Gross 8/27/99 - GEOCITIES.ws
... C. Zygote (fertilized oocyte)-goes through fallopian tube to uterus 1. after zygote is formed-undergo rapid series of cell division— cleavage(figure 2 handout) 2. Daughter cells are identical-no genetic recombination. Size of zygote stays same—divided cells shrink with each divisionincrease ratio o ...
... C. Zygote (fertilized oocyte)-goes through fallopian tube to uterus 1. after zygote is formed-undergo rapid series of cell division— cleavage(figure 2 handout) 2. Daughter cells are identical-no genetic recombination. Size of zygote stays same—divided cells shrink with each divisionincrease ratio o ...
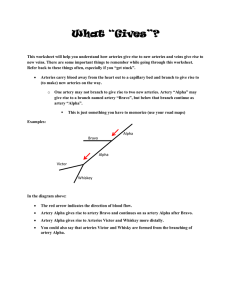
What “Gives”? - www.jgibbs-vvc
... This worksheet will help you understand how arteries give rise to new arteries and veins give rise to new veins. There are some important things to remember while going through this worksheet. Refer back to these things often, especially if you “get stuck”. ...
... This worksheet will help you understand how arteries give rise to new arteries and veins give rise to new veins. There are some important things to remember while going through this worksheet. Refer back to these things often, especially if you “get stuck”. ...
RLF- 6. Pectoral, Ax#*KZ+#W
... via the humerus (arm bone) (figs. 1 – 1, 6 – 3 & ppt. 1) - clavicle attaches to axial skeleton at the sternum (sternoclavicular joint) (ppt. 2) - sternum also provides anterior attachment for the ribs a. Humerus (fig. 6 – 3 & ppt. 1): review importance of: • head, greater and lesser tubercles, inter ...
... via the humerus (arm bone) (figs. 1 – 1, 6 – 3 & ppt. 1) - clavicle attaches to axial skeleton at the sternum (sternoclavicular joint) (ppt. 2) - sternum also provides anterior attachment for the ribs a. Humerus (fig. 6 – 3 & ppt. 1): review importance of: • head, greater and lesser tubercles, inter ...
PELVIS AND PERINEUM
... Diamond-shaped area below pelvic Diaphragm: Same boundaries as inferior pelvic aperture. Divided into two triangles: Anal triangle. Urogenital triangle. ...
... Diamond-shaped area below pelvic Diaphragm: Same boundaries as inferior pelvic aperture. Divided into two triangles: Anal triangle. Urogenital triangle. ...
Anatomy Block 5 Oral Quiz Review
... visceral peritoneum exists where the gut tube exits and enters the abdominal cavity. ...
... visceral peritoneum exists where the gut tube exits and enters the abdominal cavity. ...
Arteries - Princeton ISD
... Arteries and veins are composed of three tunics – tunica interna, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen – central blood-containing space ...
... Arteries and veins are composed of three tunics – tunica interna, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen – central blood-containing space ...
3-Major Veins of the Body
... between the veins of portal circulation and those of systemic circulation. o The anastomotic channels become dilated (varicosed) in case of portal hypertension. ...
... between the veins of portal circulation and those of systemic circulation. o The anastomotic channels become dilated (varicosed) in case of portal hypertension. ...
Dissector Bold terms 3
... -Right Astro-omental (from gastroduodenal branch of common hepatic) -Hepatic portal vein -Left/right portal veins -Left/right gastric veins Spleen -Visceral surface (stomach, left kidney, transverse colon, pancreas) -Diaphragmatic surface (ribs 9-11) Liver -Right/left lobes -Inferior border (separat ...
... -Right Astro-omental (from gastroduodenal branch of common hepatic) -Hepatic portal vein -Left/right portal veins -Left/right gastric veins Spleen -Visceral surface (stomach, left kidney, transverse colon, pancreas) -Diaphragmatic surface (ribs 9-11) Liver -Right/left lobes -Inferior border (separat ...
right and left brachiocephalic veins
... vena cava (SC ); the azygos vein; arch of the aorta and the descending thoracic aorta; pulmonary trunk, right and left pulmonary arteries and ligamentum arteriosum connecting the aortic arch and left pulmonary artery noting the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooking below the ligamentu ...
... vena cava (SC ); the azygos vein; arch of the aorta and the descending thoracic aorta; pulmonary trunk, right and left pulmonary arteries and ligamentum arteriosum connecting the aortic arch and left pulmonary artery noting the course of the left recurrent laryngeal nerve hooking below the ligamentu ...
26-arches+venous&lymphatics2008-05
... It passes upward in front of medial malleolus. In the leg : It ascends in company with saphenous nerve in superficial fascia of medial side of leg, then behind knee and curves forward on medial side of thigh. It pierces the cribriform fascia of saphenous opening in the deep fascia of thigh to joi ...
... It passes upward in front of medial malleolus. In the leg : It ascends in company with saphenous nerve in superficial fascia of medial side of leg, then behind knee and curves forward on medial side of thigh. It pierces the cribriform fascia of saphenous opening in the deep fascia of thigh to joi ...
1 3 Blood Supply to the Head and Neck The nutrients and oxygen
... The nutrients and oxygen necessary to sustain life are carried to all the cells of all of the tissues by the arteries. Veins and lymphatics pick up the waste products of cell metabolism and, together with deoxygenated red blood cells, return them to various areas. The blood is then rejuvenated and r ...
