The Doppler Effect
... He later discovered that the light from almost all distant galaxies was red shifted. Edwin Hubble later showed that the farther away the galaxies are, the faster they seem to be receding from us. ...
... He later discovered that the light from almost all distant galaxies was red shifted. Edwin Hubble later showed that the farther away the galaxies are, the faster they seem to be receding from us. ...
The Doppler Effect
... He later discovered that the light from almost all distant galaxies was red shifted. Edwin Hubble later showed that the farther away the galaxies are, the faster they seem to be receding from us. ...
... He later discovered that the light from almost all distant galaxies was red shifted. Edwin Hubble later showed that the farther away the galaxies are, the faster they seem to be receding from us. ...
ISP 205 Review Questions, Week 13
... 2. A pulsating variable star has a period of 10 days. About how many times more luminous is it than the Sun? Refer to Fig. 15.12 in the textbook. ...
... 2. A pulsating variable star has a period of 10 days. About how many times more luminous is it than the Sun? Refer to Fig. 15.12 in the textbook. ...
Lecture 26 - Empyrean Quest Publishers
... A. reddening--preferential scattering-blue light (why sky is blue). B. absorption--this affects flux and measured distance. 2. Molecular Clouds--H2 molecules--dense MC are star formation regions (stellar nurseries like Orion Nebula). ...
... A. reddening--preferential scattering-blue light (why sky is blue). B. absorption--this affects flux and measured distance. 2. Molecular Clouds--H2 molecules--dense MC are star formation regions (stellar nurseries like Orion Nebula). ...
Shooting Stars - Pepperscience
... Dinosaurs all died Impact on Earth would produce large amounts of debris Blocked out sunlight Collision every 200-300 years 1908 in Russia – 2000km What could we do to prevent this? ...
... Dinosaurs all died Impact on Earth would produce large amounts of debris Blocked out sunlight Collision every 200-300 years 1908 in Russia – 2000km What could we do to prevent this? ...
obafgkm - Piscataway High School
... Astronomers cannot physically measure properties of stars. They rely on interpreting data that can be gathered from the earth. Determine what information about stars can be revealed using the following methods: Parallax effect ...
... Astronomers cannot physically measure properties of stars. They rely on interpreting data that can be gathered from the earth. Determine what information about stars can be revealed using the following methods: Parallax effect ...
The Mass of the Galaxy - University of California, Berkeley
... million years it will decay to the ground state (anti-aligned). Or a 21-cm photon can be absorbed and align the spins. Because the Galaxy is transparent, it is hard to tell where the emission is coming from along the line-of-sight. But because we know its precise wavelength, Doppler shifts in this l ...
... million years it will decay to the ground state (anti-aligned). Or a 21-cm photon can be absorbed and align the spins. Because the Galaxy is transparent, it is hard to tell where the emission is coming from along the line-of-sight. But because we know its precise wavelength, Doppler shifts in this l ...
Document
... a. The latter has a diameter of almost two billion miles. b. If you counted one star a second it would take you more than thirty thousand years to count 100 billion. c. But, during your lifetime, as always, new stars are being crated. d. The solar system is located in the Milky Way Galaxy. e. Stars ...
... a. The latter has a diameter of almost two billion miles. b. If you counted one star a second it would take you more than thirty thousand years to count 100 billion. c. But, during your lifetime, as always, new stars are being crated. d. The solar system is located in the Milky Way Galaxy. e. Stars ...
Size & Distance Comparison (Powerpoint)
... Light travels from the Moon to Light takes just over 4 years to the Earth in just over a second reach us from the next star ...
... Light travels from the Moon to Light takes just over 4 years to the Earth in just over a second reach us from the next star ...
NEW GCSE REVISION Beginning of the Universe - crypt
... From this data, the approximate value of the Hubble constant in km/s per megaparsec is . . . ...
... From this data, the approximate value of the Hubble constant in km/s per megaparsec is . . . ...
Final Exam Study Guide
... If Alpha Centauri were two times farther, its brightness would be ______________. If Alpha Centauri were 2.5 times farther, its absolute magnitude would ___________. Also called a solar storm, this is a burst of plasma released into the solar wind: __________. The sunspot cycle has a period of _____ ...
... If Alpha Centauri were two times farther, its brightness would be ______________. If Alpha Centauri were 2.5 times farther, its absolute magnitude would ___________. Also called a solar storm, this is a burst of plasma released into the solar wind: __________. The sunspot cycle has a period of _____ ...
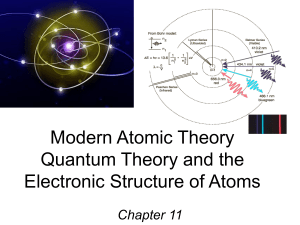
atomic emission spectrum
... this frequency into wavelength (nm). Does this frequency fall in the visible region? ...
... this frequency into wavelength (nm). Does this frequency fall in the visible region? ...
transition
... photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is reached, and the radiation dominated era i ...
... photons and small pieces of slightly clumped matter. The Universe remains ionized as the electrons can not yet recombine with the protons to make neutral hydrogen. When the temperature cools to 3000K, recombination happens, the surface of last scattering is reached, and the radiation dominated era i ...
Science Implications of Various Servicing Options
... Figure reproduced from Universe by Freedman and Kaufmann ...
... Figure reproduced from Universe by Freedman and Kaufmann ...
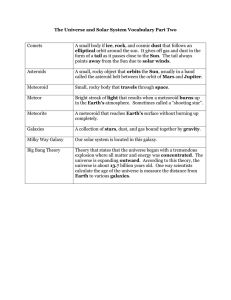
Vocabulary Part Two
... Bright streak of light that results when a meteoroid burns up in the Earth’s atmosphere. Sometimes called a “shooting star”. ...
... Bright streak of light that results when a meteoroid burns up in the Earth’s atmosphere. Sometimes called a “shooting star”. ...
The ISM and Stellar Birth
... • Scatter light from cooler stars • Mostly scatters blue light (like our atmosphere) – so they appear blue. • Dust grains must have sizes ranging from 0.01mm down to 100 nm • See absorption spectrum of nebula in the star’s spectrum • Doppler broadening due to motion of gas molecules • Lines split in ...
... • Scatter light from cooler stars • Mostly scatters blue light (like our atmosphere) – so they appear blue. • Dust grains must have sizes ranging from 0.01mm down to 100 nm • See absorption spectrum of nebula in the star’s spectrum • Doppler broadening due to motion of gas molecules • Lines split in ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.