New clues to the location of visual consciousness
... In normal binocular vision, sensory information from the two eyes is fused into a single, three-dimensional visual impression. Stereopsis, the ability to fuse two, two-dimensional images into a three-dimensional image, is the flip-side of binocular rivalry. Individuals with misaligned eyes can suffe ...
... In normal binocular vision, sensory information from the two eyes is fused into a single, three-dimensional visual impression. Stereopsis, the ability to fuse two, two-dimensional images into a three-dimensional image, is the flip-side of binocular rivalry. Individuals with misaligned eyes can suffe ...
A1984TF19600002
... to the medial or lateral visual cortex, and even in the auditory, somatosensory, and motor 4cortex. The 1965 paper of Hubel and Wiesel describing the organization of areas 17, 18, and 19 helped us define the separate subcortical projections from each area. The superficial laminae of the superior col ...
... to the medial or lateral visual cortex, and even in the auditory, somatosensory, and motor 4cortex. The 1965 paper of Hubel and Wiesel describing the organization of areas 17, 18, and 19 helped us define the separate subcortical projections from each area. The superficial laminae of the superior col ...
Final - Center for Neural Science
... Part II. Multiple Choice (1.5 points each). Write your name and fill in the circles using a #2 pencil on the accompanying scantron card. 1) In the study of perceptual processes, the term “transduction” is defined to be a) temporal patterning of nerve impulses. b) neural processing. c) the conversio ...
... Part II. Multiple Choice (1.5 points each). Write your name and fill in the circles using a #2 pencil on the accompanying scantron card. 1) In the study of perceptual processes, the term “transduction” is defined to be a) temporal patterning of nerve impulses. b) neural processing. c) the conversio ...
Session 4
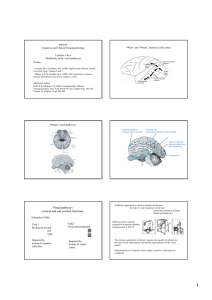
... Two Major Processing Streams There appear to be 2 major processing streams (although there are cross connections between them): 1. The Dorsal Stream: Includes areas MT, MST, VIP, 7a, etc. Processes motion, stereo, spatial relationships The "where" pathway. 2. The Ventral Stream: Includes areas V4, ...
... Two Major Processing Streams There appear to be 2 major processing streams (although there are cross connections between them): 1. The Dorsal Stream: Includes areas MT, MST, VIP, 7a, etc. Processes motion, stereo, spatial relationships The "where" pathway. 2. The Ventral Stream: Includes areas V4, ...
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
... electrophysiological recordings from dorsal stream neurons neurons that fire during reaching neurons firing during saccades towards stationary objects neurons responding to moving objects if followed by gaze ...
primary visual cortex - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. review the pathway by which visual information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. 2. identify the locations and functions of the primary cortex, secondary cortex, and association areas for the visual system. ...
... By the end of today’s class, you should be able to: 1. review the pathway by which visual information is transmitted from receptors to the brain. 2. identify the locations and functions of the primary cortex, secondary cortex, and association areas for the visual system. ...
Jay_21Mar2013
... Functional Organization of Macaque Visual Cortex How are visual cortical areas distinguished from each other? Function Anatomy Connectivity Topography ...
... Functional Organization of Macaque Visual Cortex How are visual cortical areas distinguished from each other? Function Anatomy Connectivity Topography ...
3680Lecture13 - U of L Class Index
... Recurrent Signals in Object Perception • curve tracing – monkey indicates whether a particular segment is on a particular curve – requires attention to scan the curve and “select” all segments that belong together – that is: make a representation of the entire curve – takes time ...
... Recurrent Signals in Object Perception • curve tracing – monkey indicates whether a particular segment is on a particular curve – requires attention to scan the curve and “select” all segments that belong together – that is: make a representation of the entire curve – takes time ...
Click here to a word document of this Fact
... Depending on the exact location of the damage to the visual pathways, different amounts of vision may be affected with different names (relative hemianopia, quadrantinopia, incongruent hemianopia), however functional changes still occur. Those experiencing homonymous hemianopia may not be aware that ...
