Optical Fiber Communication
... On the basis of number of modes:on the basis of number of modes of propagation the optical fiber are classified into two types: (i) Single mode fiber (SMF) and (ii) Multi-mode fiber (MMF) • Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber h ...
... On the basis of number of modes:on the basis of number of modes of propagation the optical fiber are classified into two types: (i) Single mode fiber (SMF) and (ii) Multi-mode fiber (MMF) • Single-mode fibers – in single mode fiber only one mode can propagate through the fiber. This type of fiber h ...
Two-Color Two-Photon Excitation Using Femtosecond Laser Pulses
... laser systems being used for spectroscopy and two-photon microscopy. We demonstrate measurements of 2c2p excitation fluorescence using femtosecond pulses from a Ti:Sa laser. Since these experiments were carried out using a time-gated camera system as a detector which is normally used for fluorescenc ...
... laser systems being used for spectroscopy and two-photon microscopy. We demonstrate measurements of 2c2p excitation fluorescence using femtosecond pulses from a Ti:Sa laser. Since these experiments were carried out using a time-gated camera system as a detector which is normally used for fluorescenc ...
Elements of the wave-particle duality of light
... a screen. We can reduce the intensity of the beam in such a way that according to a standard concept of quantum mechanics there will be only one quantum of light (photon) present in the apparatus at any given time. If we now place a detector behind each slit, we will see that they do not respond sim ...
... a screen. We can reduce the intensity of the beam in such a way that according to a standard concept of quantum mechanics there will be only one quantum of light (photon) present in the apparatus at any given time. If we now place a detector behind each slit, we will see that they do not respond sim ...
Exponential and Power-Law Kinetics in Single-Molecule
... as the short “off” times. The difference in the time scales of the “off” times visible in panels b and c becomes evident if one looks at the “off” event of panel b in the enlarged time scale of panel c. The “off” event at about 1.8 s, which is visible as a sharp spike in panel b, is very long compar ...
... as the short “off” times. The difference in the time scales of the “off” times visible in panels b and c becomes evident if one looks at the “off” event of panel b in the enlarged time scale of panel c. The “off” event at about 1.8 s, which is visible as a sharp spike in panel b, is very long compar ...
Femtosecond Laser Spectroscopy
... *Note that if you want the bandwidth in nm, you must know the central wavelength of the laser. ...
... *Note that if you want the bandwidth in nm, you must know the central wavelength of the laser. ...
Practice Exercise 1
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
03_Worked_Examples
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
... Begin by counting each kind of atom on the two sides of the arrow. There are one Na, one O, and two H on the left side, and one Na, one O, and three H on the right. The Na and O atoms are balanced, but the number of H atoms is not. To increase the number of H atoms on the left, let’s try placing the ...
Development of Lightning Simulator
... can calibrate the color of the simulated light output based on a correlated color temperature (CCT). The CCT of the simulated light can range over from 4269 K to 15042 K. The lightning simulator is useful for the test light source of the optical/image sensor of the lightning observation. Also for sc ...
... can calibrate the color of the simulated light output based on a correlated color temperature (CCT). The CCT of the simulated light can range over from 4269 K to 15042 K. The lightning simulator is useful for the test light source of the optical/image sensor of the lightning observation. Also for sc ...
Properties and sensing characteristics of surface
... was placed onto a rotary block of a variable-angle spectroscopic ellipsometer (Woollam VASE® ellipsometer, J. A. Woollam, Lincoln, Neb.) to allow for very fine variation of the angular prism position with respect to the optical path of the ellipsometer. The system was illuminated by continuous monoc ...
... was placed onto a rotary block of a variable-angle spectroscopic ellipsometer (Woollam VASE® ellipsometer, J. A. Woollam, Lincoln, Neb.) to allow for very fine variation of the angular prism position with respect to the optical path of the ellipsometer. The system was illuminated by continuous monoc ...
