Final for Astro 322, Prof. Heinke, April 23rd, 2010 Formula sheet
... a) We use HST to observe a bright star in the nearby galaxy M51 that varies periodically, with a period of 8.5 days. What kind of star is this likely to be? b) The star has an average visual magnitude of 25.53. Measurements of its optical spectra suggest a color excess E(B − V ) = 0.1 due to extinct ...
... a) We use HST to observe a bright star in the nearby galaxy M51 that varies periodically, with a period of 8.5 days. What kind of star is this likely to be? b) The star has an average visual magnitude of 25.53. Measurements of its optical spectra suggest a color excess E(B − V ) = 0.1 due to extinct ...
Discussion Activity #13
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
Atomic Spectroscopy With Reference To The Textbook Atomic
... Science of Light and Matter • Light is electromagnetic energy radiation • Propagates through empty space or material medium as waves or particles (photons) • Wavelength of radiation defines ‘color’ • Visible light wavelength range: 4000 (Blue) – 7000 (Red) Angstroms OR 400 – 700 nanometers ...
... Science of Light and Matter • Light is electromagnetic energy radiation • Propagates through empty space or material medium as waves or particles (photons) • Wavelength of radiation defines ‘color’ • Visible light wavelength range: 4000 (Blue) – 7000 (Red) Angstroms OR 400 – 700 nanometers ...
Spectral-Type Trends: Absorption
... processes that produce the observed X-ray emission. Erin’s original: Spectral-Type Trends: Absorption Shown above on the left are the x-ray spectra of six O stars (and one B star) from the Chandra archive, arranged in order of decreasing surface temperature and mass-loss rate. As is evident from the ...
... processes that produce the observed X-ray emission. Erin’s original: Spectral-Type Trends: Absorption Shown above on the left are the x-ray spectra of six O stars (and one B star) from the Chandra archive, arranged in order of decreasing surface temperature and mass-loss rate. As is evident from the ...
Electromagnetic spectrum
... galaxy in which the spiral arms come from the ends of a bar through the nucleus, rather than from the nucleus itself A lenticular galaxy is a galaxy with a flat disk like a spiral galaxy, but with little spiral structure, and a large bulge in the nucleus ...
... galaxy in which the spiral arms come from the ends of a bar through the nucleus, rather than from the nucleus itself A lenticular galaxy is a galaxy with a flat disk like a spiral galaxy, but with little spiral structure, and a large bulge in the nucleus ...
Document
... So the spectra reveal details about the light source. We can use that same approach to study planets, stars, and galaxies. We can deduce the temperature and abundances of various chemical elements in the outer atmosphere of a star. Theorists predicted that when the universe was forming there was lit ...
... So the spectra reveal details about the light source. We can use that same approach to study planets, stars, and galaxies. We can deduce the temperature and abundances of various chemical elements in the outer atmosphere of a star. Theorists predicted that when the universe was forming there was lit ...
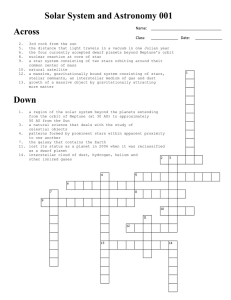
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
Big Bang Theory
... Within the first minute, 98% of all matter in the universe was formed. It began cooling ...
... Within the first minute, 98% of all matter in the universe was formed. It began cooling ...
Atomic Emission Spectrometry - San Diego Unified School District
... emission light sources. These light sources are gas discharge tubes filled with gaseous samples of various elements. They will record the spectra they observe in such a way as to relate them to the continuous spectrum they drew. They will then use the spectra they drew to identify several unlabeled ...
... emission light sources. These light sources are gas discharge tubes filled with gaseous samples of various elements. They will record the spectra they observe in such a way as to relate them to the continuous spectrum they drew. They will then use the spectra they drew to identify several unlabeled ...
2007 Q7 - Loreto Balbriggan
... observer (on the left in diagram), the waves appear to be of lower frequency and longer wavelength. The emission line spectrum of a star was analysed using the Doppler effect. Describe how an emission line spectrum is produced. ...
... observer (on the left in diagram), the waves appear to be of lower frequency and longer wavelength. The emission line spectrum of a star was analysed using the Doppler effect. Describe how an emission line spectrum is produced. ...
doc - IAC
... gases of which they were composed,’ explains Stasinska, an expert in nebulae. Astrophysics had taken its first steps. Erroneous nomenclature There are many species in the Universe that astronomers order, describe and classify according to some taxonomical scheme. Hence, nebulae may be of three types ...
