* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download thorax
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
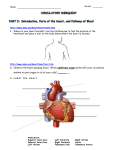
Thorax 1.On the surface of the chest ,a physician is able to locate the apex of the heart (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) at in in in at the the the the the level of the sternal angle left fourth intercostal space left fifth intercostal space right fifth intercostal space level of the xiphoid process of the sternum 2.Normal quiet expiration is achieved by contraction of the (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) elastic tissue in the thoracic wall and lungs serratus posterior superior muscles pectoralis minor muscles serratus anterior muscles diaphragm 3.Which of the following nerve fibers would be injured if the greater splanchnic nerve were severed? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) General somatic afferent (GSA)and preganglionic sympathetic fibers General visceral afferent (GVA)and postganglionic sympathetic fibers General visceral afferent (GVA)and preganglionic sympathetic fibers General somatic efferent(GSE)and postganglionic sympathetic fibers GVA and GSE fibers 4.A stab wound that severed the white rami communicantrs at the level of the six thoracic vertebra would result in degeneration of nerve cell bodies in which of the following structures? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Dorsal root ganglion and anterior horn of the spinal cord Sympathetic chain ganglion and dorsal root ganglion Sympathetic chain ganglion and posterior horn of the spinal cord Dorsal root ganglion and lateral horn of the spinal cord Anterior and lateral horn of the spinal cord 5.Where should a physician place the stethoscope to listen to the sound of the mitral valve? (A) Over the medial end of the second left intercostal space (B) Over the medial end of the second right intercostal space (C) In the left fourth intercostal space at the midclavicular line (D) In the left fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line (E) Over the right half of the lower end of the body of the sternum 6.Bleeding comes from the vein that is accompanied by the posterior interventricular artery .which of the following veins is most likely to be ruptured? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Great cardiac vein Middle cardiac vein Anterior cardiac vein Small cardiac vein Oblique veins of the left atrium 7.The largest portion of the sternocostal surface of the heart seen on a posterior-anterior chest radiograph is composed of the (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) left atrium right atrium left ventricle right ventricle base of the heart 8.If the interventricular septum is damaged , which of the following valves is most likely defective? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Pulmonary valve Mitral valve Valve of coronary sinus Tricuspid valve Aortic valve 9.An artificial cardiac pacemaker is implanted in a 54-year-old patient Which of the following conductive tissues of the heart has a defective function? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Atrioventricular(AV) bundle Atrioventricular(AV) node Sinoatrial(SA) node Purkinje fiber Moderator band 10. Which of the following bronchopulmonary segments must contain cancerous tissues if a thoracic surgeon has to remove the right middle lobar (secondary) bronchus along with lung tissue? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Medial and lateral Anterior and posterior Anterior basal and medial basal Anterior basal and posterior basal Lateral basal and posterior basal 11.A pulmonary physician finds a small mass of tumor in the eparterial bronchus . Which of the following airways is most likely blocked? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Left superior bronchus Left inferior bronchus Right superior bronchus Right middle bronchus Right inferior bronchus 12.If a blood clot blocks the circumflex branch of the left coronary artery in a patient with a typical coronary circulation,which area of the heart Musculature is most likely to be ischemic? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Anterior part of the left ventricle Anterior interventricular region Posterior interventricular region Posterior part of the left ventricle Anterior part of the right ventricle 13. Which of the following would most likely occur if the phrenic nerve is severed? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Injury to only general somatic efferent(GSE) fibers Difficulty in expiration Loss of sensation in the pericardium and mediastinal pleura Normal function of the diaphragm Loss of sensation in the costal part of the diaphragm 14. Which of the following conditions could injure the left recurrent laryngeal nerve? