Folding Of Embryo
... Results from rapid growth of the embryo Long axis increases rapidly than the sides Occurs simultaneously on both axis Constriction at the junction of embryo & yolk sac ...
... Results from rapid growth of the embryo Long axis increases rapidly than the sides Occurs simultaneously on both axis Constriction at the junction of embryo & yolk sac ...
File - COFFEE BREAK CORNER
... -‐ medially: go to paraumbilical vein à portal vein -‐ inferiorly: go to superficial epigastric vein à femoral vein ...
... -‐ medially: go to paraumbilical vein à portal vein -‐ inferiorly: go to superficial epigastric vein à femoral vein ...
Unit 2: Vertebral Column, Spinal Cord, Suboccipital Triangle
... and observe that the notches form boundaries of intervertebral foramina. The spinal cord would be located in the vertebral foramen and the spinal nerves would pass through the intervertebral foramina. Compare the size and shape of the vertebral body to those in different regions of the column. The v ...
... and observe that the notches form boundaries of intervertebral foramina. The spinal cord would be located in the vertebral foramen and the spinal nerves would pass through the intervertebral foramina. Compare the size and shape of the vertebral body to those in different regions of the column. The v ...
the y-axis spinal joints and menengeal traction device with
... health profession for hundreds of years. It has been proven to have a positive effect from an anatomical, physiological, and neurological perspective. The purpose of the traction is primarily to open the intervertebral foramina (IVF). These are the small openings between each vertebra of the spine w ...
... health profession for hundreds of years. It has been proven to have a positive effect from an anatomical, physiological, and neurological perspective. The purpose of the traction is primarily to open the intervertebral foramina (IVF). These are the small openings between each vertebra of the spine w ...
Anterior Spinothalamic Tract
... ▪ Medial Group: extends throughout the whole length of spinal cord, supplies axial muscles ▪ Lateral Group: exists in the 2 enlargements, supplies distal muscles ...
... ▪ Medial Group: extends throughout the whole length of spinal cord, supplies axial muscles ▪ Lateral Group: exists in the 2 enlargements, supplies distal muscles ...
BRACHIAL PLEXUS - By Dr Nand Lal Dhomeja ( Anatomy
... • The cords of the brachial plexus derived their names based on their relationship with the 2nd part of the axillary artery • The lateral cord and posterior cord lie – laterally to the 1st part of axillary artery – The medial cord lies posterior to it. • Below the pectoralis minor – the lateral cord ...
... • The cords of the brachial plexus derived their names based on their relationship with the 2nd part of the axillary artery • The lateral cord and posterior cord lie – laterally to the 1st part of axillary artery – The medial cord lies posterior to it. • Below the pectoralis minor – the lateral cord ...
COVENANT UNIVERSITY COLLEGE OF
... The body is long, pointed at both ends and compressed It has a dorsal fin, caudal fin and ventral fin The lateral edges of the body project out as two longitudinal fin-like folds called the metapleural folds Below the anterior end of the body, there is a funnel shaped cavity called the vesti ...
... The body is long, pointed at both ends and compressed It has a dorsal fin, caudal fin and ventral fin The lateral edges of the body project out as two longitudinal fin-like folds called the metapleural folds Below the anterior end of the body, there is a funnel shaped cavity called the vesti ...
Embryology of the heart and the great vessels
... The cardiovacular system is functionally important in development. It starts working when the embryo is between 200 to 400 microns thick. ...
... The cardiovacular system is functionally important in development. It starts working when the embryo is between 200 to 400 microns thick. ...
chapter 13 the spinal cord and spinal nerves
... 1. proprioception, awareness of movements of muscles, tendons, and joints 2. discriminative touch, the ability to feel exactly what part is touched 3. two-point discrimination, the ability to distinguish the touching of two different points on the skin, even though they are close together 4. pressur ...
... 1. proprioception, awareness of movements of muscles, tendons, and joints 2. discriminative touch, the ability to feel exactly what part is touched 3. two-point discrimination, the ability to distinguish the touching of two different points on the skin, even though they are close together 4. pressur ...