... The nutrients and oxygen necessary to sustain life are carried to all the cells of all of the tissues by the arteries. Veins and lymphatics pick up the waste products of cell metabolism and, together with deoxygenated red blood cells, return them to various areas. The blood is then rejuvenated and r ...
Slide 1
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
Branches
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
Development of the Inguinal Canal
... Normal spermatogenesis can occur only if the testes are at a temperature lower than that of the abdominal cavity. When they are located in the scrotum, they are at a temperature about 3°C lower than the abdominal temperature. The control of testicular temperature in the scrotum is not fully understo ...
... Normal spermatogenesis can occur only if the testes are at a temperature lower than that of the abdominal cavity. When they are located in the scrotum, they are at a temperature about 3°C lower than the abdominal temperature. The control of testicular temperature in the scrotum is not fully understo ...
Blood supply of the Upper Limb
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
... Discuss the radial and ulnar arteries with their relations and branches. Describe the formation of superficial and deep palmar ...
hi res PowerPoint
... Median Cricothyroid Ligament No major veins so bleeding is minimal Arteries and nerves are unaffected as they enter larynx from lateral and posterior sides. ...
... Median Cricothyroid Ligament No major veins so bleeding is minimal Arteries and nerves are unaffected as they enter larynx from lateral and posterior sides. ...
Laparoscopic anatomy of the female pelvis, from the
... system nerves along part of their course. They are of great importance surgically. As already mentioned, these are not ligaments in the strictly anatomical sense, but areas where the connective tissues are more dense, exchanging fibres with each other and prolonged by the fascias at their ends. The ...
... system nerves along part of their course. They are of great importance surgically. As already mentioned, these are not ligaments in the strictly anatomical sense, but areas where the connective tissues are more dense, exchanging fibres with each other and prolonged by the fascias at their ends. The ...
15-final Vasculature of lower limb
... Popliteal vein Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of th ...
... Popliteal vein Formed by the union of venae comitantes around the anterior & posterior tibial arteries. lies posterior to popliteal artery. Femoral vein It enters the thigh by passing through the opening in the adductor magnus . It leaves the thigh in the intermediate compartment of th ...
Azygos vein cannulation - The Southwest Respiratory and Critical
... the azygos vein. This complication is unlikely from the more commonly used right internal jugular vein access, although that approach is not free of complications. An abrupt curve at the tip of the central venous catheter showing venous wave forms and high oxygen saturations suggest azygos vein cann ...
... the azygos vein. This complication is unlikely from the more commonly used right internal jugular vein access, although that approach is not free of complications. An abrupt curve at the tip of the central venous catheter showing venous wave forms and high oxygen saturations suggest azygos vein cann ...
major arteries of the head and neck
... scalene muscle. They then ascend up the posterior side of the neck, through holes in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, known as foramen transversarium. The vertebral arteries enter the cranial cavity via the foramen magnum, and converge. They then give rise to the basilar arteries, ...
... scalene muscle. They then ascend up the posterior side of the neck, through holes in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, known as foramen transversarium. The vertebral arteries enter the cranial cavity via the foramen magnum, and converge. They then give rise to the basilar arteries, ...
Fall 2003 4a
... Systemic Anatomy Exam IV Prepared especially for the trimester one class, Fall 2003 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of you ...
... Systemic Anatomy Exam IV Prepared especially for the trimester one class, Fall 2003 Please place the single best answer in the space provided (unless designated by the letters MACA, which in this case mark all correct answers that apply) on your scantron sheet. The faculty will not answer any of you ...
Spinal Cord Organization
... All neurons in spinal cord gray matter have multipolar cell bodies. Based on axon destination, they can be divided into three major types, each of which has several subtypes: 1] Efferent neurons (embryologically derived from basal plate) send axons into the ventral root. Cell bodies of efferent neur ...
... All neurons in spinal cord gray matter have multipolar cell bodies. Based on axon destination, they can be divided into three major types, each of which has several subtypes: 1] Efferent neurons (embryologically derived from basal plate) send axons into the ventral root. Cell bodies of efferent neur ...
21-Vascular anatomy of the lower limb2015-12-15 04
... List the main arterial anastomosis. List the sites where you feel the arterial pulse. Differentiate the veins of LL into superficial & deep Describe their origin, course & termination and ...
... List the main arterial anastomosis. List the sites where you feel the arterial pulse. Differentiate the veins of LL into superficial & deep Describe their origin, course & termination and ...
artery - KSUMSC
... arteries, so the arterial pulsations help to compress and move blood in the veins especially during exercise. ...
... arteries, so the arterial pulsations help to compress and move blood in the veins especially during exercise. ...
6,7-Blood supply of the Upper Limb
... Larger terminal branch of Brachial artery. Begins in the cubital fossa & descends through anterior compartment of forearm. It enters the palm in front of flexor retinaculum. It ends by forming Superficial Palmar Arch with Superficial Palmar branch of Radial artery. ...
... Larger terminal branch of Brachial artery. Begins in the cubital fossa & descends through anterior compartment of forearm. It enters the palm in front of flexor retinaculum. It ends by forming Superficial Palmar Arch with Superficial Palmar branch of Radial artery. ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.