Coding of Visual Information in the Retina Coding of Light d D k and
... lights; g ; less useful for making distinctions in bright light. ...
... lights; g ; less useful for making distinctions in bright light. ...
The neural mechanisms of top- down attentional control
... analysis tended to blend together the attention-related activations in adjacent visual cortical areas, the contralateral attentionrelated activations in occipital cortex can be seen to cross multiple visual area borders from V2 through V4 (Fig. 5b), an observation in line with other reports10,18,22. ...
... analysis tended to blend together the attention-related activations in adjacent visual cortical areas, the contralateral attentionrelated activations in occipital cortex can be seen to cross multiple visual area borders from V2 through V4 (Fig. 5b), an observation in line with other reports10,18,22. ...
Overview of the Seven Perceptual Styles
... Often talks at length…just to hear him/herself talk! ...
... Often talks at length…just to hear him/herself talk! ...
The Visual System
... How do we map receptive fields of retinal ganglion cells? • An anesthetized animal (which doesn’t track moving stimuli with eye movements) views a video screen on which a stimulus spot is moved. The image of the spot falls on corresponding parts of the retinal surface. • An electrode is advanced in ...
... How do we map receptive fields of retinal ganglion cells? • An anesthetized animal (which doesn’t track moving stimuli with eye movements) views a video screen on which a stimulus spot is moved. The image of the spot falls on corresponding parts of the retinal surface. • An electrode is advanced in ...
Lecture 13A
... • It corrects these errors, learning to confine the call to the correct member of each category, and to respond more quickly. • However, even when the vervet produces its first calls, it does not make between-category errors, for example, issue the snake call to a bird, and so on. • That means they ...
... • It corrects these errors, learning to confine the call to the correct member of each category, and to respond more quickly. • However, even when the vervet produces its first calls, it does not make between-category errors, for example, issue the snake call to a bird, and so on. • That means they ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... complicated by the fact that signals from different modalities may originate in different coordinate frames (e.g., eye-centered or head-centered). To investigate the neural basis of self-motion perception, we record from neurons in area MSTd of macaque monkeys during optic flow (Visual condition), r ...
... complicated by the fact that signals from different modalities may originate in different coordinate frames (e.g., eye-centered or head-centered). To investigate the neural basis of self-motion perception, we record from neurons in area MSTd of macaque monkeys during optic flow (Visual condition), r ...
Neural Basis of the Ventriloquist
... Illusion accompanied by contralateral response in auditory cortex Similar to response when sound actually comes from illusory location Response occurs between 230-260ms after stimulus onset Therefore: Auditory information is present very early, but localization itself may depend on longer time scale ...
... Illusion accompanied by contralateral response in auditory cortex Similar to response when sound actually comes from illusory location Response occurs between 230-260ms after stimulus onset Therefore: Auditory information is present very early, but localization itself may depend on longer time scale ...
PSy420: Sensation and Perception (Dr. Hajnal) March 22, 2010
... The fact that faces are more difficult than many other types of objects to recognize when viewed upside-down is taken by many researchers to indicate that a) faces are recognized via structural descriptions. b) it is more difficult to segment faces from their backgrounds than other types of objects. ...
... The fact that faces are more difficult than many other types of objects to recognize when viewed upside-down is taken by many researchers to indicate that a) faces are recognized via structural descriptions. b) it is more difficult to segment faces from their backgrounds than other types of objects. ...
Visual development.
... How are the cells ordered in the visual cortex? Describe in your own words Adjacent columns of cells receive input from the same area of the retina of both eyes. One column from the left and the next column from the right eye This is repeated across the whole visual cortex to build up a ‘map’ of th ...
... How are the cells ordered in the visual cortex? Describe in your own words Adjacent columns of cells receive input from the same area of the retina of both eyes. One column from the left and the next column from the right eye This is repeated across the whole visual cortex to build up a ‘map’ of th ...
Visual development.
... How are the cells ordered in the visual cortex? Describe in your own words Adjacent columns of cells receive input from the same area of the retina of both eyes. One column from the left and the next column from the right eye This is repeated across the whole visual cortex to build up a ‘map’ of th ...
... How are the cells ordered in the visual cortex? Describe in your own words Adjacent columns of cells receive input from the same area of the retina of both eyes. One column from the left and the next column from the right eye This is repeated across the whole visual cortex to build up a ‘map’ of th ...
The visual system
... Two Visual streams: Two theories ‘What’ versus ‘How’ (Milner & Goodale, 1993) – the use to which information is put. Ventral pathway – conscious perception of objects Dorsal pathway – direct behavioral interactions with objects ...
... Two Visual streams: Two theories ‘What’ versus ‘How’ (Milner & Goodale, 1993) – the use to which information is put. Ventral pathway – conscious perception of objects Dorsal pathway – direct behavioral interactions with objects ...
A coincidence detector neural network model of selective attention
... In addition to influence from top-down spatial goals, the neural activation of each stimulus is progressively modulated by top-down signals of semantic information. We propose that a correlation control mechanism that includes coincidence detector neurons determines the correlation between semantic ...
... In addition to influence from top-down spatial goals, the neural activation of each stimulus is progressively modulated by top-down signals of semantic information. We propose that a correlation control mechanism that includes coincidence detector neurons determines the correlation between semantic ...
lecture9
... 6. Visuo-motor coordination is a computationally difficult problem for the brain. Need flexibility to correct errors. ...