17. The meninges of spinal cord and brain. The formation and ways
... the dura mater. It is a thick and tough membrane and contains channels for blood to come into the brain tissue. The one, closest to the brain and spinal cord, is called the pia mater. It is made of delicate ("pia") connective tissue with a rich supply of blood vessels. The finest middle meninges is ...
... the dura mater. It is a thick and tough membrane and contains channels for blood to come into the brain tissue. The one, closest to the brain and spinal cord, is called the pia mater. It is made of delicate ("pia") connective tissue with a rich supply of blood vessels. The finest middle meninges is ...
sciatica-in-depth-anatomy
... inside the spinal canal from the brainstem to the 1st of the 5 lumbar vertebra. At the lower most end of the cord, the fibers separate into the Cauda equina (which means horses tail) and continues down to the tail bone (coccyx). The primary function of the spinal cord is to relay information from th ...
... inside the spinal canal from the brainstem to the 1st of the 5 lumbar vertebra. At the lower most end of the cord, the fibers separate into the Cauda equina (which means horses tail) and continues down to the tail bone (coccyx). The primary function of the spinal cord is to relay information from th ...
Lecture 2. The arterial system Gross anatomy, physiology and
... Tunica Media/intermediate layer is thicker, composed of smooth muscle and connective tissue, largely of the elastic type. Tunica externa/outer layer (adventitia) is somewhat thinner than media, contains fibrous connective tissue: some muscle layers As a rule, the adventitial layer contains the vasa ...
... Tunica Media/intermediate layer is thicker, composed of smooth muscle and connective tissue, largely of the elastic type. Tunica externa/outer layer (adventitia) is somewhat thinner than media, contains fibrous connective tissue: some muscle layers As a rule, the adventitial layer contains the vasa ...
File
... and sacral nerves branch out from the spinal cord and descend inside the spinal column before leaving the vertebral column at their corresponding vertebrae. • Because of this fact there is a difference between the skeletal or bony level of vertebral fracture and the neurological level of spinal cord ...
... and sacral nerves branch out from the spinal cord and descend inside the spinal column before leaving the vertebral column at their corresponding vertebrae. • Because of this fact there is a difference between the skeletal or bony level of vertebral fracture and the neurological level of spinal cord ...
06 General information about the nervous system
... – The filum terminale, a fibrous extension of the pia mater, extends to the posterior surface of the coccyx to anchor the spinal cord. ...
... – The filum terminale, a fibrous extension of the pia mater, extends to the posterior surface of the coccyx to anchor the spinal cord. ...
peripheral vascular surgery - A
... PVC (premature ventricular contraction)-arrhythmia that precedes normal electrical impulse/may precede ventricular fibrillation Septum-wall that separates two cavities Stenosis-narrowing or constriction of a vessel Thrombus-blood clot (thrombus) TIA (transient ischemic attack)-temporary interference ...
... PVC (premature ventricular contraction)-arrhythmia that precedes normal electrical impulse/may precede ventricular fibrillation Septum-wall that separates two cavities Stenosis-narrowing or constriction of a vessel Thrombus-blood clot (thrombus) TIA (transient ischemic attack)-temporary interference ...
PDF
... grafts. This depression of chondrogenesis may, however, be due to the fact that the agar-impregnated Millipore is not adhesive towards the tissues, rendering it more difficult to assemble grafts with contact between interacting tissues. In grafts treated with collagenase plus hyaluronidase, however, ...
... grafts. This depression of chondrogenesis may, however, be due to the fact that the agar-impregnated Millipore is not adhesive towards the tissues, rendering it more difficult to assemble grafts with contact between interacting tissues. In grafts treated with collagenase plus hyaluronidase, however, ...
UB Fetal Pig Day 1 - CGW-Life-Science
... 7. With scissors, make a 3-cm incision in each corner of the pig's mouth. Your incision should extend posteriorly through the jaw. Follow the curve of the jaw instead of cutting straiht back into the neck. Spread the jaw open and examine the tongue. 8. Observe the palate on the roof of the mouth. T ...
... 7. With scissors, make a 3-cm incision in each corner of the pig's mouth. Your incision should extend posteriorly through the jaw. Follow the curve of the jaw instead of cutting straiht back into the neck. Spread the jaw open and examine the tongue. 8. Observe the palate on the roof of the mouth. T ...
