in the sentence
... 10. Use commas to set off one or more words that interrupt the flow of a sentence. Lebron James, as you can see in this video here, dominates all his opponents. 11. Use commas to set off nonessential items: clauses, ...
... 10. Use commas to set off one or more words that interrupt the flow of a sentence. Lebron James, as you can see in this video here, dominates all his opponents. 11. Use commas to set off nonessential items: clauses, ...
rules-grammar-3-t1
... • A statement is a sentence that tells something. It ends with a period ( . ) • A question is a sentence that asks something. It ends with a question mark ( ? ) • A command is a sentence that tells someone to do something. It ends with a period ( . ) • An exclamation is a sentence that shows strong ...
... • A statement is a sentence that tells something. It ends with a period ( . ) • A question is a sentence that asks something. It ends with a question mark ( ? ) • A command is a sentence that tells someone to do something. It ends with a period ( . ) • An exclamation is a sentence that shows strong ...
How to Attack the Writing Component Part 3: Multiple Choice
... • This sentence is tough because it has two singular subjects (ambient techno and trance), but with neither and nor in the mix, they don’t add up to a plural subject. The verb should be was. • Note: If the nouns in a neither…nor or either…or sentence are plural on their own, then the verb should be ...
... • This sentence is tough because it has two singular subjects (ambient techno and trance), but with neither and nor in the mix, they don’t add up to a plural subject. The verb should be was. • Note: If the nouns in a neither…nor or either…or sentence are plural on their own, then the verb should be ...
WRITING STYLE ADVICE FOR PROPOSALS
... literature shows; the results indicate; the data suggest. wordy -The main cause of these problems stems from . . . -This approach can result in the understanding of how to . . . ...
... literature shows; the results indicate; the data suggest. wordy -The main cause of these problems stems from . . . -This approach can result in the understanding of how to . . . ...
C. Exam Questions, Grades and Time Allocated for Each Question
... Choose the most appropriate alternative and mark your choice on the attached ANSWER SHEET. (20 pts) 1. The study of the language system at a particular time in its history represents a ……………. approach. a. synchronic b. diachronic c. psycholinguistic d. sociolinguistic 2. The mutually intelligible fo ...
... Choose the most appropriate alternative and mark your choice on the attached ANSWER SHEET. (20 pts) 1. The study of the language system at a particular time in its history represents a ……………. approach. a. synchronic b. diachronic c. psycholinguistic d. sociolinguistic 2. The mutually intelligible fo ...
Parts of Speech The parts of speech are the eight different kinds of
... An adverb describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often or how much. Examples: She sneezed loudly. Her sneezes are really dramatic. The sneeze exploded very noisily. A preposition is a word (or group of words) that shows a relationshi ...
... An adverb describes or modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. An adverb tells how, when, where, why, how often or how much. Examples: She sneezed loudly. Her sneezes are really dramatic. The sneeze exploded very noisily. A preposition is a word (or group of words) that shows a relationshi ...
Independent Clauses in Compound Sentences
... in Compound Sentences Definitions Independent Clause: An independent clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb, ...
... in Compound Sentences Definitions Independent Clause: An independent clause is a group of words that contains a subject and verb, ...
12th grade grammar review
... A Pronoun is a substitute for a noun. It refers to a person, place, thing, feeling, or quality but does not refer to it by its name. An antecedent is the word, phrase, or clause to which a pronoun refers, understood by the context. ...
... A Pronoun is a substitute for a noun. It refers to a person, place, thing, feeling, or quality but does not refer to it by its name. An antecedent is the word, phrase, or clause to which a pronoun refers, understood by the context. ...
Exam Review 2007-2008 When given a sentence, identify the parts
... Example: The ghost of Mr. Ofster appears in the hall every morning and terrorizes the students. This is a simple sentence because it consists of a single independent clause or complete thought. It can have more than one subject, and more than one verb and still be a simple sentence. Example: Most of ...
... Example: The ghost of Mr. Ofster appears in the hall every morning and terrorizes the students. This is a simple sentence because it consists of a single independent clause or complete thought. It can have more than one subject, and more than one verb and still be a simple sentence. Example: Most of ...
Q1 Parts of Speech Review
... 4. Some have blue tags, other have red tags. 5. Nothing can be done about the misplaced invitation. 6. Anyone can go to the amusement park. 7. Several swam downstream into the lake. ...
... 4. Some have blue tags, other have red tags. 5. Nothing can be done about the misplaced invitation. 6. Anyone can go to the amusement park. 7. Several swam downstream into the lake. ...
File
... 1. Prepositional Phrases: A prepositional phrase must start with a preposition and end with a noun, which is the object of the preposition. You should have labeled all prepositions during step 1. Ex: Alex ran into the school and grabbed his bag. 2. Appositive Phrases: An appositive is a noun that ...
... 1. Prepositional Phrases: A prepositional phrase must start with a preposition and end with a noun, which is the object of the preposition. You should have labeled all prepositions during step 1. Ex: Alex ran into the school and grabbed his bag. 2. Appositive Phrases: An appositive is a noun that ...
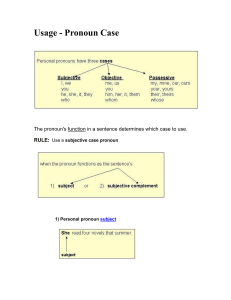
Usage - Pronoun Case
... that would be correct if the pronoun were not part of a compound element. ...
... that would be correct if the pronoun were not part of a compound element. ...
