Self-Organization of Atomic Samples in Resonators and Collective Light Forces.
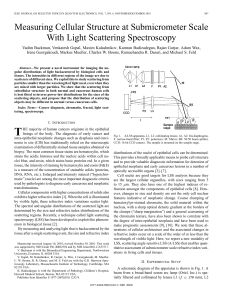
... If the observed force is to be used, e.g., for the slowing of new species at large detuning, the experimentally critical parameter is not the force magnitude, that can be very large due to the stimulated nature of the emission process, but the necessary intensity to reach threshold at the given part ...
... If the observed force is to be used, e.g., for the slowing of new species at large detuning, the experimentally critical parameter is not the force magnitude, that can be very large due to the stimulated nature of the emission process, but the necessary intensity to reach threshold at the given part ...
PS 20: Final Exam Review
... 5. A photon of blue light has 9.2 eV of energy. What is the frequency of the light? 6. Green light has a wavelength of 500 nm, how much energy is in one photon of the light. 7. Calculate the absolute refractive index for a clear plastic material, if the velocity of light in the plastic is 2.2 x 108 ...
... 5. A photon of blue light has 9.2 eV of energy. What is the frequency of the light? 6. Green light has a wavelength of 500 nm, how much energy is in one photon of the light. 7. Calculate the absolute refractive index for a clear plastic material, if the velocity of light in the plastic is 2.2 x 108 ...
1 Optical Phenomena
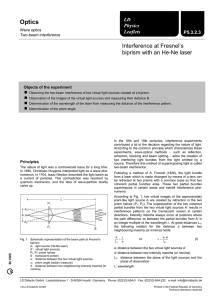
... substance is dependant on the wavelength of the light going through that substance. For example, blue light, with a shorter wavelength, bends more than red light when passing into a refracting material. The process of separating polychromatic light into its components is called dispersion. When w ...
... substance is dependant on the wavelength of the light going through that substance. For example, blue light, with a shorter wavelength, bends more than red light when passing into a refracting material. The process of separating polychromatic light into its components is called dispersion. When w ...
Chip Scale Light Deflector Enables Solid
... cientists have used the rapid deflection of beams to provide a record of events at many time scales. Conventional, electron-based streak cameras represent the fastest embodiment of this concept, but they are limited by spacecharge effects that blur the focused beam when high signal amplitudes are pr ...
... cientists have used the rapid deflection of beams to provide a record of events at many time scales. Conventional, electron-based streak cameras represent the fastest embodiment of this concept, but they are limited by spacecharge effects that blur the focused beam when high signal amplitudes are pr ...
che-20028 QC lecture 1 - Rob Jackson`s Website
... How the experiment is performed • Using a variable frequency light source, shine light onto a metal surface. • Determine the light frequency which causes electrons to be emitted. • Measure the energy of the emitted electrons, by applying a voltage across the cell in the opposite direction to balanc ...
... How the experiment is performed • Using a variable frequency light source, shine light onto a metal surface. • Determine the light frequency which causes electrons to be emitted. • Measure the energy of the emitted electrons, by applying a voltage across the cell in the opposite direction to balanc ...
Aalborg Universitet
... effects imply that the reflectivity spectra for vanishingly small gap widths δ would still feature resonant oscillations somewhat similar to those obtained for non-zero gap widths δ, but with significantly damped oscillation amplitudes. Finally, it should be mentioned that the 2D simulations describ ...
... effects imply that the reflectivity spectra for vanishingly small gap widths δ would still feature resonant oscillations somewhat similar to those obtained for non-zero gap widths δ, but with significantly damped oscillation amplitudes. Finally, it should be mentioned that the 2D simulations describ ...
Ch1 Mod Review.WXP
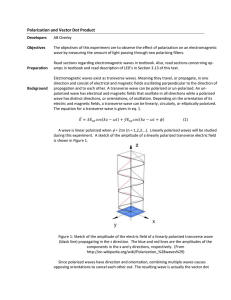
... photons as they reach the slits, and that the presence of two slits gives rise to the interference pattern. However, if the intensity of light is low enough so that only one photon approaches the opaque screen at a time, we still get the same results! 2. Light polarization. Consider light incident u ...
