Re-Examining the Mental Imagery Debate with Neuropsychological
... developed by Kosslyn (Kosslyn 1994) and this school of thought has found widespread support among cognitive scientists. It was accepted in this theory that images do not preserve perceptual phenomena perfectly. It was also accepted that a priori knowledge plays a part in reasoning with images. Howev ...
... developed by Kosslyn (Kosslyn 1994) and this school of thought has found widespread support among cognitive scientists. It was accepted in this theory that images do not preserve perceptual phenomena perfectly. It was also accepted that a priori knowledge plays a part in reasoning with images. Howev ...
S01 - Preparing for the EPPP and PPLE
... visualization, self-referencing, etc. b. Adopting an incremental theory of intelligence c. Setting specific, short-term and challenging goals d. All of the above ...
... visualization, self-referencing, etc. b. Adopting an incremental theory of intelligence c. Setting specific, short-term and challenging goals d. All of the above ...
File - CYPA Psychology
... (A) The study of natural, unanalyzed perception (B) The process of thinking and memory (C) The study of psychological mental health (D) lhe study of language development (E) The process ofconsistent patterns and organized ...
... (A) The study of natural, unanalyzed perception (B) The process of thinking and memory (C) The study of psychological mental health (D) lhe study of language development (E) The process ofconsistent patterns and organized ...
Multimodal Wayfinding: Airports as a Case Study
... wayfinding information, which is communicated to them from different sources and through different modes of communication. The analysis of such interplay is important if one wants to simulate human wayfinding in a cognitively plausible way. Such simulation of wayfinding tasks helps to determine wher ...
... wayfinding information, which is communicated to them from different sources and through different modes of communication. The analysis of such interplay is important if one wants to simulate human wayfinding in a cognitively plausible way. Such simulation of wayfinding tasks helps to determine wher ...
Chaper 1. A Brief History of Cognitive Neuroscience
... Starting in the 1930s, Clinton Woolsey, Philip Bard, and others began to discover motor and sensory “maps” in the brain. In the 1970s and 1980s, we learned that multiple maps exist in each sensory modality. We now know there are very localized areas in the brain, such as the middle temporal area whi ...
... Starting in the 1930s, Clinton Woolsey, Philip Bard, and others began to discover motor and sensory “maps” in the brain. In the 1970s and 1980s, we learned that multiple maps exist in each sensory modality. We now know there are very localized areas in the brain, such as the middle temporal area whi ...
multiple intelligences and quotient spaces
... It is necessary to highlight, that it does not exist, and will never be able to exist, a single, irrefutable and accepted list of human intelligences. There will never be a master list of 3; 7 or 100 intelligences which could be guaranteed by researchers. It might be possible that a decisive theory ...
... It is necessary to highlight, that it does not exist, and will never be able to exist, a single, irrefutable and accepted list of human intelligences. There will never be a master list of 3; 7 or 100 intelligences which could be guaranteed by researchers. It might be possible that a decisive theory ...
Behaviorism - El Salón de la Srta. Steele
... children and token economies for the management of chronic schizophrenics. It brought in discussions on what was the best way to understand the behavior of nonhuman animals, the relevance of lab study to the natural environmental occurrence of behavior, and if there is a built-in associative bias in ...
... children and token economies for the management of chronic schizophrenics. It brought in discussions on what was the best way to understand the behavior of nonhuman animals, the relevance of lab study to the natural environmental occurrence of behavior, and if there is a built-in associative bias in ...
The Psychology of the Person
... How do the fields of personality and social psychology differ? The Study of Individual Differences Social psychologists are interested in how people typically behave in respond to situational demands. Personality psychologists accept that there might be typical responses in certain situations, but ...
... How do the fields of personality and social psychology differ? The Study of Individual Differences Social psychologists are interested in how people typically behave in respond to situational demands. Personality psychologists accept that there might be typical responses in certain situations, but ...
Psychology Unit 1 - spetersopsych
... hypothesize, collect data (observe & experiment) & analyze data. Hypothesis: stating what you expect to find in a way that can be proved or disproved. Example: people who have similar opinions on important issues are likely to be attracted to one another. ...
