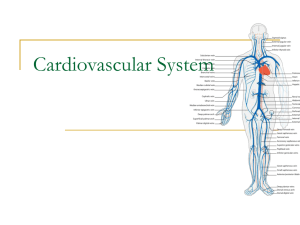
Cardiovascular System
... Three (3) important vessels originate off the arch of the aorta that supply blood to the head and arms. ...
... Three (3) important vessels originate off the arch of the aorta that supply blood to the head and arms. ...
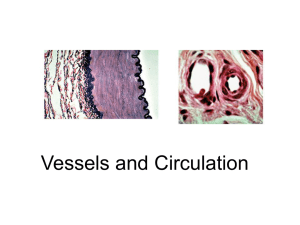
Lecture 19 - Vessels and Circulation
... which has been to the placenta for oxygenation (by gas diffusion from mom’s blood) The pair of umbilical arteries (branches from baby’s internal iliac arteries) carry blood to placenta to pick up oxygen and nutrients Fetal heart starts beating at 21 days post conception ...
... which has been to the placenta for oxygenation (by gas diffusion from mom’s blood) The pair of umbilical arteries (branches from baby’s internal iliac arteries) carry blood to placenta to pick up oxygen and nutrients Fetal heart starts beating at 21 days post conception ...
Spastic quadraparesis following a relatively minor injury
... Os odontoideum is an ossicle with smooth circumferential margins representing the odontoid process or dens. It lacks continuity with the body of C2 and its importance lies in the fact that trauma may compromise a previously asymptomatic atlanto-axial joint. We present a case of an adult male who sus ...
... Os odontoideum is an ossicle with smooth circumferential margins representing the odontoid process or dens. It lacks continuity with the body of C2 and its importance lies in the fact that trauma may compromise a previously asymptomatic atlanto-axial joint. We present a case of an adult male who sus ...
Evaluation of the Hoarse Patient
... appointment. The scope of the questionnaire reflects the varied causes of hoarseness and other dysphonias. In fact, Sataloff has shown that any body system may be responsible for the patient’s symptoms. Most patients with dysphonias come to the ENT complaining of hoarseness. A distinction should be ...
... appointment. The scope of the questionnaire reflects the varied causes of hoarseness and other dysphonias. In fact, Sataloff has shown that any body system may be responsible for the patient’s symptoms. Most patients with dysphonias come to the ENT complaining of hoarseness. A distinction should be ...
Introduction and Superficial Back
... superficial to deep in any particular region. Describe a cutaneous nerve and the pattern of cutaneous nerves on the back. Identify, and give the general attachments of, nerve and blood supply to, and the general functions of the superficial back muscles. Identify the bony prominences of the back and ...
... superficial to deep in any particular region. Describe a cutaneous nerve and the pattern of cutaneous nerves on the back. Identify, and give the general attachments of, nerve and blood supply to, and the general functions of the superficial back muscles. Identify the bony prominences of the back and ...
Gross - Unit 1 arteries and nerves
... - Superficial radial nerve courses through the Snuff Box - Supplies skin of the posterior surface of the thumb, index, and half of middle finger. (except the distal phalanges of these digits which are supplied by the median nerve.) The DEEP BRANCH passes between the 2 heads of the Supinator muscle ...
... - Superficial radial nerve courses through the Snuff Box - Supplies skin of the posterior surface of the thumb, index, and half of middle finger. (except the distal phalanges of these digits which are supplied by the median nerve.) The DEEP BRANCH passes between the 2 heads of the Supinator muscle ...
abdominal walls
... Differentiates below umbilicus into 2 layers:A-superf. Fatty layer(Campers F) B-deep membranous L (Scarpas F) its lower border attached as follow:1 -lat. to pubic tubercle F . Lata (1 finger breadth below ing leg 2-med. To pubic tuberclepubic arch &tubercle 3-in median plaintubular like envelope ...
... Differentiates below umbilicus into 2 layers:A-superf. Fatty layer(Campers F) B-deep membranous L (Scarpas F) its lower border attached as follow:1 -lat. to pubic tubercle F . Lata (1 finger breadth below ing leg 2-med. To pubic tuberclepubic arch &tubercle 3-in median plaintubular like envelope ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Introduction to
... (makes it larger) the bronchioles and the pupils. The parasympathetic nervous system works on the contrary, decreasing the heart rate, dilating the blood vessels, stimulating the digestive tract movements, constricting the bronchioles and pupils (SLUDD (salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion, ...
... (makes it larger) the bronchioles and the pupils. The parasympathetic nervous system works on the contrary, decreasing the heart rate, dilating the blood vessels, stimulating the digestive tract movements, constricting the bronchioles and pupils (SLUDD (salivation, lacrimation, urination, digestion, ...
Cardiovascular System_Lecture II - Medical
... Arteries are composed of distinct layers of tissue; The innermost layer, which is in direct contact with the flow of blood is the tunica intima, commonly called the intima. This layer is made up of mainly endothelial cells. Outside this layer is the tunica media, or media, which is made up of smooth ...
... Arteries are composed of distinct layers of tissue; The innermost layer, which is in direct contact with the flow of blood is the tunica intima, commonly called the intima. This layer is made up of mainly endothelial cells. Outside this layer is the tunica media, or media, which is made up of smooth ...
Blood Vessel Anatomy
... optic chiasma at the base of the brain; this circle unites the ant. & post. blood supplies from the internal carotid & vertebral arteries. E. Arteries of the Shoulder & Upper Extremity - major branches of the ______________ arteries include the 1. _________ A. - continuation of subclavian in the axi ...
