neuropathic pain models 1 - Pittsburgh Center for Pain Research
... pupil dilation, slurred speech, aphasia (difficulty in word finding), etc. ...
... pupil dilation, slurred speech, aphasia (difficulty in word finding), etc. ...
Arteries and Veins Worksheet
... 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder. 6) The common iliac vein which is for ...
... 4) The hepatic portal vein drains the digestive tract organs and carries this blood through the liver before it enters the systemic circulation. The hepatic veins drain the liver. 5) The internal iliac vein drains blood from the rectum and tissue of the bladder. 6) The common iliac vein which is for ...
neck injuries
... fracture (discussed under Vertical (axial) compression injury above). This is the most significant type of atlas fracture from a clinical standpoint because it is associated with neurologic impairment. Atlantoaxial subluxation When flexion occurs without a lateral or rotatory component at the upper ...
... fracture (discussed under Vertical (axial) compression injury above). This is the most significant type of atlas fracture from a clinical standpoint because it is associated with neurologic impairment. Atlantoaxial subluxation When flexion occurs without a lateral or rotatory component at the upper ...
Hypothalamic vascularization in the common tree
... proximal parts of the two internal carotid arteries (Fig 1a). It consists of optic chiasma, tuberal region and infundibulum. The optic chiasma is shown to be supplied by the three main sources (Fig 1b). The first source is from prechiasmal branches of the ophthalmic arteries (OA). They loop along th ...
... proximal parts of the two internal carotid arteries (Fig 1a). It consists of optic chiasma, tuberal region and infundibulum. The optic chiasma is shown to be supplied by the three main sources (Fig 1b). The first source is from prechiasmal branches of the ophthalmic arteries (OA). They loop along th ...
Blood Vessel Lab
... upper extremities into the right atrium of the heart. Branches of the Superior Vena Cava 48. The two, prominent brachiocephalic veins are formed by the forking (bifurcation) of the superior vena cava. They extend upward to the right and left and receive blood from the internal jugular veins and the ...
... upper extremities into the right atrium of the heart. Branches of the Superior Vena Cava 48. The two, prominent brachiocephalic veins are formed by the forking (bifurcation) of the superior vena cava. They extend upward to the right and left and receive blood from the internal jugular veins and the ...
Arteries to the Neck, Head, and Brain
... 3. Left and right common carotid arteries diverge into internal and external carotid arteries – External carotid artery goes up the side of the head giving off branches to structures in the neck, face, jaw, and base of the skull – Internal carotid artery follows a deeper course along the pharynx to ...
... 3. Left and right common carotid arteries diverge into internal and external carotid arteries – External carotid artery goes up the side of the head giving off branches to structures in the neck, face, jaw, and base of the skull – Internal carotid artery follows a deeper course along the pharynx to ...
Distal - Fun Anatomy
... Action: flex DIP of digits 2-5. Assist flex of PIP, MP, and wrist PERIPHERAL NERVE + spinal cord level of origin: median nerve to digits 2 + 3. Ulnar nerve to digits 4 + 5 Spinal segments: C8, T1 ...
... Action: flex DIP of digits 2-5. Assist flex of PIP, MP, and wrist PERIPHERAL NERVE + spinal cord level of origin: median nerve to digits 2 + 3. Ulnar nerve to digits 4 + 5 Spinal segments: C8, T1 ...
ppt
... the colon, and equal numbers occur in the jejunum and ileum (1/1500 births). Atresias in the upper duodenum are probably ...
... the colon, and equal numbers occur in the jejunum and ileum (1/1500 births). Atresias in the upper duodenum are probably ...
Additional lateral root of the Ulnar and Median nerves
... Apart from the fourth branch emerging from the lateral chord, the rest of the brachial plexus follows the regular pattern, and no other variation can be observed. ...
... Apart from the fourth branch emerging from the lateral chord, the rest of the brachial plexus follows the regular pattern, and no other variation can be observed. ...
An unusual case of accessory head of coracobrachialis muscle
... interpretation of unusual clinical signs or during physical or diagnostic imaging. This case study is a description of an anatomical variation between the coracobrachialis muscle and brachial plexus. In a routine dissection in the human anatomy laboratory, we were faced with an anatomical variation ...
... interpretation of unusual clinical signs or during physical or diagnostic imaging. This case study is a description of an anatomical variation between the coracobrachialis muscle and brachial plexus. In a routine dissection in the human anatomy laboratory, we were faced with an anatomical variation ...
BIO 218 F 2012 CH 26 martini lecture Outline
... Stabilizes blood pH Prevents the loss of valuable nutrients Eliminates organic matter Synthesizes calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) Prevents dehydration Aids the liver with some of its functions ...
... Stabilizes blood pH Prevents the loss of valuable nutrients Eliminates organic matter Synthesizes calcitriol (active form of vitamin D) Prevents dehydration Aids the liver with some of its functions ...
vein - SLCC Anatomy
... merges with internal jugular vein to form brachiocephalic vein merges with brachiocephalic vein from opposite side to form superior vena cava ...
... merges with internal jugular vein to form brachiocephalic vein merges with brachiocephalic vein from opposite side to form superior vena cava ...
spinal nerves
... The chickenpox virus can invade the ganglia along the spinal cord and remain latent until adulthood. It can then be activated by suppression of the immune system. It will then travel through sensory axons of a single dermatome and erupt onto the skin in a single dermatome on one side of the body (un ...
