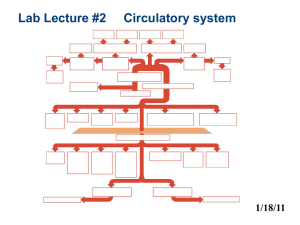
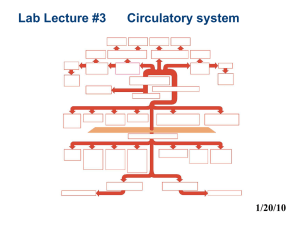
Arteries
... • RBCs continually produced and recycled • 1 percent replaced each day • 3 million new RBCs enter bloodstream each second • Short lifespan of 120 days, then: • Plasma membrane ruptures or cell is engulfed by macrophages • Broken down in liver, spleen, or red bone marrow ...
... • RBCs continually produced and recycled • 1 percent replaced each day • 3 million new RBCs enter bloodstream each second • Short lifespan of 120 days, then: • Plasma membrane ruptures or cell is engulfed by macrophages • Broken down in liver, spleen, or red bone marrow ...
failure, and stroke
... • Angiogenesis • Occurs when short-term autoregulation cannot meet tissue nutrient requirements • The number of vessels to a region increases and existing vessels enlarge • Common in the heart when a coronary vessel is occluded, or throughout the body in people in high-altitude areas ...
... • Angiogenesis • Occurs when short-term autoregulation cannot meet tissue nutrient requirements • The number of vessels to a region increases and existing vessels enlarge • Common in the heart when a coronary vessel is occluded, or throughout the body in people in high-altitude areas ...
Blood Flow
... • Angiogenesis • Occurs when short-term autoregulation cannot meet tissue nutrient requirements • The number of vessels to a region increases and existing vessels enlarge • Common in the heart when a coronary vessel is occluded, or throughout the body in people in high-altitude areas ...
... • Angiogenesis • Occurs when short-term autoregulation cannot meet tissue nutrient requirements • The number of vessels to a region increases and existing vessels enlarge • Common in the heart when a coronary vessel is occluded, or throughout the body in people in high-altitude areas ...
08 Vasculature of lower limb
... Popliteal vein Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of th ...
... Popliteal vein Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of th ...
Extra Embryonic Membranes
... constantly spreads over the yolk mass and eventually yolk sac encloses the mass of yolk in a large measure. The yolk sac, however, not surrounds the yolk fully. A small passage is left on the ventral side for the embryo to absorb the remains of albumen at a later stage. Immediately with the formatio ...
... constantly spreads over the yolk mass and eventually yolk sac encloses the mass of yolk in a large measure. The yolk sac, however, not surrounds the yolk fully. A small passage is left on the ventral side for the embryo to absorb the remains of albumen at a later stage. Immediately with the formatio ...
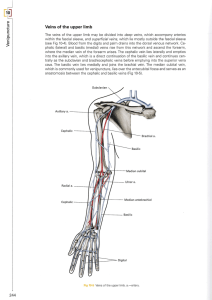
The Blood Vessels of the Upper Extremity
... The arteries of the upper limb may be damaged by penetrating wounds or may require ligation in amputation operations. Because of adequate collateral circulation around the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints, ligation of the main arteries of the upper limb is not followed by tissue necrosis or gangren ...
... The arteries of the upper limb may be damaged by penetrating wounds or may require ligation in amputation operations. Because of adequate collateral circulation around the shoulder, elbow, and wrist joints, ligation of the main arteries of the upper limb is not followed by tissue necrosis or gangren ...
CHAPTER 9 Questions
... Restricted Cervical Injection~ Both right and the left common carotid arteries are raised; tubes are placed into them and directed toward the head on both right and left side. One tube is directed toward the trunk into the right artery; the inferior portion of the left artery is ligated. Drainage is ...
... Restricted Cervical Injection~ Both right and the left common carotid arteries are raised; tubes are placed into them and directed toward the head on both right and left side. One tube is directed toward the trunk into the right artery; the inferior portion of the left artery is ligated. Drainage is ...
BLOOD SUPPLY OF EYE - Home
... passes through the optic canal within the dural sheath of optic nerve , lying inferior to it. Intraorbital part :At the apex of the orbit in the muscle cone , the artery pierces the dural sheath of the optic nerve and comes to lie lateral to the optic nerve and medial to the Oculomotor and Abducen ...
... passes through the optic canal within the dural sheath of optic nerve , lying inferior to it. Intraorbital part :At the apex of the orbit in the muscle cone , the artery pierces the dural sheath of the optic nerve and comes to lie lateral to the optic nerve and medial to the Oculomotor and Abducen ...
.g Veins of the upper Iimb
... The veins of the upper limb may be divided into deep verns, which accompany arteries within the fascial sleeve, and superficial veins, which lie mostly outside the fascial sleeve (see Fig 10-4). Blood from the digits and palm drains into the dorsal venous network. Cephalic (lateral) and basilic (med ...
... The veins of the upper limb may be divided into deep verns, which accompany arteries within the fascial sleeve, and superficial veins, which lie mostly outside the fascial sleeve (see Fig 10-4). Blood from the digits and palm drains into the dorsal venous network. Cephalic (lateral) and basilic (med ...