EXCITATION OF HELIUM ATOMS IN He
... The investigated area was at 123 mm distance from the extending electrode of the fast particle source and at 12 mm distance from the atom beam detector inlet. The distance between the detector target electrode and its input aperture was equal to 47 mm. In determination of the flux density of fast at ...
... The investigated area was at 123 mm distance from the extending electrode of the fast particle source and at 12 mm distance from the atom beam detector inlet. The distance between the detector target electrode and its input aperture was equal to 47 mm. In determination of the flux density of fast at ...
Development of a high precision interferometric set-up for the
... PMD coefficient: In case of weak cross coupling between polarization modes, the PMD coefficient is given as DGD per unit length of the fiber, and the typical units are pico second per meter. On the other hand in case of strong polarization cross coupling the coefficient is DGD divided by the square ...
... PMD coefficient: In case of weak cross coupling between polarization modes, the PMD coefficient is given as DGD per unit length of the fiber, and the typical units are pico second per meter. On the other hand in case of strong polarization cross coupling the coefficient is DGD divided by the square ...
Photo-catalytic transparent heat mirror film TiO2/TiN/TiO2
... at the 550nm wavelength, as shown in Table 2. Based on the results in Table 1, the O.S.Heavens [9] matrix is used to find a suitable thickness of each layer sufficient to enable multi-layer films to effectively transmit at the 550nm wavelength, as shown in Table 3. Then, we can simulate the theoreti ...
... at the 550nm wavelength, as shown in Table 2. Based on the results in Table 1, the O.S.Heavens [9] matrix is used to find a suitable thickness of each layer sufficient to enable multi-layer films to effectively transmit at the 550nm wavelength, as shown in Table 3. Then, we can simulate the theoreti ...
OM1 - Faculty of Engineering
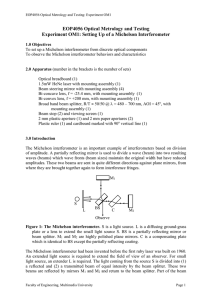
... reflected by the beam splitter. Thus, the two beams are brought together to form interference fringes. Since one beam passes through BS 3 times, a compensating plate C is required for another beam so that both beams pass through equal thickness of glass. The inclusion of a compensating plate negates ...
... reflected by the beam splitter. Thus, the two beams are brought together to form interference fringes. Since one beam passes through BS 3 times, a compensating plate C is required for another beam so that both beams pass through equal thickness of glass. The inclusion of a compensating plate negates ...
Synopsis by Lori Moore
... edges and is not infinite in extent there are error introduced into the PSD. This becomes less of a problem as the spatial frequency increases for a particular measurement. For the higher spatial frequencies the relative size of the measurement window is larger than for the lower spatial frequencies ...
... edges and is not infinite in extent there are error introduced into the PSD. This becomes less of a problem as the spatial frequency increases for a particular measurement. For the higher spatial frequencies the relative size of the measurement window is larger than for the lower spatial frequencies ...
Measurement and analysis of angle-resolved scatter
... the angular-scatter measurement of particles in which scatter from the flow channel is less than the detection limit of the sensors. This also allows us to ignore the interactive scatter– electromagnetic coupling due to multiple reflections of the scatter from particles in the channel. Also to be ex ...
... the angular-scatter measurement of particles in which scatter from the flow channel is less than the detection limit of the sensors. This also allows us to ignore the interactive scatter– electromagnetic coupling due to multiple reflections of the scatter from particles in the channel. Also to be ex ...
supporting material
... number of photons within the ROI near the center of the bead) in each image was less than 1,000 photons. The size of the ROI used to measure signal was selected so that it was large enough to accurately sample the signal yet small enough to minimize changes in intensity due to the spherical geometry ...
... number of photons within the ROI near the center of the bead) in each image was less than 1,000 photons. The size of the ROI used to measure signal was selected so that it was large enough to accurately sample the signal yet small enough to minimize changes in intensity due to the spherical geometry ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.