... hypothesize, collect data (observe & experiment) & analyze data. Hypothesis: stating what you expect to find in a way that can be proved or disproved. Example: people who have similar opinions on important issues are likely to be attracted to one another. ...
paradigm shift of personality in sports psychology
... problematic because it was not assessed in terms of its multidimensional nature. The research conducted during this time period was characterized by use of psychology theories tested in the motor domain and in laboratory settings. Cognitive approaches and filed methods from 1977 to the present In th ...
... problematic because it was not assessed in terms of its multidimensional nature. The research conducted during this time period was characterized by use of psychology theories tested in the motor domain and in laboratory settings. Cognitive approaches and filed methods from 1977 to the present In th ...
Making Sense of Internal Logic: Theory and a Case Study
... meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments investigating multidimensional visual discrimination tasks with monkeys. In these experimen ...
... meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments investigating multidimensional visual discrimination tasks with monkeys. In these experimen ...
Syllabus
... Fraud. There is a Freudian slip example. Understanding behavior as the basic goal of scientific inquiry. Correct and incorrect conclusion drawing. Psychology has a its mission the goal of predicting, controlling, describing, and explaining behavior. Drawing conclusions will be examined. I hope you w ...
... Fraud. There is a Freudian slip example. Understanding behavior as the basic goal of scientific inquiry. Correct and incorrect conclusion drawing. Psychology has a its mission the goal of predicting, controlling, describing, and explaining behavior. Drawing conclusions will be examined. I hope you w ...
Perspectives and Careers
... This perspective studies the physiological mechanisms in the brain , endocrine and nervous system that organize and control behavior The focus may be ◦ individual neurons ◦ areas of the brain ◦ specific functions like eating, emotion or learning ...
... This perspective studies the physiological mechanisms in the brain , endocrine and nervous system that organize and control behavior The focus may be ◦ individual neurons ◦ areas of the brain ◦ specific functions like eating, emotion or learning ...
Lecture3
... attempt--would seem to involve insight and planning, at least on the first occasion. Observational Learning Was 1st proposed by Albery Bandura, “Replicating others’ novel behavior through observation and imitation; also known as vicarious learning, modeling, or social learning”. In Observational Lea ...
... attempt--would seem to involve insight and planning, at least on the first occasion. Observational Learning Was 1st proposed by Albery Bandura, “Replicating others’ novel behavior through observation and imitation; also known as vicarious learning, modeling, or social learning”. In Observational Lea ...
What is Development?
... Children act on their environment and learn from those interactions; they are motivated to learn Children construct their own knowledge based on their experiences with their environment and through social interactions. Each of the four stages is related to a specific age range and children in those ...
... Children act on their environment and learn from those interactions; they are motivated to learn Children construct their own knowledge based on their experiences with their environment and through social interactions. Each of the four stages is related to a specific age range and children in those ...
AGED 601
... Restructuring-creating entirely new schemata which replace or incorporate old ones Bruner o ...
... Restructuring-creating entirely new schemata which replace or incorporate old ones Bruner o ...
CAUSES OF PSYCHOPATHOLOGY Throughout history, the search
... the same species, is one of the two broad categories of social behaviors studied by psychologists. • One of the most important areas of research on individual differences in personality is the study of temperament, characteristic styles of relating to the world. ...
... the same species, is one of the two broad categories of social behaviors studied by psychologists. • One of the most important areas of research on individual differences in personality is the study of temperament, characteristic styles of relating to the world. ...
Understanding genetic, neurophysiological, and experiential
... well in A-trials. On B-trials, parietally lesioned and unlesioned controls performed well at all delays, but DLPFC-lesioned animals searched incorrectly at the Alocation following 2- and 10-s delays. The disinhibited pattern of behavior exhibited by the DLPFC-lesioned animals parallels performance o ...
