* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ppt - University Of Oregon
Optical rogue waves wikipedia , lookup
Vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Spectral density wikipedia , lookup
Atomic absorption spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Terahertz metamaterial wikipedia , lookup
Photoacoustic effect wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Mössbauer spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
X-ray fluorescence wikipedia , lookup
Electron paramagnetic resonance wikipedia , lookup
Ultrafast laser spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
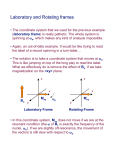
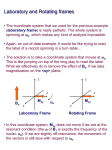
Sarah Newton University of Oregon Applied Physics Background Many applications in Chemistry and Medicine 1940's- First Signs of NMR Bloch, Purcell, and others noticed the H nuclei had magnetic properties. It could absorb RF energy when placed in a field of a strength specific to the identity of the nuclei. When absorption occurs, the nucleus is described as being in resonance. Objectives Simulate different circuits to give the best resonance Develop a detector Built within constraints: Resonance no higher than 13MHz. See CW See Pulsed Compare and analyze their similarities and differences Connection to Optics NMR and Optical Pumping have the same basic concept Optical Pumping It is a two level system that electronically excites the constituents of a medium into another energy state. i.e. Laser What is NMR? Type of Spectroscopy that manipulated the magnetic properties of nuclei within a sample That manipulation leads to finding the chemical properties and environment contained within the sample. CW/Pulsed NMR CW(Continuous Wave) NMR Experiments have a varying frequency of radiation at constant magnetic field and measuring the absorption of radiation by the different nuclei. Pulsed(Fourier Transform) NMR Resonances are not measured one after another but all nuclei are excited at the same time by a radio frequency pulse. Excited spins emit the absorbed radiation after the pulse. Intensities of several frequencies are calculated and framed into spectrum. Circuit Sim Sims Graph Circuit Methodology Magnet is powered up Sample lowered into quartz vial (connected to the circuit.) RF gain(from radio receiver) increased to max Capacitor dials on bridge circuit turned to minimize RF gain Amps of DC power supply adjusted until a signal becomes visible on the oscilloscope. The small function generator provides a “wobble” on the coils while the older generator is the driving unit Intrumentation Results (What Should have happened) In the CW -fixed frequency and varying current -Able to observe the resonant signal (“wiggle”) individual frequencies in succession In pulsed -A short pulse containing a range of frequencies -All nuclei spins are excited( with a range of frequencies) -Induces a current creating an electrical signal response at Conclusion/Summary Success!!! Circuit works and is fully functional But.. Due to the strange disappearance and reappearance of resonance at different frequencies we will go back to the drawing board. Future Work Simulations Build a better circuit Run both CW and Pulse NMR Acknowledgements Material Science Institute Stephen Gregory and Brian Boggs