the absorption, reflectivity, transmission, thickness, or index of refraction. Although somewhat less common, a substrate with spherical curvature is sometimes used so the grating can form images. The first grating that students usuall ...
... of some property of the substrate. The modulated quantity can be the absorption, reflectivity, transmission, thickness, or index of refraction. Although somewhat less common, a substrate with spherical curvature is sometimes used so the grating can form images. The first grating that students usuall ...
PDF
... To overcome this problem, a one-beam push–pull method with a holographic optical element (HOE) has been developed. 2. Sensor System Figure 1 shows an example optical layout of the optical pickup for BDs. A blue-violet laser with a wavelength of 405 nm and an objective lens with a numerical aperture ...
... To overcome this problem, a one-beam push–pull method with a holographic optical element (HOE) has been developed. 2. Sensor System Figure 1 shows an example optical layout of the optical pickup for BDs. A blue-violet laser with a wavelength of 405 nm and an objective lens with a numerical aperture ...
الشريحة 1
... constant over Band A from the source. Note in the Beer’s law plot at the bottom that using Band A gives a linear relationship. In the spectrum, Band B corresponds to a region where the absorptivity shows substantial changes. In the lower plot, note the dramatic deviation from Beer’s law that results ...
... constant over Band A from the source. Note in the Beer’s law plot at the bottom that using Band A gives a linear relationship. In the spectrum, Band B corresponds to a region where the absorptivity shows substantial changes. In the lower plot, note the dramatic deviation from Beer’s law that results ...
1942 CS V11 p44
... the bright spot and the dark circle surrounding it may be traced to a considerable distancc behind the crystal using a point-source of light and a low-power magnifier. The phenomena exhibited by a naphthalene crystal in certain respects present an exceptional simplicity. The image of a fine pin-hole ...
... the bright spot and the dark circle surrounding it may be traced to a considerable distancc behind the crystal using a point-source of light and a low-power magnifier. The phenomena exhibited by a naphthalene crystal in certain respects present an exceptional simplicity. The image of a fine pin-hole ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2015 Semester Lecture 36 – Interference
... • The effective gap between the surfaces can be adjusted by changing the pressure of a gas, or by means of piezoelectric actuators ...
... • The effective gap between the surfaces can be adjusted by changing the pressure of a gas, or by means of piezoelectric actuators ...
UV-Fluorescence-Imaging
... In general, fluorescence intensity depends on the concentration of tryptophan in the sample. However, quenching from either the protein itself or other additives can negate fluorescence from protein crystals and result in a false negative when imaged with UV, even if the crystals have a relatively h ...
... In general, fluorescence intensity depends on the concentration of tryptophan in the sample. However, quenching from either the protein itself or other additives can negate fluorescence from protein crystals and result in a false negative when imaged with UV, even if the crystals have a relatively h ...
lecture5_techniques2
... • A crystal is built up from many billions of small identical units, or unit cells. These unit cells are packed against ach other in three dimensions, much as identical boxes are packed and stored in a warehouse. The unit cell may contain one or more than one molecule. Although the number of molecul ...
... • A crystal is built up from many billions of small identical units, or unit cells. These unit cells are packed against ach other in three dimensions, much as identical boxes are packed and stored in a warehouse. The unit cell may contain one or more than one molecule. Although the number of molecul ...