* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PP – Classification
Animal cognition wikipedia , lookup
Anatomical terms of location wikipedia , lookup
Deception in animals wikipedia , lookup
International Code of Zoological Nomenclature wikipedia , lookup
Animal coloration wikipedia , lookup
Precambrian body plans wikipedia , lookup
Non-reproductive sexual behavior in animals wikipedia , lookup
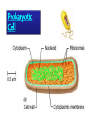
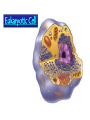
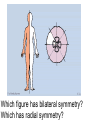
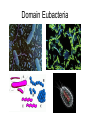
Classification ZOOLOGY The “father of modern taxonomy” was Carolus Linnaeus 1707-1778 The Old System 6 Kingdom Proposal Archebacteria EUbacteria Prokaryotic Cell Eukaryotic Cell Binomial Nomenclature: “a two-name system” First part of name: Genus first letter always capitalized Second part : species first letter always lowercase Ursus americanus American Black Bear Canis domesticus Canis lupus Autotrophs capture the light energy from sunlight and convert it to chemical energy they use for food. Heterotrophs must get energy by eating autotrophs or other heterotrophs. Decomposers (aka saprobes) are heterotrophs that recycle dead organisms by breaking them down. Fungi are decomposers. ~ Body Plans of Animals~ • An animal shows asymmetry if there is no central axis (some sponges) • An animal has radial symmetry if it can be divided along any plane, through a central axis, into equal halves. (jellyfish, sea anemone) • An animal has bilateral symmetry if it can be divided down its length into similar right and left halves forming mirror images of each other. (eel, bird, fox) Which figure has bilateral symmetry? Which has radial symmetry? Anatomical Terms for Animals Reproduction Asexual reproduction – No separate male and female parts binary fission – division of one cell or body part into two (flatworms) budding – an outgrowth from the original organism (hydra) Sexual reproduction – has male and female parts, union of two separate gametes. Domain Archaea Domain Eubacteria Domain Eukarya Kingdom Protista Amoeba Paramecium Water Mold Euglena Giardia Slime Mold Dinoflagellates Green Algae Brown Algae Diatom Kingdom Fungi All eukaryotic, multicellular, heterotrophic, sessile organisms. Includes: molds, mushrooms, rusts, and lichens. Kingdom Plantae Bryophyte (Moss) Pteridophyte (Fern) Pteridophyte (Fern) Coniferophytes (Pine Trees) Angiosperm; Dicot Angiosperm; Monocot Kingdom Animalia Human Classification Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Primates Family: Hominidae Genus: Homo Species: Sapien