Lecture 22- Meninges-2013
... delicate & highly vascular membrane that is closely adherent to the gyri and fitted into the sulci. Between the pia and arachnoid mater lies the subarachnoid space which contains; fibrous trabechulae, main blood vessels and CSF. ...
... delicate & highly vascular membrane that is closely adherent to the gyri and fitted into the sulci. Between the pia and arachnoid mater lies the subarachnoid space which contains; fibrous trabechulae, main blood vessels and CSF. ...
The Nervous System
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
The Nervous System
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
Meninges ventricles and CSF
... containing little protein and few cells. It is about 150 ml. It acts as a cushion for the brain from sudden movements of the head. ...
... containing little protein and few cells. It is about 150 ml. It acts as a cushion for the brain from sudden movements of the head. ...
Linea alba conus medullaris: a stable anatomical
... which becomes smaller across its course in the lumbar subdural space. The greater part, 15 cm in length, is free in the subdural space and the last 5 cm are enclosed in the filum durae mater spinalis, which leave the sacral canal through the sacral foramen to adhere the periost of the second lumbar ...
... which becomes smaller across its course in the lumbar subdural space. The greater part, 15 cm in length, is free in the subdural space and the last 5 cm are enclosed in the filum durae mater spinalis, which leave the sacral canal through the sacral foramen to adhere the periost of the second lumbar ...
Spinal cord, plexuses, reflexes, tracts
... • Step on tack (pain fibers send signal to spinal cord • Interneurons branch to different spinal cord segments • Motor fibers in several segments are activated • More than one muscle group activated to lift foot off of tack ...
... • Step on tack (pain fibers send signal to spinal cord • Interneurons branch to different spinal cord segments • Motor fibers in several segments are activated • More than one muscle group activated to lift foot off of tack ...
The Regional Anatomy of the Upper limb
... Medially---the pronator teres; Speriorly--- the base An imaginary line between the two humeral epicondyles. The contents---- from the lateral to medial sides radial n. , lateral antebrachial cutaneous n. , tendon of biceps brachii, terminal part of brachial a. and vein, median n. few deep cubital ...
... Medially---the pronator teres; Speriorly--- the base An imaginary line between the two humeral epicondyles. The contents---- from the lateral to medial sides radial n. , lateral antebrachial cutaneous n. , tendon of biceps brachii, terminal part of brachial a. and vein, median n. few deep cubital ...
BDS Ist YEAR EXAMINATION 2008-09
... Which of the following statements is incorrect for lateral meniscus of knee? ...
... Which of the following statements is incorrect for lateral meniscus of knee? ...
anterior abdominal wall and inguinal area
... B. soft tissue landmarks: umbilicus, linea alba, linea semilunaris (lateral rectus line), groove of the groin, superficial inguinal ring, inguinal ligament C. abdominal regions 1. planes identifying 9 regions (for convenience 2 horizontal & 2 vertical lines) a. 2 horizontal lines (1) transpyloric pl ...
... B. soft tissue landmarks: umbilicus, linea alba, linea semilunaris (lateral rectus line), groove of the groin, superficial inguinal ring, inguinal ligament C. abdominal regions 1. planes identifying 9 regions (for convenience 2 horizontal & 2 vertical lines) a. 2 horizontal lines (1) transpyloric pl ...
The Nervous System
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
... We are going to watch the first 4 minutes of this video on the Brachial Plexus. You are not expected to memorize the details of each of the plexuses. However, it is important to understand the general structure of a plexus (roots, trunks, branches, cords, nerves) and how that structure allows most m ...
Major Concepts of Anatomy and Physiology
... Baroreceptors: Pressure-sensitive receptors in the arteries that signal the CV center to control the carotid sinus reflex and the aortic reflex – also regulates the baroreflexes. Chemoreceptors: Sensors in the aorta and the carotid sinus of the brain that detect changes in blood oxygen, carbon dioxi ...
... Baroreceptors: Pressure-sensitive receptors in the arteries that signal the CV center to control the carotid sinus reflex and the aortic reflex – also regulates the baroreflexes. Chemoreceptors: Sensors in the aorta and the carotid sinus of the brain that detect changes in blood oxygen, carbon dioxi ...
The Infracolic Compartment
... I) the artery arises from the ileocolic a. and usually is single. II) the vein drains into the hepatic portal vein. the appendicular v. the ileocolic v. the superior mesenteric v. hepatic portal v. appendicitis the bacterial emboli enter the liver by the course and lead to hepatic abscess. ...
... I) the artery arises from the ileocolic a. and usually is single. II) the vein drains into the hepatic portal vein. the appendicular v. the ileocolic v. the superior mesenteric v. hepatic portal v. appendicitis the bacterial emboli enter the liver by the course and lead to hepatic abscess. ...
Brachial Plexus slides
... To paralyze a muscle completely, it is thus necessary to section several spinal nerves or to destroy several segments of the spinal cord. ...
... To paralyze a muscle completely, it is thus necessary to section several spinal nerves or to destroy several segments of the spinal cord. ...