... optic chiasma at the base of the brain; this circle unites the ant. & post. blood supplies from the internal carotid & vertebral arteries. E. Arteries of the Shoulder & Upper Extremity - major branches of the ______________ arteries include the 1. _________ A. - continuation of subclavian in the axi ...
vc_palsycurrent
... avoided during the procedure as it would distort the cord Needle is ideally placed lateral to the vocal fold about 2 mm deep at the level of vocal process ...
... avoided during the procedure as it would distort the cord Needle is ideally placed lateral to the vocal fold about 2 mm deep at the level of vocal process ...
Cords of the Brachial Plexus - جامعة الكوفة
... The plexus can be divided into roots, trunks, divisions, and cords (figure -1-). The roots of C5 and 6 unite to form the upper trunk, the root of C7 continues as the middle trunk, and the roots of C8 and T1 unite to form the lower trunk. Each trunk then divides into anterior and posterior divisions. ...
... The plexus can be divided into roots, trunks, divisions, and cords (figure -1-). The roots of C5 and 6 unite to form the upper trunk, the root of C7 continues as the middle trunk, and the roots of C8 and T1 unite to form the lower trunk. Each trunk then divides into anterior and posterior divisions. ...
heart and blood vessels ppt
... - thick in diameter - contain smooth muscle cells - can control blood flow to body regions ...
... - thick in diameter - contain smooth muscle cells - can control blood flow to body regions ...
Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord
... run into spinal cord alongside the dorsal and ventral nerve roots These intercostal and lumbar radicular arteries arise from the aorta, provide major anastomoses and supplement the blood flow to the spinal cord Largest of the anterior radicular arteries is known as the artery of Adamkiewicz, whi ...
... run into spinal cord alongside the dorsal and ventral nerve roots These intercostal and lumbar radicular arteries arise from the aorta, provide major anastomoses and supplement the blood flow to the spinal cord Largest of the anterior radicular arteries is known as the artery of Adamkiewicz, whi ...
Chapter 4 Third Week of Human Development
... the third week in the extraembryonic mesoderm covering yolk sac, connecting stalk, and chorion. Without significant amount of yolk, the embryo needs blood vessels to supply nutrition and oxygen. At the end of the 2nd week the embryo obtains nutrition from maternal blood through diffusion; During the ...
... the third week in the extraembryonic mesoderm covering yolk sac, connecting stalk, and chorion. Without significant amount of yolk, the embryo needs blood vessels to supply nutrition and oxygen. At the end of the 2nd week the embryo obtains nutrition from maternal blood through diffusion; During the ...
Five Essential Components to the Reflex Arc
... • Baroreceptors are sensors located in the blood vessels of the human body. They are stretched when blood goes through them, and that tells them if the blood pressure is too high or low. They tell the brain, which can then cause the blood vessels to dilate (decreasing peripheral resistance and lower ...
... • Baroreceptors are sensors located in the blood vessels of the human body. They are stretched when blood goes through them, and that tells them if the blood pressure is too high or low. They tell the brain, which can then cause the blood vessels to dilate (decreasing peripheral resistance and lower ...
Pelvis Forum
... vessel may occur in atherosclerotic disease; significant anastomoses occur between: – a. Uterine and Ovarian (aorta) – b. Iliolumbar/circumflex iliac and lumbar (from aorta) – c. Lateral sacral and median sacral (aorta at division to internal iliacs) – d. Middle rectal and superior rectal (IMA) – e. ...
... vessel may occur in atherosclerotic disease; significant anastomoses occur between: – a. Uterine and Ovarian (aorta) – b. Iliolumbar/circumflex iliac and lumbar (from aorta) – c. Lateral sacral and median sacral (aorta at division to internal iliacs) – d. Middle rectal and superior rectal (IMA) – e. ...
Chapter 21
... Conus medularis - it is the end of the spinal cord Denticulate ligaments – pia mater attaching the spinal cord t the vertebral wall Filum terminale – pia mater extension from the conus medularis to the coccix ...
... Conus medularis - it is the end of the spinal cord Denticulate ligaments – pia mater attaching the spinal cord t the vertebral wall Filum terminale – pia mater extension from the conus medularis to the coccix ...
Body cavities and abdominal regions
... – A middle tissue mass diving the lungs into two cavities – Includes the pericardial cavity, esophagus, trachea, and large blood vessels. ...
... – A middle tissue mass diving the lungs into two cavities – Includes the pericardial cavity, esophagus, trachea, and large blood vessels. ...
The Nervous System
... ( tract ): a bundle of nerve fibers which have the same origin, termination, pathway and function Reticular formation 网状结构: an admixture of cross-crossing fibers with larger or smaller groups of nerve cells occupying the meshes ...
... ( tract ): a bundle of nerve fibers which have the same origin, termination, pathway and function Reticular formation 网状结构: an admixture of cross-crossing fibers with larger or smaller groups of nerve cells occupying the meshes ...
Blood Basics
... to learn more about the human anatomy because there are certain similarities between the two species. While studying Rhesus monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the ...
... to learn more about the human anatomy because there are certain similarities between the two species. While studying Rhesus monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the ...
The Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and the
... A delicate vascular membrane that closely invests the spinal cord Denticulate ligament齿状韧带: consist of 21 pairs triangular ligaments extending from spinal cord on each side between anterior and posterior roots of spinal nerves to spinal dura mate; these ligaments help to fix position of spinal cord. ...
... A delicate vascular membrane that closely invests the spinal cord Denticulate ligament齿状韧带: consist of 21 pairs triangular ligaments extending from spinal cord on each side between anterior and posterior roots of spinal nerves to spinal dura mate; these ligaments help to fix position of spinal cord. ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.