Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerve
... spinal cord begins at the foramen magnum and ends at L1/L2 as the conus medullaris. Caudal to the conus medullaris is the cauda equina, which consists of spinal nerve roots from the more caudal segments of the spinal cord. The spinal cord and most of the cauda equina is enclosed by the dural sac whi ...
... spinal cord begins at the foramen magnum and ends at L1/L2 as the conus medullaris. Caudal to the conus medullaris is the cauda equina, which consists of spinal nerve roots from the more caudal segments of the spinal cord. The spinal cord and most of the cauda equina is enclosed by the dural sac whi ...
Resection of Bilateral C1 Neurofibromas Using a Unilateral
... The patient's head was then secured in a Mayfield headholder, followed by registration for neuronavigation. After the patient was adequately padded and secured, the ipsilateral shoulder was taped and pulled towards the feet to exaggerate the corridor between the patient's head and shoulder. A hockey ...
... The patient's head was then secured in a Mayfield headholder, followed by registration for neuronavigation. After the patient was adequately padded and secured, the ipsilateral shoulder was taped and pulled towards the feet to exaggerate the corridor between the patient's head and shoulder. A hockey ...
Chorion
... 16-day embryo. Cytotrophoblast and associated mesoderm have become the chorion, and chorionic villi are elaborating. The embryo exhibits all three germ layers, a yolk sac, and an allantois, which forms the basis of the umbilical cord. ...
... 16-day embryo. Cytotrophoblast and associated mesoderm have become the chorion, and chorionic villi are elaborating. The embryo exhibits all three germ layers, a yolk sac, and an allantois, which forms the basis of the umbilical cord. ...
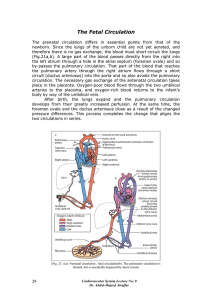
The Fetal Circulation The prenatal circulation differs in essential
... and is the common trunk (brachiocephalic trunk, innominate artery) of the right subclavian and right common carotid arteries. The second and third branches leaving the aortic arch are the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery. The two common carotid arteries run cephalad and divi ...
... and is the common trunk (brachiocephalic trunk, innominate artery) of the right subclavian and right common carotid arteries. The second and third branches leaving the aortic arch are the left common carotid artery and the left subclavian artery. The two common carotid arteries run cephalad and divi ...
the portal vein
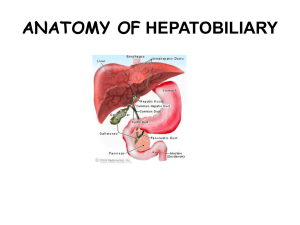
... • is about 18 cm (7 inches) across and 15 cm (6 inches) deep at its deepest part -- range : 6-12 cm in percussion at right mic line • medical terms to do with the liver often start in hepato- or hepatic from the Greek hepar for liver. ...
... • is about 18 cm (7 inches) across and 15 cm (6 inches) deep at its deepest part -- range : 6-12 cm in percussion at right mic line • medical terms to do with the liver often start in hepato- or hepatic from the Greek hepar for liver. ...
incomplete formation of posterior cord of brachial plexus: a case report
... branching patterns of brachial plexus are quite common and have been reported time and again by several authors. The variations can occur in the formation of trunks, divisions, cords, at the ...
... branching patterns of brachial plexus are quite common and have been reported time and again by several authors. The variations can occur in the formation of trunks, divisions, cords, at the ...
Axilla and Brachial Region - UNE Faculty/Staff Index Page
... Profunda Brachii Resist abduction (deep A of arm) of Olecranon, Extend forearm & Stabilize elbow ...
... Profunda Brachii Resist abduction (deep A of arm) of Olecranon, Extend forearm & Stabilize elbow ...
The Meninges and Blood Vessels of Brain and Spinal Cord, and the
... Cerebral Dural Mater Sinuses of duramater ...
... Cerebral Dural Mater Sinuses of duramater ...
12-Aortic Arches2009-01-26 02:4412.5 MB
... The narrowing is distal to the ductus arteriosus. The ductus usually remains open to communicate pulmonary artery with the descending aorta Even with an open ductus arteriosus blood flow to the lower body can be impaired. Allows development of collateral circulation during the fetal period. ...
... The narrowing is distal to the ductus arteriosus. The ductus usually remains open to communicate pulmonary artery with the descending aorta Even with an open ductus arteriosus blood flow to the lower body can be impaired. Allows development of collateral circulation during the fetal period. ...
4.3.3 Go With The Flow
... • Note that the heart is responsible for pumping blood to all of the organs of the body, but remember, the tissue of the heart also needs to be bathed in blood. The hard-working muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen. The muscle of the heart receives blood through tiny vessels called the coronary ...
... • Note that the heart is responsible for pumping blood to all of the organs of the body, but remember, the tissue of the heart also needs to be bathed in blood. The hard-working muscle needs a constant supply of oxygen. The muscle of the heart receives blood through tiny vessels called the coronary ...
Laparoscopic repair of inguinal hernia
... dissection is the antero-superior iliac spine while inferior limit laterally is the psoas muscle. Dissection should be avoided in the "triangle of doom" which is bounded medially by the vas deferens and laterally by the gonadal vessels. The tacker application and application of electrosurgery should ...
