Anatomy and Terminology of the Spine
... The space that runs down the length of the vertebral column from the head to the tailbone is the called the spinal canal or vertebral foramen. A large nerve bundle, the spinal cord, which is an extension of the brain, runs inside the spinal canal from C1 to L1. The spinal canal has openings called n ...
... The space that runs down the length of the vertebral column from the head to the tailbone is the called the spinal canal or vertebral foramen. A large nerve bundle, the spinal cord, which is an extension of the brain, runs inside the spinal canal from C1 to L1. The spinal canal has openings called n ...
AXILLA LEARNING OBJECTIVES To know about the location of
... It extends along side of thorax to lower border of serratus anterior giving its branches. Injury: during surgery for breast cancer, specifically radical mastectomies involving removal of axillary lymph nodes from a blow to ribs on an outstretched arm gives rise to “winged scapula” ...
... It extends along side of thorax to lower border of serratus anterior giving its branches. Injury: during surgery for breast cancer, specifically radical mastectomies involving removal of axillary lymph nodes from a blow to ribs on an outstretched arm gives rise to “winged scapula” ...
AXILLA LEARNING OBJECTIVES • Know the position, shape of
... Anterior division of lower trunk continues as medial cord Cords lie around axillary artery Posterior cord - axillary and radial nerves. Lateral cord - musculocutaneous and lateral head of median nerves Medial cord - ulnar and medial head of median nerves ...
... Anterior division of lower trunk continues as medial cord Cords lie around axillary artery Posterior cord - axillary and radial nerves. Lateral cord - musculocutaneous and lateral head of median nerves Medial cord - ulnar and medial head of median nerves ...
the spinal cord and spinal nerves
... motor neurons called gamma motor neurons – originating from the spinal cord and controlling contraction of the ends of the muscle spindle cells. - Are responsible for regulating the sensitivity of the muscle spindles. Axons of these sensory neurons synapse directly with motor neurons in the spinal c ...
... motor neurons called gamma motor neurons – originating from the spinal cord and controlling contraction of the ends of the muscle spindle cells. - Are responsible for regulating the sensitivity of the muscle spindles. Axons of these sensory neurons synapse directly with motor neurons in the spinal c ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... internal which blood of sphincter abranches capillary branches carotid pressure Endothelial controls branches: divides bed: off topr. cells Bd R to Supplies gastroepiploic: flow ...
... internal which blood of sphincter abranches capillary branches carotid pressure Endothelial controls branches: divides bed: off topr. cells Bd R to Supplies gastroepiploic: flow ...
Blood Vessels - Dr. Justo Lopez Website
... tissue fluid and the waste passes from the tissue fluid to the blood through the capillaries. Lungs: Oxygen passes from the air to the blood and carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the air through the capillaries. ...
... tissue fluid and the waste passes from the tissue fluid to the blood through the capillaries. Lungs: Oxygen passes from the air to the blood and carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the air through the capillaries. ...
23Meninges+CSF
... delicate & highly vascular membrane that is closely adherent to the gyri and fitted into the sulci. Between the pia and arachnoid mater lies the subarachnoid ...
... delicate & highly vascular membrane that is closely adherent to the gyri and fitted into the sulci. Between the pia and arachnoid mater lies the subarachnoid ...
thorax
... Match each of the following descriptions with the appropriate lettered structure in this computed tomography(CT) scan of the heart from a 42-year-old man who complains of chest pain and breathing problems.His electrocardiogram(ECG)shows left ventricular hypertrophy. 46.Stenosis of this structure may ...
... Match each of the following descriptions with the appropriate lettered structure in this computed tomography(CT) scan of the heart from a 42-year-old man who complains of chest pain and breathing problems.His electrocardiogram(ECG)shows left ventricular hypertrophy. 46.Stenosis of this structure may ...
04 Brachial Pluxes2012-09-08 02:453.3 MB
... It runs in the spiral groove of humerus, deep to lateral head of triceps. At the lateral end of the spiral groove, it turns forwards and pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior compartment of the arm in groove between brachialis medially and ...
... It runs in the spiral groove of humerus, deep to lateral head of triceps. At the lateral end of the spiral groove, it turns forwards and pierces the lateral intermuscular septum to enter the anterior compartment of the arm in groove between brachialis medially and ...
File
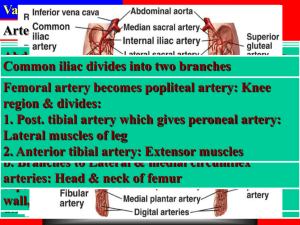
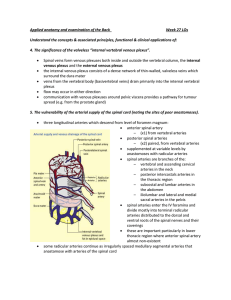
... three longitudinal arteries which descend from level of foramen magnum: anterior spinal artery – (x1) from vertebral arteries posterior spinal arteries – (x2) paired, from vertebral arteries supplemented at variable levels by anastomoses with radicular arteries spinal arteries are branches o ...