... photons as they reach the slits, and that the presence of two slits gives rise to the interference pattern. However, if the intensity of light is low enough so that only one photon approaches the opaque screen at a time, we still get the same results! 2. Light polarization. Consider light incident u ...
ATR Accessories: An Overview
... a zinc selenide focusing element which is in direct contact with the diamond. The focusing element provides interfacing optics for the IR radiation into the diamond crystal. Both components of the DiComp ATR work over the spectral range of interest for the majority of applications and have similar r ...
... a zinc selenide focusing element which is in direct contact with the diamond. The focusing element provides interfacing optics for the IR radiation into the diamond crystal. Both components of the DiComp ATR work over the spectral range of interest for the majority of applications and have similar r ...
Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
... are oscillating perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. The cross product E B always gives the direction in which the wave travels. • Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or a material substance. • All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, an ...
... are oscillating perpendicular to the direction in which the wave travels. The cross product E B always gives the direction in which the wave travels. • Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or a material substance. • All electromagnetic waves move through a vacuum at the same speed, an ...
CHAPTER 15. LASER AND FIBER OPTICS The laser is essentially
... parameters. It is a small effect that becomes important only when the other pulsebroadening effects have been essentially eliminated. The waveguide dispersion results from the dependence of the field distribution in the fiber on the ratio between the core radius and the wavelength. If this ratio is ...
... parameters. It is a small effect that becomes important only when the other pulsebroadening effects have been essentially eliminated. The waveguide dispersion results from the dependence of the field distribution in the fiber on the ratio between the core radius and the wavelength. If this ratio is ...
Unit 9, Section 2B - % Comp and Colligative Prop
... which the vapor pressure escaping from a liquid exceeds atmospheric pressure pushing down on the surface of the liquid – The boiling point of a liquid increases when molecules of a solute are added – surface blocked by molecules of solute ...
... which the vapor pressure escaping from a liquid exceeds atmospheric pressure pushing down on the surface of the liquid – The boiling point of a liquid increases when molecules of a solute are added – surface blocked by molecules of solute ...
Algebra-based Physics II
... FACT: All objects are continuously absorbing and emitting radiation. When light (or any EM radiation) falls on an opaque body, part of it is reflected, and part of it is absorbed. Light-colored bodies reflect most of the radiation incident on them. Dark-colored bodies absorb most of the radiation in ...
... FACT: All objects are continuously absorbing and emitting radiation. When light (or any EM radiation) falls on an opaque body, part of it is reflected, and part of it is absorbed. Light-colored bodies reflect most of the radiation incident on them. Dark-colored bodies absorb most of the radiation in ...
Circular Dichroism (CD) and Optical Rotatory Dispersion (ORD
... -In ORD, the dispersive peak is quite spread out – if two bands are close to each other then it is difficult to distinguish them. ...
... -In ORD, the dispersive peak is quite spread out – if two bands are close to each other then it is difficult to distinguish them. ...
Laboratory 2 Thomas Young and the Wave
... in your experiment, L is the total distance from slit-to-mirror-to-image. CAUTION: Do not look into the laser beam or even at a directly reflected beam. Laser light is very intense and can damage your eyes more than you think. Handle optical devices in such a way that your fingers do not touch the o ...
... in your experiment, L is the total distance from slit-to-mirror-to-image. CAUTION: Do not look into the laser beam or even at a directly reflected beam. Laser light is very intense and can damage your eyes more than you think. Handle optical devices in such a way that your fingers do not touch the o ...
Bessel Beam Theory - u.arizona.edu
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
... Diffraction is a feature of the wave nature of light. It can occur anytime a beam of light passes through an aperture that is large with respect to its wavelength1. According to the Huygens-Fresnel Principle2, every point of the wavefront that is unobstructed by the hindrance serves as a source of s ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.