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) A pericardial incision medial to the ligamentum arteriosum Scar tissue in front of the subclavian artery A tumor in the posterior mediastinum An aneurysm in the aortic arch A knife wound on the arch of the azygos vein 15. Which of the following conditions could result from infarction limited to the interventricular septum ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) a myocardial Tricuspid valve insufficiency Pulmonary valve insufficiency Inferior vena caval valve insufficiency Mitral valve insufficiency Aortic valve insufficiency 16.Lung cancer is located in the vicinity of the cardiac notch ,a deep indentation on the lung. Which of the following lobes is most likely to be excised ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Superior lobe of the right lung Middle lobe of the right lung Inferior lobe of the right lung Superior lobe of the left lung Inferior lobe of the left lung 17. Which of the following conditions reprsents the normal changes that occur in the circulation at or soon after birth ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Decreased blood flow through the lungs Anatomical closure of the ductus arteriosus Increased left atrial pressure Anatomical closure of the foramen ovale Functional closure of the right umbilical vein 18.Destructive changes in the right atrium could damage which of the following structures ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Papillary muscles Chordae tendineae Septomarginal trabecula Pectinate muscles Trabeculae carneae cordis 19.A sudden occlusion at the origin of the descending(thoracic) aorta would most likely decrease blood flow in which of the following intercostal arteries? (A) Upper six anterior (B) All of the posterior (C) Upper two posterior (D) Lower anterior (E) Lower nine posterior 20.The right coronary artery (A) (B) (C) (D) is shorter in length than the left one supplies blood to the sinoatrial(SA) node causes myocardial infarction in the apex of the heart if it is occluded provides maximal blood flow during systole and minimal during diastole (E) arises from the aortic arch 21. Which of the following describes a characteristic of the left lung? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Horizontal fissure A groove for the superior vena cava Three lobar (secondary)bronchi Lingula of lung A larger capacity than the right lung 22.A victim of an automobile accident experiences difficulty in expiration . Which of the following muscles is most likely injured? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Levator costarum Innermost intercostal muscles External intercostal muscles Diaphragm Muscles of the abdominal wall 23. In a 78-year-old patient with an advanced cancer in the superior mediastinum , Which of the following structures may be spared ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Brachiocephalic veins Trachea Lower portion of the left common carotid artery Arch of the aorta Hemiazygos vein 24.A tumor located just superior to the root of the right lung may block blood flow in which of the following veins? (A) Hemiazygos vein (B) Azygos vein (C) Right subclavian vein (D) Right brachiocephalic vein (E) Accessory hemiazygos vein 25.A lesion of the right vagus nerve near the trachea in the superior mediastinum could cause which of the following condition? (A) Loss of sensation carried by the recurrent laryngeal (B) Lack of parasympathetic fibers in the anterior esophageal plexus (C) Functional injury to the anterior vagal trunk at the lower part of the esophagus (D) Reduction in cardiac rate (E) Injury to parasympathetic preganglionic fibers 26.The ductus arteriosus has which of the following properties? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Anatomical closure right after birth Carrying highly oxygenated blood during prenatal life Functional closure several weeks after birth Connection of the right pulmonary vein to the aorta Shunt of blood from the pulmonary trunk to the aorta before birth ,by passing the pulmonary circulation 27.Left ventricular hypertrophy could result from which of the following condition? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) A constricted pulmonary trunk An abnormally small left atrioventricular (AV) opening Improper closing of the pulmonary valves An abnormally large right AV opening Stenosis of the aorta 28.The left primary bronchus (A) has a larger diameter than the right primary bronchus (B) often receives more foreign bodies via the trachea than the right primary bronchus (C) gives rise to the eparterial bronchus (D) is longer than the right primary bronchus (E) runs under the arch of the azygos vein 29.The hemiazygos vein (A) receives the left superior intercostal vein (B) receives the lower left posterior intercostal vein (C) empties into the superior vena cava (D) is connected to the inferior vena cava (E) enter the thorax through the esophageal opening 30.On posterior-anterior chest radiographs which of the following structures forms the right border of the cardivascular silhouette? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Arch of the aorta Pulmonary trunk Superior vena cava Ascending aorta Left ventricle 31.Which of the following veins typically drains into the right or left brachiocephalic vein? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Azygos Hemiazygos Right superior intercostal Left superior intercostal Internal thoracic 32.During the cardiac cycle,which of the following events occurs? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Atrioventricular(AV) valves close during diastole Aortic valve closes during systole Pulmonary valve opens during diastole Blood flow in coronary arteries maximal during diastole Aortic valve closes at the same time as AV valve 33.Which of the following condition may occur at or soon after birth ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Anatomical closure of the ductus venosus Anatomical closure of the foramen ovale Anatomical closure of the ductus arteriosus Obiliteration of the left umbilical vein Obiliteration of the right umbilical vein 34. Which of the following anatomic features would most likely be found at the level of the sternal angle? (A) Bifurcation of the trachea (B) Beginning of the ascending aorta (C) Middle of the aortic arch (D) Articulation of the third rib with the sternum (E) Superior border of the superior mediastinum 35. Which of the following structures would most likely articulate with the third rib ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Manubrium of the aternum Body of the second thoracic vertebra Spinous process of the third thoracic vertebra Body of the fouth thoracic vertebra Transverse process of the second thoracic vertebra 36.A large tumor confined in the posterior mediastinum may compress which of the following structures? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Ascending aorta Trachea Descending aorta Arch of the aorta Arch of the azygos vein 37. Which of the following structures is correctly paired with its nerve supply? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Mediastinal pleura-intercostal nerves Peripheral part of the diaphragmatic pleura-phrenic nerves Visceral pleura-general visceral afferent (GVA) pain fibers Gland in the bronchial tree-parsympathetic fibers Smooth muscle in the pulmonary artery- parsympathetic fibers 38.The near-simultaneous closure of which of the following valves produces the fist heart sound ? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Aortic and tricuspid Aortic and pulmonary Tricuspid and mitral Mitral and pulmonary Tricuspid and pulmonary 39. Which of the following structures loops around the arch of the aorta near the ligamentum arteriosum? (A) Left vagus nerve (B) Left phrenic nerve (C) Left sympathetic trunk (D) Left recurrent laryngeal nerve (E) Left greater splanchnic nerve 40.The right atrium (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) receives blood from the oblique cardiac veins associated with the apex of the heart contains the sinoatrial(SA) node enlarges briefly in response to coarctation of the aorta is hypertrophied by pulmonry stenosis 41. Which of the following structures maintains constant tension on the cusps of the atrioventric-ular(AV) valves? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Crista terminalis Septomarginal trabecula Chordae tendineae Pectinate muscle Anulus fibrosus 42.If the right coronary artery is blocked by a fat globule after giving off the right marginal artery,which of the following structures may have oxygen deficiency? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Right atrium Sinoatrial(SA) node Atrioventricular(AV) node Apex of the heart Root of the pulmonary trunk 43.A surgical resident ligates the phrenic nerve instead of the accompanying artery descending between the mediastinal pleura and the pericar-dium . Which of the following arteries did he intend to ligate? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Internal thoracic Musculophrenic Pericardiacophrenic Right coronary artery Superior(supreme) thoracic 44.When the diaphragm contracts , which of the following conditions most likely occurs? (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) Decreased thoracic volume Increased abdominal volume Increased lung volume Air flow out of the bronchi Increased thoracic pressure 45.During a pleural tap,a needle may injure the intercostal neurovascular bundle because it is located (A) (B) (C) (D) (E) above the upper border of the ribs deep to the upper border of the ribs beneath the lower border of the ribs between the external and internal intercostals between the transverse thoracis and subcostalis Match each of the following descriptions with the appropriate lettered structure in this computed tomography(CT) scan of the heart from a 42-year-old man who complains of chest pain and breathing problems.His electrocardiogram(ECG)shows left ventricular hypertrophy. 46.Stenosis of this structure may produce left ventricular hypertrophy 47.Structure that is most likely to be removed by a pulmonary surgeon in a surgical resection of a lobe(lobectomy) to remove lung cancer in the apex of the right lung . 48. Structure that branches into the bronchial arteries 49. Structure into which the azygos vein drains venous blood 50. Structure from which the left coronary artery arises Match each of the following description with approprriate lettered structure in the superior cross-sectional view of the heart 51.Runs toward the apex of the heart and supplies atrial blood to the anterior right ventricle 52.Supplies arterial blood to the sinoatrial (SA) node 53.Arises from the left aortic sinus 54.Gives rise to the anterior interventricular artery 55.Has a sound that is best heard through a stethoscope at the fifth intercostal space at the midclavicular line