... Depending on the exact location of the damage to the visual pathways, different amounts of vision may be affected with different names (relative hemianopia, quadrantinopia, incongruent hemianopia), however functional changes still occur. Those experiencing homonymous hemianopia may not be aware that ...
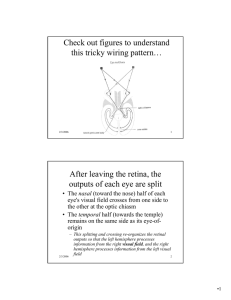
After leaving the retina, the outputs of each eye are split
... – Architecture: microanatomy can differ widely across brain areas • For example, V1 is also referred to as "striate cortex" because it has a series of stripes that run parallel to the surface; these stripes end abruptly at the end of V1. ...
... – Architecture: microanatomy can differ widely across brain areas • For example, V1 is also referred to as "striate cortex" because it has a series of stripes that run parallel to the surface; these stripes end abruptly at the end of V1. ...
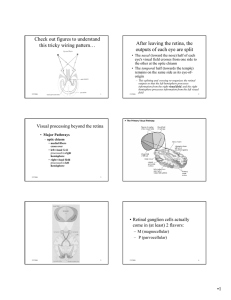
Check out figures to understand this tricky wiring pattern… After
... – Each V1 does not simply receive input from the opposite eye; the outputs of each retina are split (left half/right half) and then run through the LGN to the appropriate V1 • Just as the image of the world is inverted when projected onto the retina, the retinotopic V1 map is upside down (and the ri ...
... – Each V1 does not simply receive input from the opposite eye; the outputs of each retina are split (left half/right half) and then run through the LGN to the appropriate V1 • Just as the image of the world is inverted when projected onto the retina, the retinotopic V1 map is upside down (and the ri ...
A1982ND73700001
... monograph about the evoked potentials (EPs) in the literature at all. Later, throughout the world, a tremendous surge of work in the field of EPs brought extensive knowledge of the physiology and pathophysiology of the human brain and even knowledge about the mechanisms of the mind. The work is stil ...
... monograph about the evoked potentials (EPs) in the literature at all. Later, throughout the world, a tremendous surge of work in the field of EPs brought extensive knowledge of the physiology and pathophysiology of the human brain and even knowledge about the mechanisms of the mind. The work is stil ...
Primary visual cortex
... different orientations Selective adaptation for spatial frequency: Evidence that human visual system contains neurons selective for spatial frequency ...
... different orientations Selective adaptation for spatial frequency: Evidence that human visual system contains neurons selective for spatial frequency ...
Visual Processing - West Virginia University
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
Document
... hippocampal subdivisions that also receive input directly from the cIPL. (2) To the posterior parahippocampal cortex (areas TF, TH and TFO), which projects in turn to the CA1/prosubicular subdivisions of the ...
... hippocampal subdivisions that also receive input directly from the cIPL. (2) To the posterior parahippocampal cortex (areas TF, TH and TFO), which projects in turn to the CA1/prosubicular subdivisions of the ...
Study Guide 3
... 34. Describe three different functional classes of neurons found in primary visual cortex. 35. What is a cortical module? An orientation column? An ocular dominance column? 36. What is the difference between cortical "blobs" and interblob areas? 37. What feature(s) of the visual stimulus are most im ...
... 34. Describe three different functional classes of neurons found in primary visual cortex. 35. What is a cortical module? An orientation column? An ocular dominance column? 36. What is the difference between cortical "blobs" and interblob areas? 37. What feature(s) of the visual stimulus are most im ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM PERIPHERAL MECHANISMS 1) Light enters
... ii. Off-center: H-bipolar synapses, inhibits AP iii. Axons of ganglion cells form optic nerve c. Other cells i. Horizontal cells (lateral inhibition network)– inhibit neighboring synapses when stimulated light detection produces opposite response in cells in surrounded area = center-surround organ ...
... ii. Off-center: H-bipolar synapses, inhibits AP iii. Axons of ganglion cells form optic nerve c. Other cells i. Horizontal cells (lateral inhibition network)– inhibit neighboring synapses when stimulated light detection produces opposite response in cells in surrounded area = center-surround organ ...
