Pectoral region and axilla
... second or third intercostal nerves.It will often communicate with the medial brachial cutaneous nerve. The intercostobrachial nerve primarily supplies the skin on the floor of the axilla and some of the adjacent regions of the arm. ...
... second or third intercostal nerves.It will often communicate with the medial brachial cutaneous nerve. The intercostobrachial nerve primarily supplies the skin on the floor of the axilla and some of the adjacent regions of the arm. ...
The_Ruminant_Gastrointestinal_Tract_3
... arise from the mesoderm. The nerves which innervate these tissues have their origin in the neural ectoderm. Liver and pancreas develop as branching, tubular extensions from the duodenum. The form of the digestive tube at an early embryonic age looks like this: ...
... arise from the mesoderm. The nerves which innervate these tissues have their origin in the neural ectoderm. Liver and pancreas develop as branching, tubular extensions from the duodenum. The form of the digestive tube at an early embryonic age looks like this: ...
CLINICAL ANATOMY OF THE ESOPHAGUS, STOMACH
... biliary tract begins with the right and left hepatic duct. The common hepatic duct makes up the left border of the triangle of Calot, and is continuous with the common bile duct, and the division, which is fairly arbitrary, occur at the level of the cystic duct. The common bile duct is approximately ...
... biliary tract begins with the right and left hepatic duct. The common hepatic duct makes up the left border of the triangle of Calot, and is continuous with the common bile duct, and the division, which is fairly arbitrary, occur at the level of the cystic duct. The common bile duct is approximately ...
methodological developments to practical classes on neurology for
... objects by touch is known as: ...
... objects by touch is known as: ...
The Reproductive System: Embryology and Human Development
... For clarity, the uterus is shown after the embryo has been removed and the umbilical cord cut. Blood flows into the placenta through ruptured maternal arteries. It then flows around chorionic villi, which contain fetal blood vessels. Fetal blood arrives through paired umbilical arteries and leaves t ...
... For clarity, the uterus is shown after the embryo has been removed and the umbilical cord cut. Blood flows into the placenta through ruptured maternal arteries. It then flows around chorionic villi, which contain fetal blood vessels. Fetal blood arrives through paired umbilical arteries and leaves t ...
Veins of the Face and the Neck The facial vein is formed at the
... The internal jugular vein is a large vein that receives blood from the brain, face, and neck .It starts as a continuation of the sigmoid sinus and leaves the skull through the jugular foramen.. It ends by joining the subclavian vein behind the medial end of the clavicle to form the brachiocephalic v ...
... The internal jugular vein is a large vein that receives blood from the brain, face, and neck .It starts as a continuation of the sigmoid sinus and leaves the skull through the jugular foramen.. It ends by joining the subclavian vein behind the medial end of the clavicle to form the brachiocephalic v ...
scrotum & prostate - Orange Coast College
... 2. Usually seen on left (why??) 3. Can be palpated a. feels like a “bag of worms” ...
... 2. Usually seen on left (why??) 3. Can be palpated a. feels like a “bag of worms” ...
SCROTUM & PROSTATE - Hastaneciyiz's Blog
... 2. Usually seen on left (why??) 3. Can be palpated a. feels like a “bag of worms” ...
... 2. Usually seen on left (why??) 3. Can be palpated a. feels like a “bag of worms” ...
Clinical Anatomy of the Spine
... Chapter 1 – Surface Anatomy of the Back and Vertebral Levels of Clinically Important Structures Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and ANS Several muscles are commonly visible in the back region. The trapezius is a large, flat, triangular muscle that originates in the midline from the E ...
... Chapter 1 – Surface Anatomy of the Back and Vertebral Levels of Clinically Important Structures Clinical Anatomy of the Spine, Spinal Cord, and ANS Several muscles are commonly visible in the back region. The trapezius is a large, flat, triangular muscle that originates in the midline from the E ...
Histological Organization of Blood Vessels
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
... In areas such as the brain, heart, and stomach, a continuous, rich flow of blood is required In these areas, more than one artery supplies a specific area These arteries (collateral arteries) typically fuse forming an arterial anastomosis If one arteriole is blocked, the other one will suppl ...
Medial surface Central sulcus on axial imaging cs cs pM pocs
... 3. posterior ear line: perpendicular to the baseline through the mastoid process 4. condylar line: perpendicular to the baseline through the mandibular condyle 5. T-H lines can then be used to approximate the sylvian fissure (see below) and the motor cortex (also see below) ©2001 Mark S Greenberg, M ...
... 3. posterior ear line: perpendicular to the baseline through the mastoid process 4. condylar line: perpendicular to the baseline through the mandibular condyle 5. T-H lines can then be used to approximate the sylvian fissure (see below) and the motor cortex (also see below) ©2001 Mark S Greenberg, M ...
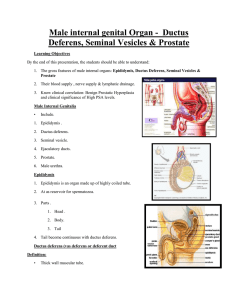
Male internal genital Organ - Ductus Deferens, Seminal Vesicles
... 3. In greater pelvis. 4. In lesser pelvis. Course & relation of ductus deferens 1. Begins as continuation of tail of epididymus. 2. Along posterior border of the testis . ...
... 3. In greater pelvis. 4. In lesser pelvis. Course & relation of ductus deferens 1. Begins as continuation of tail of epididymus. 2. Along posterior border of the testis . ...