... dissection is the antero-superior iliac spine while inferior limit laterally is the psoas muscle. Dissection should be avoided in the "triangle of doom" which is bounded medially by the vas deferens and laterally by the gonadal vessels. The tacker application and application of electrosurgery should ...
INTRODUCTION & BACK - China Medical University
... myelogram (injection of a radio-opaque dye into the subarachnoid space followed by a radiograph). In order to inject the dye without injury to the spinal cord, the injection is usually done below what vertebral level? A. L1 ...
... myelogram (injection of a radio-opaque dye into the subarachnoid space followed by a radiograph). In order to inject the dye without injury to the spinal cord, the injection is usually done below what vertebral level? A. L1 ...
Vocal Cord Paralysis Medialization Laryngoplasty
... Reconstituted with Lidocaine or Saline Lasts 3-6 months requires low volume (~.2ml) when placed just deep to the vocal ligament in the vocalis muscle (varies with dilution) Injection into superficial lamina propria must be avoided or rigidity of cord will occur ...
... Reconstituted with Lidocaine or Saline Lasts 3-6 months requires low volume (~.2ml) when placed just deep to the vocal ligament in the vocalis muscle (varies with dilution) Injection into superficial lamina propria must be avoided or rigidity of cord will occur ...
Angiology_SLDC
... • Alternate routes of blood flow developed primarily within the arterial system which help to compensate for atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis in the body. Collateral circulation develops with time and exercise. ...
... • Alternate routes of blood flow developed primarily within the arterial system which help to compensate for atherosclerosis and arteriosclerosis in the body. Collateral circulation develops with time and exercise. ...
Structure of the Posterior Abdominal Wall
... connective tissue called Wharton’s jelly. Embedded in this are the remains of the yolk sac, the vitelline duct, the remains of the allantois, and the umbilical blood vessels. ...
... connective tissue called Wharton’s jelly. Embedded in this are the remains of the yolk sac, the vitelline duct, the remains of the allantois, and the umbilical blood vessels. ...
lumbar plexus
... of sensation of skin of anteromedial aspects of the thigh, medial side of knee, leg and foot ...
... of sensation of skin of anteromedial aspects of the thigh, medial side of knee, leg and foot ...
Lecture # 20: The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... functions of the spinal cord. 2- Name the three coverings of the central nervous system and give the characteristics, location, and function of each. 3- Identify ventral root, dorsal root, and dorsal root ganglion and give the composition of each. 4- Discuss white matter, gray matter, tracts, and nu ...
... functions of the spinal cord. 2- Name the three coverings of the central nervous system and give the characteristics, location, and function of each. 3- Identify ventral root, dorsal root, and dorsal root ganglion and give the composition of each. 4- Discuss white matter, gray matter, tracts, and nu ...
axilla - KSUMSC
... muscle and is attached to the clavicle Below it splits to enclose the pectoralis minor muscle Then continues downward as the suspensory ligament of the axilla Then joins the fascial floor of armpit ...
... muscle and is attached to the clavicle Below it splits to enclose the pectoralis minor muscle Then continues downward as the suspensory ligament of the axilla Then joins the fascial floor of armpit ...
BLOOD VESSELS
... Veins generally pass between skeletal muscles whose squeezing effects facilitate venous return. This is known as skeletal muscle pump ...
... Veins generally pass between skeletal muscles whose squeezing effects facilitate venous return. This is known as skeletal muscle pump ...
V. Blood Pressure
... B. Arteries and Arterioles 1. Arteries are ______________________________________ that are adapted for __________________________________________________________________ 2. Arteries give rise to _______________________________________________ 3. The three layers of the wall of an artery are ________ ...
... B. Arteries and Arterioles 1. Arteries are ______________________________________ that are adapted for __________________________________________________________________ 2. Arteries give rise to _______________________________________________ 3. The three layers of the wall of an artery are ________ ...
Shier, Butler, and Lewis: Hole`s Human Anatomy and Physiology
... B. Arteries and Arterioles 1. Arteries are ______________________________________ that are adapted for __________________________________________________________________ 2. Arteries give rise to _______________________________________________ 3. The three layers of the wall of an artery are ________ ...
... B. Arteries and Arterioles 1. Arteries are ______________________________________ that are adapted for __________________________________________________________________ 2. Arteries give rise to _______________________________________________ 3. The three layers of the wall of an artery are ________ ...
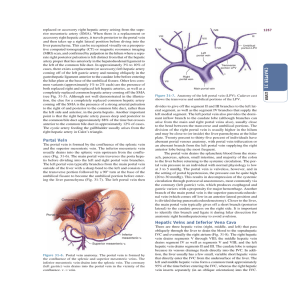
CHAPTER 31 Portal Vein Hepatic Veins and Inferior
... divides to give off the segment II and III branches to the left lateral segment, as well as the segment IV branches that supply the left medial segment. The left portal vein also provides the dominant inflow branch to the caudate lobe (although branches can arise from the main and right portal veins ...
... divides to give off the segment II and III branches to the left lateral segment, as well as the segment IV branches that supply the left medial segment. The left portal vein also provides the dominant inflow branch to the caudate lobe (although branches can arise from the main and right portal veins ...
Neuraxial Blockade Anatomy and Landmarks
... administration of thoracic epidurals It is helpful to count up and down to help ensure you are placing the thoracic epidural in the appropriate area for postoperative analgesia ...
... administration of thoracic epidurals It is helpful to count up and down to help ensure you are placing the thoracic epidural in the appropriate area for postoperative analgesia ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.