
Chemistry Final Exam Review 2013
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
... 1. Which idea of John Dalton is no longer considered part of the modern view of atoms? a. Atoms are extremely small. b. Atoms of the same element have identical masses. c. Atoms combine in simple whole number ratios to form compounds. d. Atoms of different elements can combine in different ratios to ...
3er LUGAR, CATEGORÍA MAYOR INGLÉS XVII Certamen Nacional
... reliant on quantum physics and it solves the problem of light being a wave or a particle dilemma considering it as neither of them but instead as photons that have both wave-like and particle-like properties. This is still a new field for physicists to study and the most of its applications are s ...
... reliant on quantum physics and it solves the problem of light being a wave or a particle dilemma considering it as neither of them but instead as photons that have both wave-like and particle-like properties. This is still a new field for physicists to study and the most of its applications are s ...
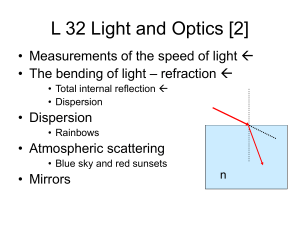
L32
... Refraction the bending of light • One consequence of the fact that light travels more slowly in say water compared to air is that a light ray must bend when it enters water this is called refraction • the amount of refraction (bending) that occurs depends on how large the index of refraction (n) ...
... Refraction the bending of light • One consequence of the fact that light travels more slowly in say water compared to air is that a light ray must bend when it enters water this is called refraction • the amount of refraction (bending) that occurs depends on how large the index of refraction (n) ...
124-07_Reflection_and_Refraction
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
... This laboratory is to show that the very simple principles of reflection and refraction can lead to sophisticated ideas about optical instrument. We begin with a ray box that has a slotted mask in front of a light bulb to produce a set of thin beams (or "rays"). The rays lie along a plane surface (a ...
Light, Light Bulbs and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
... waves of 400 nm wavelength cause us to see violet and we see 700 nm wavelength electromagnetic waves as red. In between are wavelengths corresponding to all the colours of the rainbow or visible spectrum: indigo, blue, green, yellow and orange. Sunlight is a continuous spectrum of all these visible ...
... waves of 400 nm wavelength cause us to see violet and we see 700 nm wavelength electromagnetic waves as red. In between are wavelengths corresponding to all the colours of the rainbow or visible spectrum: indigo, blue, green, yellow and orange. Sunlight is a continuous spectrum of all these visible ...
Chemistry 201/211 - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... low temperature and high pressure low temperature and low pressure high temperature and high pressure high temperature and low pressure ...
... low temperature and high pressure low temperature and low pressure high temperature and high pressure high temperature and low pressure ...
Physics 280/Jones Week 02 In-Class Problems Fall 2014 1
... the plates is off when light strikes one plate and liberates an electron, but before the electron reaches the second plate, the voltage is increased to stopping potential so that the electron slows down, comes to a stop, and then accelerates back towards the plate, impacting the plate with the same ...
... the plates is off when light strikes one plate and liberates an electron, but before the electron reaches the second plate, the voltage is increased to stopping potential so that the electron slows down, comes to a stop, and then accelerates back towards the plate, impacting the plate with the same ...
Red Tide Specifications
... Specify standard or SAG+. Light enters the spectrometer, passes through the SMA Connector, Slit, and Filter, and then reflects off the Collimating Mirror onto the Grating. Diffracts light from the Collimating Mirror and directs the diffracted light onto the ...
... Specify standard or SAG+. Light enters the spectrometer, passes through the SMA Connector, Slit, and Filter, and then reflects off the Collimating Mirror onto the Grating. Diffracts light from the Collimating Mirror and directs the diffracted light onto the ...
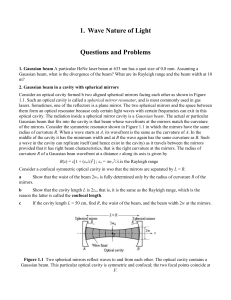
1. Wave Nature of Light
... 1. Gaussian beam A particular HeNe laser beam at 633 nm has a spot size of 0.8 mm. Assuming a Gaussian beam, what is the divergence of the beam? What are its Rayleigh range and the beam width at 10 m? 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned ...
... 1. Gaussian beam A particular HeNe laser beam at 633 nm has a spot size of 0.8 mm. Assuming a Gaussian beam, what is the divergence of the beam? What are its Rayleigh range and the beam width at 10 m? 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned ...
Compact Beam Steering
... enabled us to assess system performance in terms of optical transmission, tracking bandwidth, Size, Weight and Power (SWaP) and steering accuracy. Due to the success of the sing-wavelength breadboard system, in Phase II we were able to move on to an achromatic Risley prism beam steering design. When ...
... enabled us to assess system performance in terms of optical transmission, tracking bandwidth, Size, Weight and Power (SWaP) and steering accuracy. Due to the success of the sing-wavelength breadboard system, in Phase II we were able to move on to an achromatic Risley prism beam steering design. When ...
key - nuclear physic..
... iii. On the figure above, sketch the approximate paths of both these rays as they pass through the glass and back out into the vacuum. Ignore any reflected light. Clearly show the change in direction of the rays, if any, at each surface and be sure to distinguish carefully any differences between th ...
... iii. On the figure above, sketch the approximate paths of both these rays as they pass through the glass and back out into the vacuum. Ignore any reflected light. Clearly show the change in direction of the rays, if any, at each surface and be sure to distinguish carefully any differences between th ...
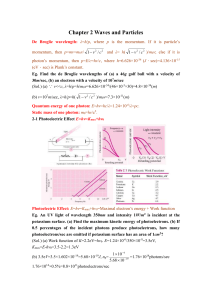
Chapter 2 Waves and Particles De Broglie wavelength: λ=h/p, where
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
... Eg. An UV light of wavelength 350nm and intensity 1W/m2 is incident at the potassium surface. (a) Find the maximum kinetic energy of photoelectrons. (b) If 0.5 percentages of the incident photons produce photoelectrons, how many photoelectrons/sec are emitted if potassium surface has an area of 1cm2 ...
L 35 Modern Physics [1]
... classical explanation According to classical physics, if the intensity of the light is strong enough, enough energy should be absorbed by the electrons to make them pop out The wavelength of the light should not make a difference. ...
... classical explanation According to classical physics, if the intensity of the light is strong enough, enough energy should be absorbed by the electrons to make them pop out The wavelength of the light should not make a difference. ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.


















![L 35 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001036078_1-1a4f17b9367db590f7dcb987ef21bbe6-300x300.png)