The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas
... illustrates that, despite their differences, the sensory regions of the cortex must be cooperating with each other by integrating the sensory stimuli they receive from the outside world. Now, on page 1206 of this issue (1), Macaluso et al. report an elegant example of this cooperation and provide em ...
... illustrates that, despite their differences, the sensory regions of the cortex must be cooperating with each other by integrating the sensory stimuli they receive from the outside world. Now, on page 1206 of this issue (1), Macaluso et al. report an elegant example of this cooperation and provide em ...
The NTVA framework: Linking Cognition and Neuroscience
... Desimone, 1985). This effect is readily explained by NTVA's concept of filtering based on attentional weights. A second frequently observed effect of attention is a modest change in firing rates with a single stimulus in the receptive field. This finding can be explained by the pigeonholing mechanis ...
... Desimone, 1985). This effect is readily explained by NTVA's concept of filtering based on attentional weights. A second frequently observed effect of attention is a modest change in firing rates with a single stimulus in the receptive field. This finding can be explained by the pigeonholing mechanis ...
Revision material
... How do cells in the ventral spinal cord respond to differing levels of Shh? The genomic sequence of the “AMPA” receptor encodes a Ca2+ channel but most AMPA receptors are only permeable to Na+. Explain. Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the f ...
... How do cells in the ventral spinal cord respond to differing levels of Shh? The genomic sequence of the “AMPA” receptor encodes a Ca2+ channel but most AMPA receptors are only permeable to Na+. Explain. Describe briefly the optical factors that affect visual acuity. Write short notes on two of the f ...
The Mind in Peak Performance
... performance • Optimize frequency and amplitude to facilitate memory and sequencing • Teach emotional self regulation to – Decrease anxiety, depression, anger, and facilitate relationships and social integration ...
... performance • Optimize frequency and amplitude to facilitate memory and sequencing • Teach emotional self regulation to – Decrease anxiety, depression, anger, and facilitate relationships and social integration ...
Document
... pinholes and holding them in exact coincidence, and yet at the same time he can concentrate his attention on any part of the dark field he likes, so that when the spark comes, he will get an impression about objects in that particular region only. In this experiment the attention is entirely indepen ...
... pinholes and holding them in exact coincidence, and yet at the same time he can concentrate his attention on any part of the dark field he likes, so that when the spark comes, he will get an impression about objects in that particular region only. In this experiment the attention is entirely indepen ...
Symposium Poster - uospur
... expressed by OSNs. • OSNs that express the same odorant receptor project to a single glomerulus, where they synapse with mitral and tufted cells, which project axons to the cortex. • The glomeruli are arranged spatially in a stereotyped manner, forming identical maps in the left and right olfactory ...
... expressed by OSNs. • OSNs that express the same odorant receptor project to a single glomerulus, where they synapse with mitral and tufted cells, which project axons to the cortex. • The glomeruli are arranged spatially in a stereotyped manner, forming identical maps in the left and right olfactory ...
Visual N1
The visual N1 is a visual evoked potential, a type of event-related electrical potential (ERP), that is produced in the brain and recorded on the scalp. The N1 is so named to reflect the polarity and typical timing of the component. The ""N"" indicates that the polarity of the component is negative with respect to an average mastoid reference. The ""1"" originally indicated that it was the first negative-going component, but it now better indexes the typical peak of this component, which is around 150 to 200 milliseconds post-stimulus. The N1 deflection may be detected at most recording sites, including the occipital, parietal, central, and frontal electrode sites. Although, the visual N1 is widely distributed over the entire scalp, it peaks earlier over frontal than posterior regions of the scalp, suggestive of distinct neural and/or cognitive correlates. The N1 is elicited by visual stimuli, and is part of the visual evoked potential – a series of voltage deflections observed in response to visual onsets, offsets, and changes. Both the right and left hemispheres generate an N1, but the laterality of the N1 depends on whether a stimulus is presented centrally, laterally, or bilaterally. When a stimulus is presented centrally, the N1 is bilateral. When presented laterally, the N1 is larger, earlier, and contralateral to the visual field of the stimulus. When two visual stimuli are presented, one in each visual field, the N1 is bilateral. In the latter case, the N1’s asymmetrical skewedness is modulated by attention. Additionally, its amplitude is influenced by selective attention, and thus it has been used to study a variety of attentional processes.