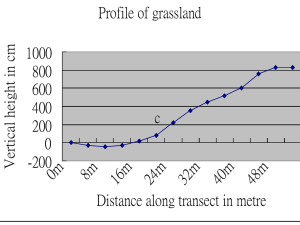
Science and Health 5
... To classify organisms into groups, scientists study many characteristics. They study the number of cells and whether the cells have a nucleus, and cell parts. They also look at body form and how an organism gets food. They observe if it moves from place to place. Even how organisms reproduce is stud ...
... To classify organisms into groups, scientists study many characteristics. They study the number of cells and whether the cells have a nucleus, and cell parts. They also look at body form and how an organism gets food. They observe if it moves from place to place. Even how organisms reproduce is stud ...
Feeding young through mammary glands
... names to name animals? (Be sure to include 2 reasons why we don’t use common names AND why we do use binomial nomenclature) ...
... names to name animals? (Be sure to include 2 reasons why we don’t use common names AND why we do use binomial nomenclature) ...
lec---17
... of plants, and the body fluids and tissues of animals. Some species parasitize animals. They range in length from less than 1 mm to more than a meter. The body of Nematode is covered with a tough exoskeleton, the cuticle. They have a complete digestive tract. Nematodes usually engage in sexual ...
... of plants, and the body fluids and tissues of animals. Some species parasitize animals. They range in length from less than 1 mm to more than a meter. The body of Nematode is covered with a tough exoskeleton, the cuticle. They have a complete digestive tract. Nematodes usually engage in sexual ...
Taxonomy of Australian Birds
... including the specific names of the different sub species. Preferably it should be unique within a family in case the genus is changed later on. It is not unique across families. There are different forms for each gender. The gender must be the same as the genus. Most specific names ending in –us, – ...
... including the specific names of the different sub species. Preferably it should be unique within a family in case the genus is changed later on. It is not unique across families. There are different forms for each gender. The gender must be the same as the genus. Most specific names ending in –us, – ...
Family Etmopteridae "The Lantern Sharks"
... Juveniles feed on eurybathic crustaceans Adults feed on teleost fish and cephalopods ...
... Juveniles feed on eurybathic crustaceans Adults feed on teleost fish and cephalopods ...
Species found in the trip:
... normal spiders. They kill prey by secreting fluid from their stink glands. With regard to the number of legs they posses, each apparent body segment is actually composed of two adjacent segments fused together, so there is in fact only one pair if legs per body segment. ...
... normal spiders. They kill prey by secreting fluid from their stink glands. With regard to the number of legs they posses, each apparent body segment is actually composed of two adjacent segments fused together, so there is in fact only one pair if legs per body segment. ...
Practice Questions for Second Hour Exam
... Part I: True or False Questions. 1. When we say that two species are closely related, it means that one of them evolved from the other. 2. Present evidence suggests that life on Earth first arose approximately 545 million years ago. 3. Allopolyploidy can result in the formation of a new species in a ...
... Part I: True or False Questions. 1. When we say that two species are closely related, it means that one of them evolved from the other. 2. Present evidence suggests that life on Earth first arose approximately 545 million years ago. 3. Allopolyploidy can result in the formation of a new species in a ...
arGyresthia FriUlii sP. n., a new sPeCies From the JUlian Pre
... Furthermore larval characters and the peculiar upsidedown resting position of the adults are typical for the subfamily. Argyresthia was formerly divided into two genera, viz. Argyresthia with separate, and Blastotere with stalked veins R4 and R5 of the forewing (Friese 1969). However, nowadays these ...
... Furthermore larval characters and the peculiar upsidedown resting position of the adults are typical for the subfamily. Argyresthia was formerly divided into two genera, viz. Argyresthia with separate, and Blastotere with stalked veins R4 and R5 of the forewing (Friese 1969). However, nowadays these ...
Resume - OPResume.com
... Administered drugs to animals when necessary Effectively kept record of parturition, mortality, vaccination, drug administration, litter number, etc Supervised undergraduate students attached to the zoological garden on industrial training by providing leadership, instructions and coordinating stude ...
... Administered drugs to animals when necessary Effectively kept record of parturition, mortality, vaccination, drug administration, litter number, etc Supervised undergraduate students attached to the zoological garden on industrial training by providing leadership, instructions and coordinating stude ...
cretaceous mammals of southern utah. ii. marsupials and marsupial
... Oklahoma Musem of Natural History and Department of Zoology, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 73019 ABSTRACT—The Wahweap Formation of southern Utah is probably early Campanian in age. Its mammalian fauna is generally similar to that of the Aquilan upper Milk River Formation, Alberta, but dif ...
... Oklahoma Musem of Natural History and Department of Zoology, University of Oklahoma, Norman, Oklahoma 73019 ABSTRACT—The Wahweap Formation of southern Utah is probably early Campanian in age. Its mammalian fauna is generally similar to that of the Aquilan upper Milk River Formation, Alberta, but dif ...
A new Celaenorrhinus species (Lepidoptera: Hesperiidae) from a
... endemic Javanese species C. toxopei de Jong, 1981. It differs, however, from the latter species in wing shape (in C. toxopei the termen of the forewing is straight) and in the following genitalic characters: in the male, the cucullus is broader and not curved inwards, and the costal process is much ...
