CHEM 210 Chapter 5 Wrap-up
... Optical Activity • The property possessed by chiral substances of rotating the plane of polarization of planepolarized light • The electric field (like the magnetic field) of light is oscillating in all possible planes • When this light passes through a polarizer (Polaroid lens), we get plane-polar ...
... Optical Activity • The property possessed by chiral substances of rotating the plane of polarization of planepolarized light • The electric field (like the magnetic field) of light is oscillating in all possible planes • When this light passes through a polarizer (Polaroid lens), we get plane-polar ...
one way
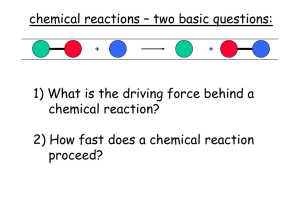
... Chemical kinetics how fast are chemical reactions? v = velocity of a chemical reaction The velocity of a given chemical reaction generally depends on three parameters: - the concentration of the educts - the temperature - the presence or the absence of a catalyst ...
... Chemical kinetics how fast are chemical reactions? v = velocity of a chemical reaction The velocity of a given chemical reaction generally depends on three parameters: - the concentration of the educts - the temperature - the presence or the absence of a catalyst ...
幻灯片 1
... To understand how fluorescence can be used to enhance an image we need to discuss the structure of an atom. Schrödinger's wave equation is used to describe the possible electron waves that can exist inside the Coulomb field of the atom, not unlike the allowed vibrations for an harmonic oscillator. E ...
... To understand how fluorescence can be used to enhance an image we need to discuss the structure of an atom. Schrödinger's wave equation is used to describe the possible electron waves that can exist inside the Coulomb field of the atom, not unlike the allowed vibrations for an harmonic oscillator. E ...
secon harmonic generation
... From your data of IV.C, plot the magnitude of the SHG signal versus input power. Fit the data to a power law, ie. PSHG A PIR m where A is a constant. Determine the exponent m. Plot your data and fit on the same plot. From the theory we worked on in class, show that you expect that m=2. HINT: the ...
... From your data of IV.C, plot the magnitude of the SHG signal versus input power. Fit the data to a power law, ie. PSHG A PIR m where A is a constant. Determine the exponent m. Plot your data and fit on the same plot. From the theory we worked on in class, show that you expect that m=2. HINT: the ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... using deionised water and boiled with 150ml of deionised water for 10 min and the extract was filtered and used for further experiments. In a conical flask 0.5ml of 0.01M HAucl 4 is is dissolved in 20ml of deionised water, then drop wise green tea extract is added with stirring on a magnetic stirrer ...
... using deionised water and boiled with 150ml of deionised water for 10 min and the extract was filtered and used for further experiments. In a conical flask 0.5ml of 0.01M HAucl 4 is is dissolved in 20ml of deionised water, then drop wise green tea extract is added with stirring on a magnetic stirrer ...
Supporting Information - Royal Society of Chemistry
... Conductivity: The measured conductance C (S) was introduced in eq S1 to obtain conductivity χ (S cm–1) using the factory provided cell constant k. The obtained conductivities, χ, were converted to molar conductivities (Λ = χ/[SDS]) and plotted versus the square root of SDS concentration (Figure S1), ...
... Conductivity: The measured conductance C (S) was introduced in eq S1 to obtain conductivity χ (S cm–1) using the factory provided cell constant k. The obtained conductivities, χ, were converted to molar conductivities (Λ = χ/[SDS]) and plotted versus the square root of SDS concentration (Figure S1), ...
Experimental Techniques of Optics PHYC 476,477, 302L Instructor:
... You will be asked to sign an "agreement of understanding" form on the first session of this course. ...
... You will be asked to sign an "agreement of understanding" form on the first session of this course. ...
Module 27: Polarization-II Lecture 27: Polarization-II
... no when E is perpendicular to the x axis. Here the x axis is referred to as the optic axis. The optical properties are the same in all directions perpendicular ~ is along the optic axis. Crystals may to the optic axis and it is different if E have more than one optic axis. Here we only consider a si ...
... no when E is perpendicular to the x axis. Here the x axis is referred to as the optic axis. The optical properties are the same in all directions perpendicular ~ is along the optic axis. Crystals may to the optic axis and it is different if E have more than one optic axis. Here we only consider a si ...
Review - misshoughton.net
... Types of Light Emissions Fluorescence Types of Luminescence Electromagnetic Spectrum 2. Properties of Light and Reflection Fermat’s Principle Laws of Reflection Ray diagrams Drawing ray diagrams using plane mirrors 3. Concave Mirrors & Convex Mirrors Properties Drawing ray diagra ...
... Types of Light Emissions Fluorescence Types of Luminescence Electromagnetic Spectrum 2. Properties of Light and Reflection Fermat’s Principle Laws of Reflection Ray diagrams Drawing ray diagrams using plane mirrors 3. Concave Mirrors & Convex Mirrors Properties Drawing ray diagra ...
INFRA-RED OPTICAL COMMUNICATION SYSTEMS*
... density. A ruby laser was used by American scientists to project a beam of light from Earth to Moon(l) using a 30 cm telescope in the transmitter and, despite the diffusing nature of the Moon’s surface, the return signal was successfully picked up and detected using a 120 cm telescope in the receive ...
... density. A ruby laser was used by American scientists to project a beam of light from Earth to Moon(l) using a 30 cm telescope in the transmitter and, despite the diffusing nature of the Moon’s surface, the return signal was successfully picked up and detected using a 120 cm telescope in the receive ...
LOC07b Photoelectric Effect Part 2: The Einstein Equation
... Plug in the mercury lamp. It will take a few seconds for it to warm up. The window through which the light enters is covered by filters that only allow certain colors of light to pass. The filters are chosen to coincide with strong emission lines from mercury. The four wavelengths chosen are 390 nm, ...
... Plug in the mercury lamp. It will take a few seconds for it to warm up. The window through which the light enters is covered by filters that only allow certain colors of light to pass. The filters are chosen to coincide with strong emission lines from mercury. The four wavelengths chosen are 390 nm, ...
1/16/2015 Photoelectric Effect Part II The Einstein Equation
... Plug in the mercury lamp. It will take a few seconds for it to warm up. The window through which the light enters is covered by filters that only allow certain colors of light to pass. The filters are chosen to coincide with strong emission lines from mercury. The four wavelengths chosen are 390 nm, ...
... Plug in the mercury lamp. It will take a few seconds for it to warm up. The window through which the light enters is covered by filters that only allow certain colors of light to pass. The filters are chosen to coincide with strong emission lines from mercury. The four wavelengths chosen are 390 nm, ...
Optimizing Fluorescence Signal Quality
... Increasing Excitation Light Intensity An object should already be placed in the microscope. This object need not be fluorescent or biological; lens paper for example may work fine. All or some of the following excitation hardware should be adjusted to maximize illumination while minimizing backgro ...
... Increasing Excitation Light Intensity An object should already be placed in the microscope. This object need not be fluorescent or biological; lens paper for example may work fine. All or some of the following excitation hardware should be adjusted to maximize illumination while minimizing backgro ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.