... 6. Visuo-motor coordination is a computationally difficult problem for the brain. Need flexibility to correct errors. ...
day2-morning2
... • The first step in the listening process is the reception of a stimulus or message- both the auditory and visual message. • The hearing process is based on a complex set of physical interactions between the ear and the brain. • Besides using the hearing mechanism, we listen through our visual syste ...
... • The first step in the listening process is the reception of a stimulus or message- both the auditory and visual message. • The hearing process is based on a complex set of physical interactions between the ear and the brain. • Besides using the hearing mechanism, we listen through our visual syste ...
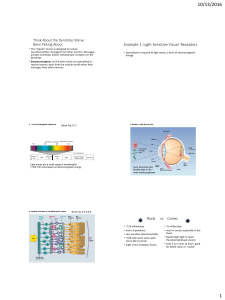
Think About the Dendrites We`ve Been Talking About
... 2 Theories of Color Vision Proposed in 1800’s Trichromatic Theory – 3 different types of color receptors work together to represent all colors of the spectrum. Opponent Process Theory – cells in the visual pathway receive input about pairs of colors (R-G or B-Y). One color makes them fire faster, ...
... 2 Theories of Color Vision Proposed in 1800’s Trichromatic Theory – 3 different types of color receptors work together to represent all colors of the spectrum. Opponent Process Theory – cells in the visual pathway receive input about pairs of colors (R-G or B-Y). One color makes them fire faster, ...
Modulation of early cortical processing during divided attention to
... movements. All had normal or corrected-to-normal vision. The experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, and conformed to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent and received a m ...
... movements. All had normal or corrected-to-normal vision. The experimental procedures were approved by the Institutional Review Board at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, and conformed to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants provided written informed consent and received a m ...
Lecture S&P
... “on” and “off” regions Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond best to a particular stimulus anywhere in its receptive field ...
... “on” and “off” regions Complex – also rectangular, larger receptive fields, respond best to a particular stimulus anywhere in its receptive field ...
Danczi Csaba László - 2nd WORLD CONGRESS OF ARTS
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
... stimulus moving continuously across the cutaneous surface (2). The presence of extensive connections between superficial and deep regions of the colliculus in the cat supports the idea that receptive field organization in the deep layers is modulated by visual input from the overlying layers. Thus, ...
Second-Order Patterns in Human Visual Cortex`` on ``Orientation
... Texture patterns— homogeneous regions of repeated structures—are the predominant feature of natural visual scenes. The zebra, a 1938 optical art painting by Victor Vasarely, illustrates how different textures segregate and define figures from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive ...
... Texture patterns— homogeneous regions of repeated structures—are the predominant feature of natural visual scenes. The zebra, a 1938 optical art painting by Victor Vasarely, illustrates how different textures segregate and define figures from their background. Despite the ease with which we perceive ...
Visually Induced Ocular Torsion
... stimulus. The response amplitude was small, only compensating for a minor portion of the stimuli tilt. The response was well conjugate for the right and left eye. In the first study, a visual scene enriched with spatial clues important for maintaining posture was found to induce significantly more t ...
... stimulus. The response amplitude was small, only compensating for a minor portion of the stimuli tilt. The response was well conjugate for the right and left eye. In the first study, a visual scene enriched with spatial clues important for maintaining posture was found to induce significantly more t ...
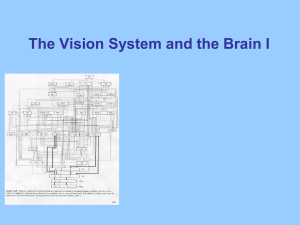
Lectures for 5th week: Visual System I
... • Today: how the brain begins to represent sensory information & processes it to form integrated percepts ...
... • Today: how the brain begins to represent sensory information & processes it to form integrated percepts ...
Top-down influence in early visual processing: a Bayesian perspective
... Fig. 2. (a) The spatial profile of a V1 neuron’s response to the contours of both real and illusory squares, in a temporal window 100 – 150 ms after stimulus onset. The real or illusory square was placed at different spatial locations relative to the receptive field of the cell. This cell responded ...
... Fig. 2. (a) The spatial profile of a V1 neuron’s response to the contours of both real and illusory squares, in a temporal window 100 – 150 ms after stimulus onset. The real or illusory square was placed at different spatial locations relative to the receptive field of the cell. This cell responded ...
Visual N1
The visual N1 is a visual evoked potential, a type of event-related electrical potential (ERP), that is produced in the brain and recorded on the scalp. The N1 is so named to reflect the polarity and typical timing of the component. The ""N"" indicates that the polarity of the component is negative with respect to an average mastoid reference. The ""1"" originally indicated that it was the first negative-going component, but it now better indexes the typical peak of this component, which is around 150 to 200 milliseconds post-stimulus. The N1 deflection may be detected at most recording sites, including the occipital, parietal, central, and frontal electrode sites. Although, the visual N1 is widely distributed over the entire scalp, it peaks earlier over frontal than posterior regions of the scalp, suggestive of distinct neural and/or cognitive correlates. The N1 is elicited by visual stimuli, and is part of the visual evoked potential – a series of voltage deflections observed in response to visual onsets, offsets, and changes. Both the right and left hemispheres generate an N1, but the laterality of the N1 depends on whether a stimulus is presented centrally, laterally, or bilaterally. When a stimulus is presented centrally, the N1 is bilateral. When presented laterally, the N1 is larger, earlier, and contralateral to the visual field of the stimulus. When two visual stimuli are presented, one in each visual field, the N1 is bilateral. In the latter case, the N1’s asymmetrical skewedness is modulated by attention. Additionally, its amplitude is influenced by selective attention, and thus it has been used to study a variety of attentional processes.