Unit 1 Lecture 3
... functional properties of arteries are elasticity that allows blood vessels expand to accommodate the blood expelled during ventricular contraction and contractility; vasodilation is an increase in vessel size whereas vasoconstriction is a decrease in vessel size. Arterioles are very small microscopi ...
... functional properties of arteries are elasticity that allows blood vessels expand to accommodate the blood expelled during ventricular contraction and contractility; vasodilation is an increase in vessel size whereas vasoconstriction is a decrease in vessel size. Arterioles are very small microscopi ...
Part A
... at the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo • Placenta is fully formed and functional by the end of the third month • Placenta also secretes human placental lactogen, human chorionic thyrotropin, and relaxin ...
... at the uterine cavity face of the implanted embryo • Placenta is fully formed and functional by the end of the third month • Placenta also secretes human placental lactogen, human chorionic thyrotropin, and relaxin ...
Placenta Previa
... occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the lower part of the uterus instead of to the top. The placenta forms around the implanted embryo, resulting in a placenta positioned in the lower part of the uterus, instead of in the normal position at the top. A placenta previa completely blocks the ope ...
... occurs when the fertilized egg attaches to the lower part of the uterus instead of to the top. The placenta forms around the implanted embryo, resulting in a placenta positioned in the lower part of the uterus, instead of in the normal position at the top. A placenta previa completely blocks the ope ...
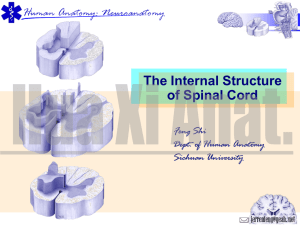
Gross Anatomy of the Spinal Cord
... Spinal Cord Enlargements of the Spinal Cord Caused by amount of gray matter in segment Cervical enlargement Nerves of shoulders and upper limbs ...
... Spinal Cord Enlargements of the Spinal Cord Caused by amount of gray matter in segment Cervical enlargement Nerves of shoulders and upper limbs ...
Which of the following places on the diaphragm are weak? a
... 8. The correct statement about the topography of the prostate is: a) Below the urinary bladder b) In the scrotum c) In the region of the bulb of the penis d) In the region of the spongy part of the urethra 9. The correct statement about the peritoneal relation of the ovarium is: a) Completely covere ...
... 8. The correct statement about the topography of the prostate is: a) Below the urinary bladder b) In the scrotum c) In the region of the bulb of the penis d) In the region of the spongy part of the urethra 9. The correct statement about the peritoneal relation of the ovarium is: a) Completely covere ...
The spinal cord is a complex cable of nerves that connects the brain
... The spinal cord begins at the brainstem and ends at about the second lumbar vertebra. The sensory, motor, and interneurons discussed previously are found in specific parts of the spinal cord and nearby structures. Sensory neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal (dorsal root) ganglion. Their axo ...
... The spinal cord begins at the brainstem and ends at about the second lumbar vertebra. The sensory, motor, and interneurons discussed previously are found in specific parts of the spinal cord and nearby structures. Sensory neurons have their cell bodies in the spinal (dorsal root) ganglion. Their axo ...
Document
... upper limb. It begins in the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) and extends into the axilla. • The brachial plexus is formed by the union of the anterior rami of the (C5-8) and T1 nerves, which constitute the roots of brachial plexus • The roots usually pass through the gap between the ant ...
... upper limb. It begins in the lateral cervical region (posterior triangle) and extends into the axilla. • The brachial plexus is formed by the union of the anterior rami of the (C5-8) and T1 nerves, which constitute the roots of brachial plexus • The roots usually pass through the gap between the ant ...
Development of the Gastrointestinal Tract
... of mesoderm, but this need not be pancreatic mesoderm. Differentiation of the islets of Langerhans does not require the presence of mesoderm or of pancreatic acini. It was originally thought that the Islets were derived from the neural crest. Evidence from quail-chick chimera cell tracers and transg ...
... of mesoderm, but this need not be pancreatic mesoderm. Differentiation of the islets of Langerhans does not require the presence of mesoderm or of pancreatic acini. It was originally thought that the Islets were derived from the neural crest. Evidence from quail-chick chimera cell tracers and transg ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.