... endemic Javanese species C. toxopei de Jong, 1981. It differs, however, from the latter species in wing shape (in C. toxopei the termen of the forewing is straight) and in the following genitalic characters: in the male, the cucullus is broader and not curved inwards, and the costal process is much ...
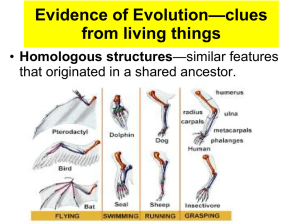
Evidence of Evolution—clues from living things
... • During the early stages of development, all vertebrate embryos look similar. • Does this mean they share a common ancestor? ...
... • During the early stages of development, all vertebrate embryos look similar. • Does this mean they share a common ancestor? ...
endangered animals
... the Asian Elephant (also known as the Indian Elephant). Other species have become extinct since the last ice age, which ended about 10,000 years ago, the Mammoth being the most famous of these. Elephants are mammals, and the largest land animals alive today. At birth it is common for an elepha ...
... the Asian Elephant (also known as the Indian Elephant). Other species have become extinct since the last ice age, which ended about 10,000 years ago, the Mammoth being the most famous of these. Elephants are mammals, and the largest land animals alive today. At birth it is common for an elepha ...
981-5023-1
... Figure 4, Habitat of Brachymyrmex cordemoyi, King Saud University Campus, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. (Photo: S. Salman). ...
... Figure 4, Habitat of Brachymyrmex cordemoyi, King Saud University Campus, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. (Photo: S. Salman). ...
File
... Arthropods: Phylum of animals with bilateral symmetry, segmentation and exoskeleton. asexual reproduction: form of reproduction where offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Bilateral symmetry: Body plan where animal can be divided into matching halves with central plane. ...
... Arthropods: Phylum of animals with bilateral symmetry, segmentation and exoskeleton. asexual reproduction: form of reproduction where offspring are genetically identical to the parent. Bilateral symmetry: Body plan where animal can be divided into matching halves with central plane. ...
Habitat and Lifestyle - Calgary Christian School
... release nutrients, which are used by other organisms ...
... release nutrients, which are used by other organisms ...
Taxonomy and Classification Powerpoint
... • Think back to the Jones Beach lab where you classified and sorted organisms. • What do scientists sort organisms based on? ...
... • Think back to the Jones Beach lab where you classified and sorted organisms. • What do scientists sort organisms based on? ...
Symbiosis is a relationship between two organisms: it
... the anemone neither benefits nor suffers. Parasitism: Parasites are organisms that harm their symbiotic partners. Parasitism is incredibly common in nature: depending on the definition, more than half of all species may go through at least one parasitic stage in their life cycle. There are many wel ...
... the anemone neither benefits nor suffers. Parasitism: Parasites are organisms that harm their symbiotic partners. Parasitism is incredibly common in nature: depending on the definition, more than half of all species may go through at least one parasitic stage in their life cycle. There are many wel ...
Checklist prior to submission (English)
... Section headers (Materials and methods, Results, and so on) are necessary for Regular paper, whereas unnecessary for Short Communication except Acknowledgements and References. Italicize scientific names of microorganisms, from domains, phyla, to genera, and species. Purchased companies should be gi ...
... Section headers (Materials and methods, Results, and so on) are necessary for Regular paper, whereas unnecessary for Short Communication except Acknowledgements and References. Italicize scientific names of microorganisms, from domains, phyla, to genera, and species. Purchased companies should be gi ...
Unit 4: Evolution
... have adapted to similar environments. B. The animals share a common ancestry but have adapted to different environments. C. The animals at one time lived in different environments but now share an environment. D. The animals use their forelimbs for identical activities but live in different environm ...
... have adapted to similar environments. B. The animals share a common ancestry but have adapted to different environments. C. The animals at one time lived in different environments but now share an environment. D. The animals use their forelimbs for identical activities but live in different environm ...
UTKEEB464_Lecture5_Jargon_2015
... Taxon = OTU (operational taxon unit) = Leaf = Terminal = Terminal Node ...
... Taxon = OTU (operational taxon unit) = Leaf = Terminal = Terminal Node ...
Section 3.1
... and classifying living things. • A Swedish scientist and explorer named Carolus Linnaeus (1707–1778) developed a system of classification in the 1700s. • There are currently seven levels of classification. ...
... and classifying living things. • A Swedish scientist and explorer named Carolus Linnaeus (1707–1778) developed a system of classification in the 1700s. • There are currently seven levels of classification. ...
zoology_introductionx1
... A. All are composed of cells (animals are multicellular, heterotrophic organisms) 1. Cell Theory is a basic tenet of biology. The cell theory states that: a) all living things are composed of cells b) the cell is the fundamental unit of life c) all cells in our modern atmosphere and conditions must ...
... A. All are composed of cells (animals are multicellular, heterotrophic organisms) 1. Cell Theory is a basic tenet of biology. The cell theory states that: a) all living things are composed of cells b) the cell is the fundamental unit of life c) all cells in our modern atmosphere and conditions must ...