... The chickenpox virus can invade the ganglia along the spinal cord and remain latent until adulthood. It can then be activated by suppression of the immune system. It will then travel through sensory axons of a single dermatome and erupt onto the skin in a single dermatome on one side of the body (un ...
“Suppliers of advanced neuro embolisation coils” Foramen magnum
... • Sensory loss is usually dissociated, with bilateral spinothalamic loss (40%) (caused by ipsilateral root and spinothalamic tract compromise) and dorsal column dysfunction (26%). • Rarely: papilloedema (7%), Horner's (4%), hiccups (2%). Intracranial extension of the lesion is indicated by: • Downbe ...
... • Sensory loss is usually dissociated, with bilateral spinothalamic loss (40%) (caused by ipsilateral root and spinothalamic tract compromise) and dorsal column dysfunction (26%). • Rarely: papilloedema (7%), Horner's (4%), hiccups (2%). Intracranial extension of the lesion is indicated by: • Downbe ...
the major blood vessels of the wing of the ostrich
... the antebrachium and manus comes from the ulnar artery and its branches, the deep and superficial ulnar arteries. In the present study, the radial artery was found to form the mam blood supply to the wing. The ulnar artery was poorly develofed and represented only the superficial ulnar artery o othe ...
... the antebrachium and manus comes from the ulnar artery and its branches, the deep and superficial ulnar arteries. In the present study, the radial artery was found to form the mam blood supply to the wing. The ulnar artery was poorly develofed and represented only the superficial ulnar artery o othe ...
Chapter 01 FlexArt
... stimulate quadriceps to contract, producing knee jerk. 5 At same time, a branch of the afferent nerve fiber stimulates inhibitory motor neuron in spinal cord. 6 That neuron inhibits alpha motor neuron that supplies hamstring muscles. 7 Hamstring contraction is inhibited so hamstrings (knee flexors) ...
... stimulate quadriceps to contract, producing knee jerk. 5 At same time, a branch of the afferent nerve fiber stimulates inhibitory motor neuron in spinal cord. 6 That neuron inhibits alpha motor neuron that supplies hamstring muscles. 7 Hamstring contraction is inhibited so hamstrings (knee flexors) ...
Invertebrate Chordate Notes
... tuh kord) — a long, semirigid, rod-like structure located between the digestive system and the dorsal hollow nerve cord. ...
... tuh kord) — a long, semirigid, rod-like structure located between the digestive system and the dorsal hollow nerve cord. ...
PAC01 Abdomen
... artery, a branch of the femoral artery, and from the inferior epigastric artery. Scrotal veins are of the same name as the arteries they parallel. Nerves are associated with the genitofemoral nerves from L1 & L2, ilioinguinal from L1, pudental nerve from S2,S3,&S4, and posterior femoral cutaneous n ...
... artery, a branch of the femoral artery, and from the inferior epigastric artery. Scrotal veins are of the same name as the arteries they parallel. Nerves are associated with the genitofemoral nerves from L1 & L2, ilioinguinal from L1, pudental nerve from S2,S3,&S4, and posterior femoral cutaneous n ...
Brachial Plexus
... • Nerve injuries can result from: Blunt force trauma, poor posture or chronic repetitive stress. ...
... • Nerve injuries can result from: Blunt force trauma, poor posture or chronic repetitive stress. ...
an uncommon variation in the formation of trunks of the brachial
... triangle from the trunks run in the cervico axillary canal behind the clavicle, will form the cords in the axilla. The cords are related to the second part of axillary artery. The branches of the cords are given off in the axilla (1). Variations in the formation of brachial plexus are common and oft ...
... triangle from the trunks run in the cervico axillary canal behind the clavicle, will form the cords in the axilla. The cords are related to the second part of axillary artery. The branches of the cords are given off in the axilla (1). Variations in the formation of brachial plexus are common and oft ...
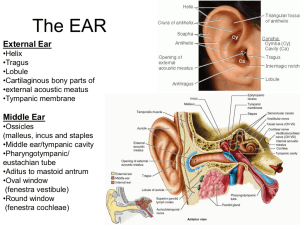
The EAR - Ipswich-Year2-Med-PBL-Gp-2
... • L coronary artery supplies L atrium and ventricle, most of IV septum including Bundle of His and Branches and small part of R ventricle (none of R atrium) A cross-section of the right and left ventricles demonstrates the most common pattern of distribution of blood from the RCA (red) and LCA (pink ...
... • L coronary artery supplies L atrium and ventricle, most of IV septum including Bundle of His and Branches and small part of R ventricle (none of R atrium) A cross-section of the right and left ventricles demonstrates the most common pattern of distribution of blood from the RCA (red) and LCA (pink ...
File
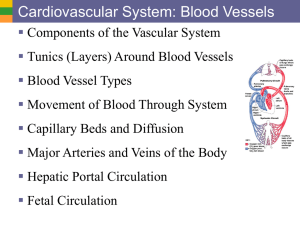
... The systemic circulation Includes the arteries and arterioles that carry blood containing oxygen and nutrients from the left ventricle to systemic capillaries throughout the body, plus the venules and veins that carry blood ...
... The systemic circulation Includes the arteries and arterioles that carry blood containing oxygen and nutrients from the left ventricle to systemic capillaries throughout the body, plus the venules and veins that carry blood ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.