PRONOUNS
... INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS Interrogative pronouns introduce questions. They are what, which, who, whom, and whose ex. What is the best brand of yogurt? **Who or Whom** Who-nominative case for subject and predicate nominative Whom-objective case for direct object, object of the preposition, and indirect ...
... INTERROGATIVE PRONOUNS Interrogative pronouns introduce questions. They are what, which, who, whom, and whose ex. What is the best brand of yogurt? **Who or Whom** Who-nominative case for subject and predicate nominative Whom-objective case for direct object, object of the preposition, and indirect ...
Grammar units 1 and 2 guided notes
... o Incorrect: I knew, down in my heart that Taylor Swift was awesome. o Incorrect: I knew down in my heart, that Taylor Swift was awesome. o Not technically incorrect but can be unclear: I knew down in my heart that Taylor Swift was awesome. o You need both commas to fully form the parenthetical. o A ...
... o Incorrect: I knew, down in my heart that Taylor Swift was awesome. o Incorrect: I knew down in my heart, that Taylor Swift was awesome. o Not technically incorrect but can be unclear: I knew down in my heart that Taylor Swift was awesome. o You need both commas to fully form the parenthetical. o A ...
pronoun handout with notes
... ‘It’ is a necessary pronoun in many instances. However, problems with the word “it” occur when the writer uses the word in an indefinite way. In the following examples, try to find the antecedent to ‘it.’ a) In the article it says that more women than men die of heart disease. b) It is clear that Wi ...
... ‘It’ is a necessary pronoun in many instances. However, problems with the word “it” occur when the writer uses the word in an indefinite way. In the following examples, try to find the antecedent to ‘it.’ a) In the article it says that more women than men die of heart disease. b) It is clear that Wi ...
copy editing quiz - Glenna Collett Design
... In this sentence, the phrase “fixes dates” applies to both primaries and holding conventions and should be preceded by “and.” When “and” is added, there is no need for a comma to precede it. The sentence has a single subject and two predicates. It hears appeals from local committees and fixes dates ...
... In this sentence, the phrase “fixes dates” applies to both primaries and holding conventions and should be preceded by “and.” When “and” is added, there is no need for a comma to precede it. The sentence has a single subject and two predicates. It hears appeals from local committees and fixes dates ...
The Seven Deadly Sins of Writing
... It is often better to use a plural noun and pronoun than to use a singular noun and pronoun. Note that indefinite pronouns such as each and everyone are singular. Examples: Each student must meet his or her advisor. (correct but awkward) Each student must meet with their advisor. (incorrect: singula ...
... It is often better to use a plural noun and pronoun than to use a singular noun and pronoun. Note that indefinite pronouns such as each and everyone are singular. Examples: Each student must meet his or her advisor. (correct but awkward) Each student must meet with their advisor. (incorrect: singula ...
See p. 69
... Underline the correct word in parentheses. (See p. 159; 257) 1. Gertrude Ederle is in the record books for (women’s, womens’) sports. 2. One of (Ederles’, Ederle’s) major accomplishments was being the first woman to swim the English Channel on August 6, 1926. 3. Several (newspaper’s, newspapers’) he ...
... Underline the correct word in parentheses. (See p. 159; 257) 1. Gertrude Ederle is in the record books for (women’s, womens’) sports. 2. One of (Ederles’, Ederle’s) major accomplishments was being the first woman to swim the English Channel on August 6, 1926. 3. Several (newspaper’s, newspapers’) he ...
Common Writing Errors Workshop
... 1. _____ SPELLING/HOMOPHONES/COMMONLY CONFUSED WORDS drive English teachers muy loco. Use the correct spelling of words, use spell checkers carefully, and use the words in the correct way. Spelling should not be an issue in high school. 2. _____ CAPITALIZATION. Capitals are needed at the beginning o ...
... 1. _____ SPELLING/HOMOPHONES/COMMONLY CONFUSED WORDS drive English teachers muy loco. Use the correct spelling of words, use spell checkers carefully, and use the words in the correct way. Spelling should not be an issue in high school. 2. _____ CAPITALIZATION. Capitals are needed at the beginning o ...
Skill 1: Appositive Phrase
... Instead there was a button that did it for you. Those who don't know any better come into neighborhood scared. Skill 6: Adverb Clause (or Subordinate Clause) The adverb clause tells more about the sentence in which it appears. Like the adjective clause, the adverb clause is a dependent clause that c ...
... Instead there was a button that did it for you. Those who don't know any better come into neighborhood scared. Skill 6: Adverb Clause (or Subordinate Clause) The adverb clause tells more about the sentence in which it appears. Like the adjective clause, the adverb clause is a dependent clause that c ...
Sentence Fragments - San Jose State University
... being used to show linkages between sentences. 1. Because there are few standards regulating the trading of energy futures. 2. Though he doesn't know how to operate that piece of machinery. ✓ Use a conjunctive adverb (e.g. however, therefore, also) to link two separate ...
... being used to show linkages between sentences. 1. Because there are few standards regulating the trading of energy futures. 2. Though he doesn't know how to operate that piece of machinery. ✓ Use a conjunctive adverb (e.g. however, therefore, also) to link two separate ...
Pronouns
... interrogative, demonstrative, indefinite, and relative. In order for a sentence to work, the pronoun must clearly refer to the antecedent – the noun that it replaces. The pronoun and antecedent must agree in number with the noun or phrase it references. Therefore, if a noun or pronoun is singular or ...
... interrogative, demonstrative, indefinite, and relative. In order for a sentence to work, the pronoun must clearly refer to the antecedent – the noun that it replaces. The pronoun and antecedent must agree in number with the noun or phrase it references. Therefore, if a noun or pronoun is singular or ...