Moran Furman
... ventral stream culminates in areas of the inferior temporal lobe, and it is involved primarily in object recognition and related perceptual functions. The dorsal stream culminates in association areas of the parietal lobe, and it is involved in spatial relationships among objects and visual guidance ...
... ventral stream culminates in areas of the inferior temporal lobe, and it is involved primarily in object recognition and related perceptual functions. The dorsal stream culminates in association areas of the parietal lobe, and it is involved in spatial relationships among objects and visual guidance ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
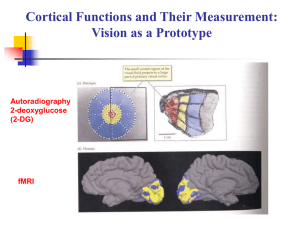
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
... sulcus and the inferior parietal lobule. These same areas showed significant activations also during the tactile and visual angle discrimination conditions. As expected, auditory, visual and tactile primary sensory regions also were activated during the respective conditions. Ventral occipital brain ...
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception
... –Rods: black and white/low light vision –Cones: color and daylight vision •Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
... –Rods: black and white/low light vision –Cones: color and daylight vision •Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
Are We Paying Attention Yet?
... This data supports the interdependence hypothesis and does not rule out the identity hypothesis This data does NOT support the independence hypothesis ...
... This data supports the interdependence hypothesis and does not rule out the identity hypothesis This data does NOT support the independence hypothesis ...
MCB105 QUIZ 5 2016 wA
... owls and why? [1] instructive signal/ visual responses to allow alignment of visual and auditory space - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these ...
... owls and why? [1] instructive signal/ visual responses to allow alignment of visual and auditory space - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these ...
view - Scan. Vet. Press
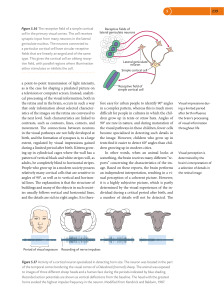
... as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristics of the images on the retina are conveyed to the ...
... as is the case for shaping a pixelated picture on a television or computer screen. Instead, analytical processing of the visual information, both in the retina and in the brain, occurs in such a way that only information about selected characteristics of the images on the retina are conveyed to the ...
Visual Field and the Human Visual System
... PET Activations of Word vs. Nonword Stimuli Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
... PET Activations of Word vs. Nonword Stimuli Brain shows much greater activation as subjects look at visual words (2nd row) than when they view a static fixation point (top row). ...
Slide ()
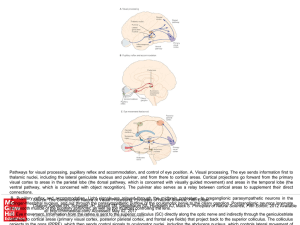
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
Review 2 - Texas A&M University
... • When neurons in different parts of the cortex are firing to the same object, the pattern of firing is synchronized (they fire at the same time, and in the same manner). • So when neurons are firing in synchrony, the corresponding features are bound together. ...
... • When neurons in different parts of the cortex are firing to the same object, the pattern of firing is synchronized (they fire at the same time, and in the same manner). • So when neurons are firing in synchrony, the corresponding features are bound together. ...
Nature Reviews Neuroscience Highlight
... categorize the stimuli set as either cat or dog. Freedman et al. then looked for neurons that reflected the different categories. A population of neurons in the lateral prefrontal cortex reflected the category of the visual stimuli. A typical neuron was more active in response to one of the categori ...
... categorize the stimuli set as either cat or dog. Freedman et al. then looked for neurons that reflected the different categories. A population of neurons in the lateral prefrontal cortex reflected the category of the visual stimuli. A typical neuron was more active in response to one of the categori ...
Lecture 2 - Computer Science
... Computational Vision CSCI 363, Fall 2012 Lecture 2 Introduction to Vision Science ...
... Computational Vision CSCI 363, Fall 2012 Lecture 2 Introduction to Vision Science ...
Attending to Contrast
... hard-to-see, stimuli, irrespective of other stimulus properties like orientation. This result might even account for the observation of Maunsell and colleagues that V4 neurons respond more strongly for all orientations, because the effective contrast at each orientation, which was fixed in that expe ...
... hard-to-see, stimuli, irrespective of other stimulus properties like orientation. This result might even account for the observation of Maunsell and colleagues that V4 neurons respond more strongly for all orientations, because the effective contrast at each orientation, which was fixed in that expe ...
