* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Region 11: Heart, Trachea, and Lungs Landmarks -
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Artificial heart valve wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
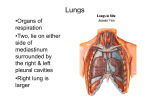
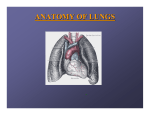
Region 11: Heart, Trachea, and Lungs Landmarks --apex: about 8cm (5.5-12.5 cm) from median plane in left 5th intercostal space --base: posterior aspect of heart; mainly formed by left atrium and a small part of the right atrium *pulmonary vens, the superior vena cava, and inferior vena cava connect with the base --Heart Valves a. pulmonary valve: listen in 2nd intercostal space on left b. aortic valve: listen in 2nd intercostal space on right c. mitral valve: listen in 5th intercostal space about 3 ½ inches to left of midline d. tricuspid valve: listen over lower left border of sternum Arteries of the Heart --right coronary artery a. sinoatrial nodal artery: 60% from proximal portion of right coronary a., 40% from beginning of left circumflex a. b. posterior interventricular branch/posterior descending artery (PDA): runs in posterior interventricular sulcus c. atrioventricular nodal branch: in 80% of population --left coronary artery a. anterior interventricular branch/left anterior descending artery (LAD): runs in anterior interventricular sulcus, has perforating and diagonal branches b. circumflex branch Veins of the Heart (terminate principally in the coronary sinus) --great cardiac vein *begins in anterior interventricular sulcus and travels with anterior interventricular a., then the circumflex a. --middle cardiac vein *begins in posterior interventricular sulcus and travels with posterior interventricular a. --small cardiac vein *in posterior right coronary sulcus with right coronary a. Chambers of the Heart (2 receiving-atria, 2 pumping-ventricles) --Right Atrium: receives deoxygenated blood from body (via sup. and inf. vena cava) and the heart (via coronary sinus) a. sinus venarum: smooth part b/w 2 vena cava b. crista terminalis: internal to sulcus terminalis c. pectinate muscles (musculi pectinati): pundled muscle fibers in auricle d. fossa ovale and limbus of fossa ovale e. sinuatrial node and atrioventricular node --Right Ventricle: receives blood from right atrium and pumps it to lungs via pulmonary a. a. right atrioventricular/tricuspid valve b. trabecula carnae: thick muscle bundles giving the ventricle its rugged texture c. septomarginal trabecula (septal limb and moderator band): goes from interventricular septum to the root of the anterior papillary muscle and carries theright bundle branch d. papillary muscles; conical projections of ventricular muscle related to the cusps (anterior, posterior, septal) e. chorda tendinae: fibrous cords attaching papillary muscles to the valve cusps f. infundibulum (conus arteriosus, outflow tract): separated from rough, trabecular portion (inflow tract) by the supraventricular crest --Left Atrium: receives oxygenated blood from lungs via pulmonary veins a. smooth walled portion receives oxygenated blood from 4 pulomonary vv. b. auricle; has pectinate muscles c. valve of the foramen ovale --Left Ventricle: receives blood from the left atrium and pumps it throughout the body via the aorta a. left atrioventricular valve (mitral, bicuspid) b. trabecula carnae c. papillary muscles (anterior and posterior) and corda tendinae d. aortic vestibule (outflow tract) e. membranous part of the interventricular septum: right below the right and posterior cusps of the aortic valve Valves of the Heart --Atrioventricular valves *separates the atria from the ventricles *valves have rigns, cusps, chorda tendinae, and papillary muscles *Right atrioventricular valve/Tricuspid valve (3 cusps) *Left atrioventricular valve/Mitral/Bicuspid valve (2 cusps) --Semilunar valves *pulmonary valve *aortic valve Conduction System of the Heart --Sinuatrial node (pacemaker): junction of the superior vena cava and right atrium, near the end of the sulcus terminalis just deep to the epicardium --Atrioventricular node: right side of the interatrial septum above and in front of the opening for the coronary sinus --Atrioventricular bundle (Bundle of His) *runs below the membranous part of the interventricular septum *divides into right and left bundle branches Nerves of the Heart (modify the heart’s intrinsic rhythmicity) --cardiac nerves: from the vagus and sympathetic chain Trachea and Bronchi (bronchioles: airways less than 1.5 mm diameter) --Trachea *2-2.5 cm diameter in adults *10-12 cm long in adults, beginning at C6, ending at upper T5 *has 16-20 C-shaped cartilage rings deficient in back part, next to esophagus --last cartilage is carina *right bronchus (primary) 25 degrees from vertical center *left bronchus (primary): 37 degrees from vertical center --Right Primary Bonchus *enters hilum of right lung *is wider, shorter (2.5 cm long) and more vertical than left bronchus (why more foreign objects enter right bronchus) *primary and secondary bronchi have C-shaped cartilages *secondary bronchi: 3, 1 each to superior, middle, and inferior lobes a. eparterial bronchus: the right superior lobar bronchus: named for its position superior to right pulmonary artery *tertiary bronchi: supply bronchopulmonary (lobule) segment of each lobe a. superior lobe b. middle lobe c. lower lobe --Left Primary Bronchus *enters hilum of left lung * narrower and longer (5cm) and less vertical than right bronchus *secondary bronchi: 2, 1 to superior and inferior lobes: there is no epiarterial bronchus on the left side *tertiary bronchi a. superior lobe: has 2 divisions b. inferior lobe Lungs --are free in pleural cavities, except at the hilus, which contains the root of each lung and pulmonary ligament --right lung: 2 fissure separate the lung into 3 lobes a. upper lobe: served by 3 segmentsapical, anterior, posterior b. middle lobe: 2 segmentslateral and medial c. lower lobe: 5 segmentssuperior, medial basal, anterior basal, lateral basal, posterior basal d. 2 fissures --oblique fissure: separates the upper and middle lobes from the lower lobe --horizontal fissure: separates the middle form the upper lobe --left lung: oblique fissure separates the lung into 2 lobes a. upper lobe: 4 segmentsapico-posterior, anterior, superior lingular, inferior lingular b. lower lobe: 5 segmentssuperior, medial basal, anterior basal, lateral basal, posterior basal Blood Supply --Right pulmonary artery: at root of the lung it is anterior/inferior to superior lobar (epiarterial) bronchus --Left pulmonary artery --Bronchial arteries *2 left branches (superior and inferior) and 1 right branch *left branches come directly off the aorta *right branch comes off an itnercostal artery or one of the left bronchial arteries --2 pulmonary veins *superior and inferior, serve each lung *lie anterior and inferior to other structures (bronchi, pulmonary arteries) at the hilus of the lungs --lymphatics *superficial plexus lies in or near the visceral pleura *deep plexus follows the conducting system a. bronchopulmonary (hilar) nodes: at primary/secondary bronchial segment junctions b. tracheobronchial nodes: at trachea and primary bronchial junctions