05-Kidney, Ureter
... the posterior abdominal wall It lie high up on either side of the vertebral column ...
... the posterior abdominal wall It lie high up on either side of the vertebral column ...
Blood supply to the femoral head
... From 4 to 7 The Epiphysial plate has established a firm barrier between epiphysis and metaphysis The Metaphysial blood flow decreases to ...
... From 4 to 7 The Epiphysial plate has established a firm barrier between epiphysis and metaphysis The Metaphysial blood flow decreases to ...
75 - Spine Trauma and Spinal Cord Injury
... which are suggestive of an associated intrathoracic injury or myocardial contusion. Thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures: Check for abdominal or pelvic tenderness. For instance, up to 50% of patients with a transverse process fracture7 and 33% of patients with a Chance fracture8 have concurrent ...
... which are suggestive of an associated intrathoracic injury or myocardial contusion. Thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures: Check for abdominal or pelvic tenderness. For instance, up to 50% of patients with a transverse process fracture7 and 33% of patients with a Chance fracture8 have concurrent ...
see p. D70 - Viktor`s Notes for the Neurosurgery Resident
... – 25% of asymptomatic people have small lumbar disc protrusions visible on MRI; – some patients with disabling clinical symptoms have minimal abnormalities on MRI. MRI is imaging modality of first choice; other investigations are considered only when MRI is either contraindicated or impossible. Imag ...
... – 25% of asymptomatic people have small lumbar disc protrusions visible on MRI; – some patients with disabling clinical symptoms have minimal abnormalities on MRI. MRI is imaging modality of first choice; other investigations are considered only when MRI is either contraindicated or impossible. Imag ...
Spinal nerve
... posterior root ganglia in the spinal cord • if reactivated, travels through sensory axons to dermatomes associated with infected ganglia ...
... posterior root ganglia in the spinal cord • if reactivated, travels through sensory axons to dermatomes associated with infected ganglia ...
Study Guide
... Venous Sinuses of the Cranium • Dural venous sinuses receive blood that has circulated through the brain and orbit • Blood from these sinuses empties into internal jugular vein • Internal jugular vein exits skull through the ...
... Venous Sinuses of the Cranium • Dural venous sinuses receive blood that has circulated through the brain and orbit • Blood from these sinuses empties into internal jugular vein • Internal jugular vein exits skull through the ...
L16- Art,Veins.& ymp..
... the great saphenous vein itself. This allows the passage of high pressure blood from the deep to the superficial veins. ...
... the great saphenous vein itself. This allows the passage of high pressure blood from the deep to the superficial veins. ...
Bilateral variations of brachial plexus involving the median nerve
... (Figure 1) prior to its bifurcation into the musculocutaneous nerve and the lateral root of the median nerve. The lateral cord of brachial plexus was piercing the coracobrachialis muscle about 11.4 cm away from the acromion process of the scapula. The medial root of the medial cord, travelling to ad ...
... (Figure 1) prior to its bifurcation into the musculocutaneous nerve and the lateral root of the median nerve. The lateral cord of brachial plexus was piercing the coracobrachialis muscle about 11.4 cm away from the acromion process of the scapula. The medial root of the medial cord, travelling to ad ...
Transcripts/4_6 1
... 2. The structural difference between arteries and veins is primarily the degree of development of the tunica media. For any given size, the tunica media in an artery is thicker than in a vein. (The more rigid wall of an artery compared to the thinner, more collapsed wall of a vein usually makes it e ...
... 2. The structural difference between arteries and veins is primarily the degree of development of the tunica media. For any given size, the tunica media in an artery is thicker than in a vein. (The more rigid wall of an artery compared to the thinner, more collapsed wall of a vein usually makes it e ...
Major arteries of the body
... All arteries, carry oxygenated blood, except the pulmonary and umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs (postnatal) and to the placenta (prenatal) respectively The flow of blood depends on the pumping action of the heart There are no valves in the arteries. The branches of art ...
... All arteries, carry oxygenated blood, except the pulmonary and umbilical arteries, which carry deoxygenated blood to the lungs (postnatal) and to the placenta (prenatal) respectively The flow of blood depends on the pumping action of the heart There are no valves in the arteries. The branches of art ...
L18-Art,Veins. OF L.L2014-08-21 09:594.2 MB
... saphenous and the other joins the Popliteal vein. ...
... saphenous and the other joins the Popliteal vein. ...
17-Art,Veins. OF L.L2014-12-23 00:294.5 MB
... saphenous and the other joins the Popliteal vein. ...
... saphenous and the other joins the Popliteal vein. ...
The Whipple Operation – Illustrations
... Fig. 9. Illustration of the important surgical anatomy of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV). The SMV usually bifurcates into two main branches, one to the ileum and one to the jejunum. Adequate venous return from the small bowel requires that one or the other of these two main SMV-tributaries is i ...
... Fig. 9. Illustration of the important surgical anatomy of the superior mesenteric vein (SMV). The SMV usually bifurcates into two main branches, one to the ileum and one to the jejunum. Adequate venous return from the small bowel requires that one or the other of these two main SMV-tributaries is i ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.