Lecture 5 - TeachLine
... The primary visual cortex maintains: 1- visual hemifield location map 2- size discrimination (small and large receptive fields) 3- color coding (in monkey; in “blobs”) The primary visual cortex begins selectivity to: ...
... The primary visual cortex maintains: 1- visual hemifield location map 2- size discrimination (small and large receptive fields) 3- color coding (in monkey; in “blobs”) The primary visual cortex begins selectivity to: ...
Theory of Vision: What We Can Easily See
... The goal is to always to get a visual target in the vicinity of the eye’s detection field. From there, it becomes eligible for the next fixation. The bigger something is, the more it takes up in the ...
... The goal is to always to get a visual target in the vicinity of the eye’s detection field. From there, it becomes eligible for the next fixation. The bigger something is, the more it takes up in the ...
Slide ()
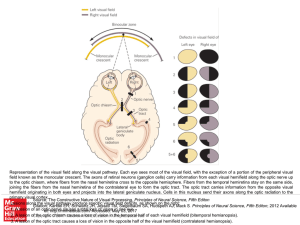
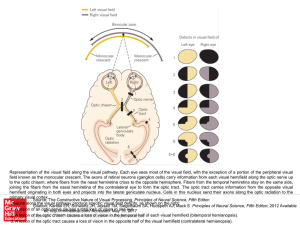
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Slide ()
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
... field known as the monocular crescent. The axons of retinal neurons (ganglion cells) carry information from each visual hemifield along the optic nerve up to the optic chiasm, where fibers from the nasal hemiretina cross to the opposite hemisphere. Fibers from the temporal hemiretina stay on the sam ...
Slide ()
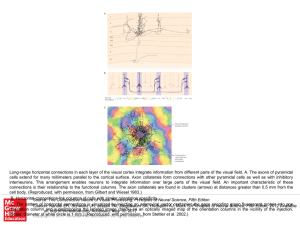
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
... Long-range horizontal connections in each layer of the visual cortex integrate information from different parts of the visual field. A. The axons of pyramidal cells extend for many millimeters parallel to the cortical surface. Axon collaterals form connections with other pyramidal cells as well as w ...
Blue= rods Green = Cones
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
... several different places in the brain • Each place in our visual field is represented by the activity of particular neurons in several different parts of our visual system • This map of the retina is represented and maintained in the LGN, primary visual cortex (V1), and other visual processing areas ...
Lesson1 Powerpoint
... forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Document
... forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
... forces/energy into electrical impulses that are mediated by neural spikes. Neural “encoding” ...
Summary - VU Research Portal
... are perceived as being in front of a background. This process is termed perceptual grouping. This PhD thesis presents experiments that aim to enhance our understanding of the neural basis of perceptual grouping in rhesus macaques and humans. Each neuron the the primary visual cortex responds to a sm ...
... are perceived as being in front of a background. This process is termed perceptual grouping. This PhD thesis presents experiments that aim to enhance our understanding of the neural basis of perceptual grouping in rhesus macaques and humans. Each neuron the the primary visual cortex responds to a sm ...
Visual N1
The visual N1 is a visual evoked potential, a type of event-related electrical potential (ERP), that is produced in the brain and recorded on the scalp. The N1 is so named to reflect the polarity and typical timing of the component. The ""N"" indicates that the polarity of the component is negative with respect to an average mastoid reference. The ""1"" originally indicated that it was the first negative-going component, but it now better indexes the typical peak of this component, which is around 150 to 200 milliseconds post-stimulus. The N1 deflection may be detected at most recording sites, including the occipital, parietal, central, and frontal electrode sites. Although, the visual N1 is widely distributed over the entire scalp, it peaks earlier over frontal than posterior regions of the scalp, suggestive of distinct neural and/or cognitive correlates. The N1 is elicited by visual stimuli, and is part of the visual evoked potential – a series of voltage deflections observed in response to visual onsets, offsets, and changes. Both the right and left hemispheres generate an N1, but the laterality of the N1 depends on whether a stimulus is presented centrally, laterally, or bilaterally. When a stimulus is presented centrally, the N1 is bilateral. When presented laterally, the N1 is larger, earlier, and contralateral to the visual field of the stimulus. When two visual stimuli are presented, one in each visual field, the N1 is bilateral. In the latter case, the N1’s asymmetrical skewedness is modulated by attention. Additionally, its amplitude is influenced by selective attention, and thus it has been used to study a variety of attentional processes.