... well in A-trials. On B-trials, parietally lesioned and unlesioned controls performed well at all delays, but DLPFC-lesioned animals searched incorrectly at the Alocation following 2- and 10-s delays. The disinhibited pattern of behavior exhibited by the DLPFC-lesioned animals parallels performance o ...
The computational modeling of analogy-making
... of analogy-making is LISA [39]. Whereas ACME required all objects in the source to be pairwise connected to all elements in the target, LISA relies on more plausible mechanisms, such as partially distributed representations of concepts, selective activation and dynamic binding as the means of associ ...
... of analogy-making is LISA [39]. Whereas ACME required all objects in the source to be pairwise connected to all elements in the target, LISA relies on more plausible mechanisms, such as partially distributed representations of concepts, selective activation and dynamic binding as the means of associ ...
Chapter Excerpt
... awareness is a result of processes of the brain. The field of behaviorism was greatly impacted by Hobbes’s philosophy. Theory of Natural Selection Discoveries in medicine and biology strongly influenced the field of psychology during the nineteenth century. Charles Darwin (1809-1882) proposed the id ...
... awareness is a result of processes of the brain. The field of behaviorism was greatly impacted by Hobbes’s philosophy. Theory of Natural Selection Discoveries in medicine and biology strongly influenced the field of psychology during the nineteenth century. Charles Darwin (1809-1882) proposed the id ...
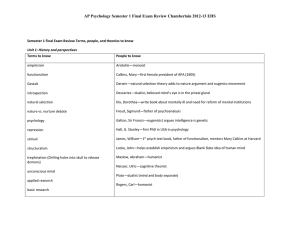
Semester 1 Final Exam Review Terms, people, and
... agonists (make neurons fire—they are chemicals so similar in structure to natural neurotransmitters that they either bind to dendritic receptors causing action potential OR they prevent reuptake of brain’s neurotransmitters by binding to axon’s reuptake valves) antagonists (make neurons NOT fire by ...
... agonists (make neurons fire—they are chemicals so similar in structure to natural neurotransmitters that they either bind to dendritic receptors causing action potential OR they prevent reuptake of brain’s neurotransmitters by binding to axon’s reuptake valves) antagonists (make neurons NOT fire by ...
Treatment of Abnormal Behavior
... d. Summarize effectiveness of specific treatments used to address specific problems. e. Discuss how cultural and ethnic context influence choice and success of treatment (e.g., factors that lead to premature termination of treatment). f. Describe prevention strategies that build resilience and promo ...
... d. Summarize effectiveness of specific treatments used to address specific problems. e. Discuss how cultural and ethnic context influence choice and success of treatment (e.g., factors that lead to premature termination of treatment). f. Describe prevention strategies that build resilience and promo ...
Introduction to Psychology
... to the body or distinct? Are ideas inborn or is the mind a blank slate filled by experience? ...
... to the body or distinct? Are ideas inborn or is the mind a blank slate filled by experience? ...
CB4 - FA1 IIPM
... associated and the organism begins to produce a behavioral response to the CS. Pavlov called this the conditioned response (CR). Popular forms of classical conditioning that are used to study neural structures and functions that underlie learning and memory include fear conditioning, eyeblink condi ...
... associated and the organism begins to produce a behavioral response to the CS. Pavlov called this the conditioned response (CR). Popular forms of classical conditioning that are used to study neural structures and functions that underlie learning and memory include fear conditioning, eyeblink condi ...
Cognitive science
Cognitive science is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the mind and its processes. It examines what cognition is, what it does and how it works. It includes research on intelligence and behaviour, especially focusing on how information is represented, processed, and transformed (in faculties such as perception, language, memory, attention, reasoning, and emotion) within nervous systems (humans or other animals) and machines (e.g. computers). Cognitive science consists of multiple research disciplines, including psychology, artificial intelligence, philosophy, neuroscience, linguistics, and anthropology. It spans many levels of analysis, from low-level learning and decision mechanisms to high-level logic and planning; from neural circuitry to modular brain organization. The fundamental concept of cognitive science is that ""thinking can best be understood in terms of representational structures in the mind and computational procedures that operate on those structures.""