... three longitudinal arteries which descend from level of foramen magnum: anterior spinal artery – (x1) from vertebral arteries posterior spinal arteries – (x2) paired, from vertebral arteries supplemented at variable levels by anastomoses with radicular arteries spinal arteries are branches o ...
the spinal cord and the spinal nerves
... DERMATOMES What are dermatomes? The skin over the entire body, with the exception of the face and top of the head, is supplied by spinal nerves that carry somatic sensory nerve impulses into the spinal cord. All spinal nerves, except C-1, serve a specific and constant segment of the skin. The area o ...
... DERMATOMES What are dermatomes? The skin over the entire body, with the exception of the face and top of the head, is supplied by spinal nerves that carry somatic sensory nerve impulses into the spinal cord. All spinal nerves, except C-1, serve a specific and constant segment of the skin. The area o ...
meninges PowerPoint Presentation
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
L21-sann -essam meninges
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
Neuroanatomy 1
... Caudal to the lumbar enlargement, the cord tapers abruptly to form a conical termination, the conus medullaris: • Situated at the level of L1/L2 • Nerve roots pass across the subarachnoid space at increasingly oblique angles from cervical to sacral From the tip of the conus medullaris runs a fine co ...
... Caudal to the lumbar enlargement, the cord tapers abruptly to form a conical termination, the conus medullaris: • Situated at the level of L1/L2 • Nerve roots pass across the subarachnoid space at increasingly oblique angles from cervical to sacral From the tip of the conus medullaris runs a fine co ...
Angiography_Anatomy_Part_1
... body tissues White Blood Cells are Leukocytes and are produced in the medullary cavity of some bones (yellow bone marrow) and lymph system. It’s job is to protect against infection and disease Platelets originate from bone marrow They repair tears in blood vessel wall and promote blood clott ...
... body tissues White Blood Cells are Leukocytes and are produced in the medullary cavity of some bones (yellow bone marrow) and lymph system. It’s job is to protect against infection and disease Platelets originate from bone marrow They repair tears in blood vessel wall and promote blood clott ...
TSM73 - Innervation of the Upper Limbs
... o The interosseous membrane holds the radius and ulna together along their whole length o The radius rotates about the capitulum allowing pronation and supination of the arm o The ulna does not rotate but allows flexion and extension at the elbow A collateral ligament arises from each of the epicond ...
... o The interosseous membrane holds the radius and ulna together along their whole length o The radius rotates about the capitulum allowing pronation and supination of the arm o The ulna does not rotate but allows flexion and extension at the elbow A collateral ligament arises from each of the epicond ...
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal
... M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like “dorsal,” “ventral,” “anterior” and “posterior” provide a means of locating structures relative to the overall orientation of the nervous system. Complications with tho ...
... M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like “dorsal,” “ventral,” “anterior” and “posterior” provide a means of locating structures relative to the overall orientation of the nervous system. Complications with tho ...
Portland Community College, Sylvania Campus BI 232 Lab
... long enough to take the quiz and then leave soon after the lab will be counted as a missed lab. Spelling can account for up to 10% off of your grade so please be careful. Also be aware of singular and plural usage because these mistakes will count as spelling errors. Absences: You cannot miss more t ...
... long enough to take the quiz and then leave soon after the lab will be counted as a missed lab. Spelling can account for up to 10% off of your grade so please be careful. Also be aware of singular and plural usage because these mistakes will count as spelling errors. Absences: You cannot miss more t ...
etiology and pathogenesis of hypoxic-ischemic
... combination of inadequate blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain. AAP and ACOG; Encephalopathy is an acute intrapartum event sufficient to cause neuronal injury evidenced by : -Metabolic acidosis (pH <7.0 and base deficit ≥12) in fetal umbilical cord arterial blood , -Need for respiratory suppo ...
... combination of inadequate blood flow and oxygen delivery to the brain. AAP and ACOG; Encephalopathy is an acute intrapartum event sufficient to cause neuronal injury evidenced by : -Metabolic acidosis (pH <7.0 and base deficit ≥12) in fetal umbilical cord arterial blood , -Need for respiratory suppo ...
Meninges ventricles and CSF
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
... membrane that surrounds the brain. It is formed of two layers; periosteal and meningeal. The periosteal layer is attached to the skull. The meningeal layer is folded forming the dural folds; falx cerebri, and tentoriam ...
D24-1 UNIT 24. DISSECTION: ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL
... xiphoid process to a pint just above the pubic symphysis, parallel and just lateral to the linea alba. From the upper end of the first incision, make a transverse incision and then a second transverse incision just below the umbilicus. Now make a transverse incision in the rectus abdominis m. just b ...
... xiphoid process to a pint just above the pubic symphysis, parallel and just lateral to the linea alba. From the upper end of the first incision, make a transverse incision and then a second transverse incision just below the umbilicus. Now make a transverse incision in the rectus abdominis m. just b ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.