Development of the Urinary System 3 Distinct Embryonic Kidney
... • the kidney ascends from pelvis into abdomen • rotates 90o laterally during ascent • vascular supply changes as it ascends: may lead to accessory renal vessels • the gonad descends: thus the relative position of the gonad and kidney reverse ...
... • the kidney ascends from pelvis into abdomen • rotates 90o laterally during ascent • vascular supply changes as it ascends: may lead to accessory renal vessels • the gonad descends: thus the relative position of the gonad and kidney reverse ...
Lecture 12- Venous System by Dr. Istiak Mahfuz
... go through the capillary network, but from the hepatic veins it receives blood which has come through the liver sinusoids. The postcaval vein has two separate embryonic origins. Anteriorly this vein develops from a caudal evagination of the right hepatic vein; posteriorly it is a continuation of the ...
... go through the capillary network, but from the hepatic veins it receives blood which has come through the liver sinusoids. The postcaval vein has two separate embryonic origins. Anteriorly this vein develops from a caudal evagination of the right hepatic vein; posteriorly it is a continuation of the ...
The uterus
... The development of ovary occur 2 weeks later than development of testes The sex cord develop extensively and the epithelium cells in this area known as pregranulosa The next stage of development involve the primitive germ cell now known as oocyte and surrounded by ring of pregranulosa cell .this ger ...
... The development of ovary occur 2 weeks later than development of testes The sex cord develop extensively and the epithelium cells in this area known as pregranulosa The next stage of development involve the primitive germ cell now known as oocyte and surrounded by ring of pregranulosa cell .this ger ...
Frontal Lobe
... Strong, crescent-shaped vertical sheet of dura located in the interhemispheric (longitudinal) fissure between the cerebral hemispheres ...
... Strong, crescent-shaped vertical sheet of dura located in the interhemispheric (longitudinal) fissure between the cerebral hemispheres ...
1. The part of a spinal nerve that supplies the true back muscles and
... Somatic afferent neurons originate from the dorsal root and dorsal rootlets. If dorsal rootlets were avulsed, somatic afferent nerve fibers would be damaged. Somatic efferent neurons originate from the ventral root and ventral rootlets. If ventral rootlets were avulsed, somatic efferent nerve fibers ...
... Somatic afferent neurons originate from the dorsal root and dorsal rootlets. If dorsal rootlets were avulsed, somatic afferent nerve fibers would be damaged. Somatic efferent neurons originate from the ventral root and ventral rootlets. If ventral rootlets were avulsed, somatic efferent nerve fibers ...
1. During an intramural baseball game a player is hit in the side of
... infections in this layer can pass into the cranial cavity through emissary veins. So, infections in the loose connective tissue can pass into intracranial structures such as the brain and meninges. This can also be called the "danger layer" of the scalp. Remember--the scalp is comprised of the foll ...
... infections in this layer can pass into the cranial cavity through emissary veins. So, infections in the loose connective tissue can pass into intracranial structures such as the brain and meninges. This can also be called the "danger layer" of the scalp. Remember--the scalp is comprised of the foll ...
Labeled diagram of the foramen magnum
... Draw an arrow and write a label on Diagram 2 to indicate the. Look at the skulls and determine the position of the foramen magnum – is its position on the anatomy of the inferior skull including: the foramen magnum, occipital condyles, mastoid. .. Labeled diagrams will be very important in a physiol ...
... Draw an arrow and write a label on Diagram 2 to indicate the. Look at the skulls and determine the position of the foramen magnum – is its position on the anatomy of the inferior skull including: the foramen magnum, occipital condyles, mastoid. .. Labeled diagrams will be very important in a physiol ...
Development of the nervous system and sense organs I
... infundibulum (part of the hypophysis) originate as an evagination from the caudal part at a level caudal to the optic stalk. The development of the optic stalk will be described in detail together with the development of the eye. D- The mesencephalon: 1- The mesencephalon develops from the fourth an ...
... infundibulum (part of the hypophysis) originate as an evagination from the caudal part at a level caudal to the optic stalk. The development of the optic stalk will be described in detail together with the development of the eye. D- The mesencephalon: 1- The mesencephalon develops from the fourth an ...
Axillary artery
... The arteries, veins, lymphatics, and nerves traverse this superior opening of the axilla to pass to or from the arm. ...
... The arteries, veins, lymphatics, and nerves traverse this superior opening of the axilla to pass to or from the arm. ...
Gateway To The Upper Limb
... The arteries, veins, lymphatics, and nerves traverse this superior opening of the axilla to pass to or from the arm. ...
... The arteries, veins, lymphatics, and nerves traverse this superior opening of the axilla to pass to or from the arm. ...
Brachial Plexus
... • The musculocutaneous nerve may fuse to or have communications with the median nerve , which can result in its absence from within the coracobrachialis muscle. • Communication between median and ulnar nerves is common in the forearm with the median nerve replacing the innervations to various muscl ...
... • The musculocutaneous nerve may fuse to or have communications with the median nerve , which can result in its absence from within the coracobrachialis muscle. • Communication between median and ulnar nerves is common in the forearm with the median nerve replacing the innervations to various muscl ...
Entodermal derivatives: formation of the gut, liver, and pancreas
... dorsal and ventral mesenteries; mesenteries; ventral ventral is is lost lost except except in in region of liver. Vetelline duct remains in umbilical cord. ...
... dorsal and ventral mesenteries; mesenteries; ventral ventral is is lost lost except except in in region of liver. Vetelline duct remains in umbilical cord. ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.