... gases of which they were composed,’ explains Stasinska, an expert in nebulae. Astrophysics had taken its first steps. Erroneous nomenclature There are many species in the Universe that astronomers order, describe and classify according to some taxonomical scheme. Hence, nebulae may be of three types ...
The Big Bang
... a spectrum because each color of light has a different wavelength. • If a star is rapidly approaching the earth, the light waves from the star will appear compressed, or pushed ...
... a spectrum because each color of light has a different wavelength. • If a star is rapidly approaching the earth, the light waves from the star will appear compressed, or pushed ...
Study Guide for Quiz on Astronomy: The Moon, Sun
... 26. Which are the gas giants? ______________________________________________________ 27. _______________________ are chunks of ice and dust with long elliptical orbits. 28. Describe the life of a main sequence star. 29. Describe the Doppler effect and how it relates to the universe expansion. 30. W ...
... 26. Which are the gas giants? ______________________________________________________ 27. _______________________ are chunks of ice and dust with long elliptical orbits. 28. Describe the life of a main sequence star. 29. Describe the Doppler effect and how it relates to the universe expansion. 30. W ...
Using Galaxy Clusters to Study Structure Evolution
... Spectra of a nearby star and a distant galaxy » Star is nearby, approximately at rest » Galaxy is distant, traveling away from us at 12,000 km/s ...
... Spectra of a nearby star and a distant galaxy » Star is nearby, approximately at rest » Galaxy is distant, traveling away from us at 12,000 km/s ...
This chapter has a brief overview of astronomical topics that we will
... This chapter has a brief overview of astronomical topics (read 33-2). Stars are born from large clouds of gas and dust. A disturbance causes the cloud to collapse and fragment into many protostars. The life of a star depends on its mass (and to a lesser extent, chemical composition). A star like the ...
... This chapter has a brief overview of astronomical topics (read 33-2). Stars are born from large clouds of gas and dust. A disturbance causes the cloud to collapse and fragment into many protostars. The life of a star depends on its mass (and to a lesser extent, chemical composition). A star like the ...
Lecture
... If electron is an excited state (e.g., from thermal jostling around) can fall back down and lose a specific amount of energy Corresponds to specific frequency/colour All possible combinations of ...
... If electron is an excited state (e.g., from thermal jostling around) can fall back down and lose a specific amount of energy Corresponds to specific frequency/colour All possible combinations of ...
GO 3_3 Interpreting Space
... produce a spectrum of colors. Joseph von Fraunhofer used a spectroscope to observe the spectrum produced by the Sun. He noticed dark lines, called spectral lines. At the time he was unaware of what these lines were. The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when ...
... produce a spectrum of colors. Joseph von Fraunhofer used a spectroscope to observe the spectrum produced by the Sun. He noticed dark lines, called spectral lines. At the time he was unaware of what these lines were. The significance of the spectral lines was discovered about 50 years later when ...
1: The scientific name for my field is astronomy
... 2: Chapters 20-22 in Earth Science deal with my field. 3: None of the chapters in the Science Interactions brown book are based on Astronomy. 4: Chapters 19-20 in the Science Interactions blue book are based on Astronomy. 5: Astronomers study anything outside the Earth’s exosphere, where the atmosph ...
... 2: Chapters 20-22 in Earth Science deal with my field. 3: None of the chapters in the Science Interactions brown book are based on Astronomy. 4: Chapters 19-20 in the Science Interactions blue book are based on Astronomy. 5: Astronomers study anything outside the Earth’s exosphere, where the atmosph ...
1. The distances to the most remote galaxies can be
... galactic parallax. spectroscopic parallax. proper motion. Cepheids. none of the above. ...
... galactic parallax. spectroscopic parallax. proper motion. Cepheids. none of the above. ...
Galaxies - Edublogs
... Black Holes – is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light can escape. Dark Matter – refers to matter in the universe that is invisible because it does not interact with light or any other kind of radiation. Star Clusters – distinct groupings of stars i.e. open ...
... Black Holes – is a region of space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light can escape. Dark Matter – refers to matter in the universe that is invisible because it does not interact with light or any other kind of radiation. Star Clusters – distinct groupings of stars i.e. open ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.