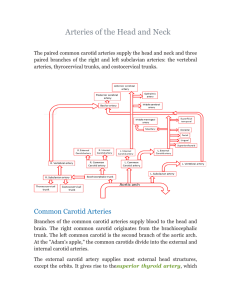
Arteries of the Head and Neck
... Arteries of the Thorax The wall of the thorax is supplied by a collection of arteries, some of which originate directly from the thoracic aorta and others from branches of the subclavian artery. Two bronchial arteries on the left and one on the right deliver systemic blood to the lung structures, in ...
... Arteries of the Thorax The wall of the thorax is supplied by a collection of arteries, some of which originate directly from the thoracic aorta and others from branches of the subclavian artery. Two bronchial arteries on the left and one on the right deliver systemic blood to the lung structures, in ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Manual
... the entrance to the stomach or esophageal area, the cardiac region which is largest, and the pyloric region where the stomach narrows to join to the small intestine. 6. At the end of the stomach, there is a sphincter, or ring-shaped muscle to control food leaving the stomach and entering the duodenu ...
... the entrance to the stomach or esophageal area, the cardiac region which is largest, and the pyloric region where the stomach narrows to join to the small intestine. 6. At the end of the stomach, there is a sphincter, or ring-shaped muscle to control food leaving the stomach and entering the duodenu ...
the reproductive system
... • Functions to support a developing embryo • Undergoes changes according to the menstrual cycle – Menstrual cycle = the monthly cycle as it affects all reproductive organs in preparation for pregnancy ...
... • Functions to support a developing embryo • Undergoes changes according to the menstrual cycle – Menstrual cycle = the monthly cycle as it affects all reproductive organs in preparation for pregnancy ...
File
... Content of the Spermatic Cord The structures are as follows: ■■ Vas deferens ■■ Testicular artery ■■ Testicular veins (pampiniform plexus) ■■ Testicular lymph vessels ■■ Autonomic nerves ■■ Remains of the processus vaginalis ■■ Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, which supplies the cremaste ...
... Content of the Spermatic Cord The structures are as follows: ■■ Vas deferens ■■ Testicular artery ■■ Testicular veins (pampiniform plexus) ■■ Testicular lymph vessels ■■ Autonomic nerves ■■ Remains of the processus vaginalis ■■ Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve, which supplies the cremaste ...
Slide 1
... Seminal receptacles Pharynx Aortic arches Crop Ventral blood vessel Ganglia Setae Carries blood back to the skin and intestines Ventral blood vessel ...
... Seminal receptacles Pharynx Aortic arches Crop Ventral blood vessel Ganglia Setae Carries blood back to the skin and intestines Ventral blood vessel ...
Title Two rare anomalies of the brachial plexus Author(s)
... *College of Nursing, Fukui Prefectural University, Oohatamachi 97-21-3, ...
... *College of Nursing, Fukui Prefectural University, Oohatamachi 97-21-3, ...
가로막, 간, 쓸개
... - The liver has functionally independent right and left parts (portal lobes) that are approximately equal in size. Each part has its own blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein and its own venous and biliary drainage. On the visceral surface, the right (part of the) liver is demarcated ...
... - The liver has functionally independent right and left parts (portal lobes) that are approximately equal in size. Each part has its own blood supply from the hepatic artery and portal vein and its own venous and biliary drainage. On the visceral surface, the right (part of the) liver is demarcated ...
Embryonic Cephalocaudal and Lateral Flexion/Folding
... Pericardioperitoneal canals- openings between the primitive pericardial and peritoneal cavities. Pleuropericardial folds - flaps of body wall at the level of the primitive pericardial cavity. They grow medially and fuse with the ventral surface of the foregut mesoderm. These folds subdivide the prim ...
... Pericardioperitoneal canals- openings between the primitive pericardial and peritoneal cavities. Pleuropericardial folds - flaps of body wall at the level of the primitive pericardial cavity. They grow medially and fuse with the ventral surface of the foregut mesoderm. These folds subdivide the prim ...
A SURGICAL APPROACH TO THE UPPER THORACIC SPINE
... examination revealed a myeloma and he received follow-up radiothera py. There was an excellent neurological recovery with good relief of back pain. ...
... examination revealed a myeloma and he received follow-up radiothera py. There was an excellent neurological recovery with good relief of back pain. ...
Blood Basics 1112
... Average adult=5liters of blood or 7-8% of their body weight. Blood is living tissue that carries oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, and carries carbon dioxide and other waste products back to the lungs, kidneys and liver for disposal. It also fights against infection and helps heal wou ...
... Average adult=5liters of blood or 7-8% of their body weight. Blood is living tissue that carries oxygen and nutrients to all parts of the body, and carries carbon dioxide and other waste products back to the lungs, kidneys and liver for disposal. It also fights against infection and helps heal wou ...
Types of Arteries
... • Fetus must supply blood to the placenta • Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Vessels to and from the Placenta ...
... • Fetus must supply blood to the placenta • Very little blood is sent through the pulmonary circuit Vessels to and from the Placenta ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.